Tankut Acarman
Embodied Footprints: A Safety-guaranteed Collision Avoidance Model for Numerical Optimization-based Trajectory Planning
Feb 15, 2023Abstract:Numerical optimization-based methods are among the prevalent trajectory planners for autonomous driving. In a numerical optimization-based planner, the nominal continuous-time trajectory planning problem is discretized into a nonlinear program (NLP) problem with finite constraints imposed on finite collocation points. However, constraint violations between adjacent collocation points may still occur. This study proposes a safety-guaranteed collision-avoidance modeling method to eliminate the collision risks between adjacent collocation points in using numerical optimization-based trajectory planners. A new concept called embodied box is proposed, which is formed by enlarging the rectangular footprint of the ego vehicle. If one can ensure that the embodied boxes at finite collocation points are collide-free, then the ego vehicle's footprint is collide-free at any a moment between adjacent collocation points. We find that the geometric size of an embodied box is a simple function of vehicle velocity and curvature. The proposed theory lays a foundation for numerical optimization-based trajectory planners in autonomous driving.
Trajectory Planning for Autonomous Parking in Complex Environments: A Tunnel-based Optimal Control Approach
Oct 11, 2019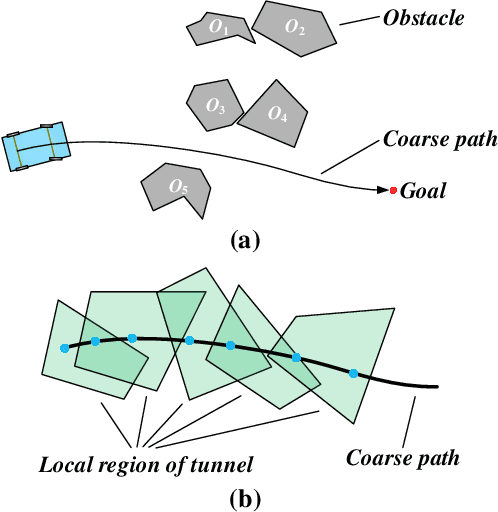
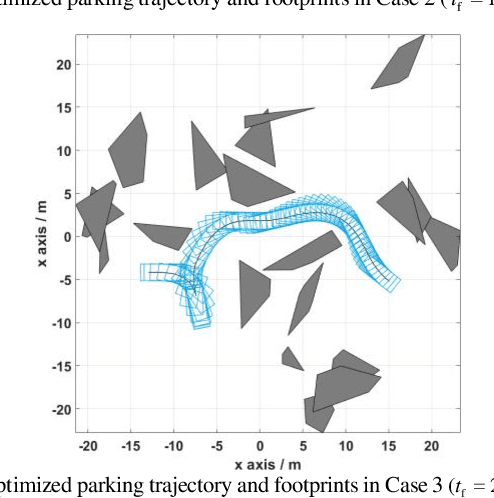


Abstract:This paper proposes a fast and accurate trajectory planning algorithm for autonomous parking. Nominally, an optimal control problem should be formulated to describe this scheme, but the dimensionality of the optimal control problem is usually large, because the vehicle needs to avoid collision with every obstacle at every moment during the entire dynamic process. Although an initial guess obtained by a sample-and-search based planner facilitates the numerical optimization process, it is still far from being as fast as real-time. To address this issue, we replace all of the collision-avoidance constraints by series of within-tunnel conditions. Concretely, we develop a tunnel-based strategy such that the vehicle is restricted to move within the tunnels which naturally separate the vehicle from the obstacles. Unification, efficiency, and robustness of the proposed trajectory planning method have been verified by simulations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge