Takanori Ugai
Multimodal Datasets and Benchmarks for Reasoning about Dynamic Spatio-Temporality in Everyday Environments
Aug 21, 2024Abstract:We used a 3D simulator to create artificial video data with standardized annotations, aiming to aid in the development of Embodied AI. Our question answering (QA) dataset measures the extent to which a robot can understand human behavior and the environment in a home setting. Preliminary experiments suggest our dataset is useful in measuring AI's comprehension of daily life. \end{abstract}
A Logical Approach to Criminal Case Investigation
Feb 13, 2024Abstract:XAI (eXplanable AI) techniques that have the property of explaining the reasons for their conclusions, i.e. explainability or interpretability, are attracting attention. XAI is expected to be used in the development of forensic science and the justice system. In today's forensic and criminal investigation environment, experts face many challenges due to large amounts of data, small pieces of evidence in a chaotic and complex environment, traditional laboratory structures and sometimes inadequate knowledge. All these can lead to failed investigations and miscarriages of justice. In this paper, we describe the application of one logical approach to crime scene investigation. The subject of the application is ``The Adventure of the Speckled Band'' from the Sherlock Holmes short stories. The applied data is the knowledge graph created for the Knowledge Graph Reasoning Challenge. We tried to find the murderer by inferring each person with the motive, opportunity, and method. We created an ontology of motives and methods of murder from dictionaries and dictionaries, added it to the knowledge graph of ``The Adventure of the Speckled Band'', and applied scripts to determine motives, opportunities, and methods.
Synthetic Multimodal Dataset for Empowering Safety and Well-being in Home Environments
Jan 26, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a synthetic multimodal dataset of daily activities that fuses video data from a 3D virtual space simulator with knowledge graphs depicting the spatiotemporal context of the activities. The dataset is developed for the Knowledge Graph Reasoning Challenge for Social Issues (KGRC4SI), which focuses on identifying and addressing hazardous situations in the home environment. The dataset is available to the public as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners developing innovative solutions recognizing human behaviors to enhance safety and well-being in
RDF-star2Vec: RDF-star Graph Embeddings for Data Mining
Dec 25, 2023Abstract:Knowledge Graphs (KGs) such as Resource Description Framework (RDF) data represent relationships between various entities through the structure of triples (<subject, predicate, object>). Knowledge graph embedding (KGE) is crucial in machine learning applications, specifically in node classification and link prediction tasks. KGE remains a vital research topic within the semantic web community. RDF-star introduces the concept of a quoted triple (QT), a specific form of triple employed either as the subject or object within another triple. Moreover, RDF-star permits a QT to act as compositional entities within another QT, thereby enabling the representation of recursive, hyper-relational KGs with nested structures. However, existing KGE models fail to adequately learn the semantics of QTs and entities, primarily because they do not account for RDF-star graphs containing multi-leveled nested QTs and QT-QT relationships. This study introduces RDF-star2Vec, a novel KGE model specifically designed for RDF-star graphs. RDF-star2Vec introduces graph walk techniques that enable probabilistic transitions between a QT and its compositional entities. Feature vectors for QTs, entities, and relations are derived from generated sequences through the structured skip-gram model. Additionally, we provide a dataset and a benchmarking framework for data mining tasks focused on complex RDF-star graphs. Evaluative experiments demonstrated that RDF-star2Vec yielded superior performance compared to recent extensions of RDF2Vec in various tasks including classification, clustering, entity relatedness, and QT similarity.
* 13 pages, 6 figures, and this paper has been accepted by IEEE Access
Synthesizing Event-centric Knowledge Graphs of Daily Activities Using Virtual Space
Jul 30, 2023



Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to be embodied in software agents, robots, and cyber-physical systems that can understand the various contextual information of daily life in the home environment to support human behavior and decision making in various situations. Scene graph and knowledge graph (KG) construction technologies have attracted much attention for knowledge-based embodied question answering meeting this expectation. However, collecting and managing real data on daily activities under various experimental conditions in a physical space are quite costly, and developing AI that understands the intentions and contexts is difficult. In the future, data from both virtual spaces, where conditions can be easily modified, and physical spaces, where conditions are difficult to change, are expected to be combined to analyze daily living activities. However, studies on the KG construction of daily activities using virtual space and their application have yet to progress. The potential and challenges must still be clarified to facilitate AI development for human daily life. Thus, this study proposes the VirtualHome2KG framework to generate synthetic KGs of daily life activities in virtual space. This framework augments both the synthetic video data of daily activities and the contextual semantic data corresponding to the video contents based on the proposed event-centric schema and virtual space simulation results. Therefore, context-aware data can be analyzed, and various applications that have conventionally been difficult to develop due to the insufficient availability of relevant data and semantic information can be developed. We also demonstrate herein the utility and potential of the proposed VirtualHome2KG framework through several use cases, including the analysis of daily activities by querying, embedding, and clustering, and fall risk detection among ...
* 17 pages, 12 figures, and this paper has been accepted by IEEE Access
Report on the First Knowledge Graph Reasoning Challenge 2018 -- Toward the eXplainable AI System
Aug 22, 2019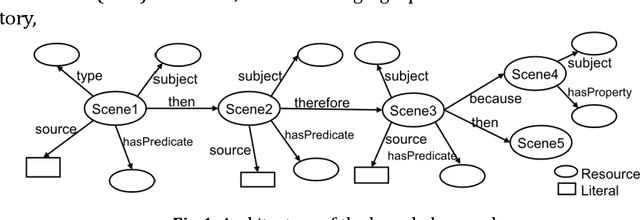
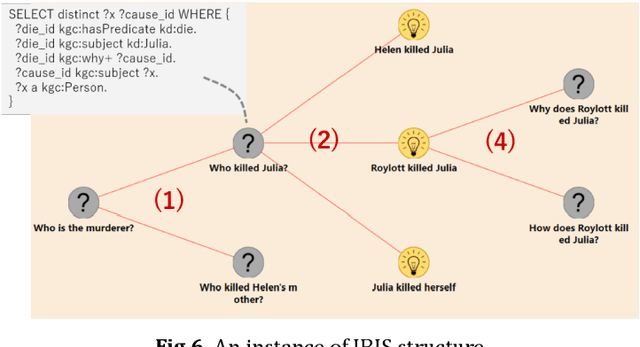
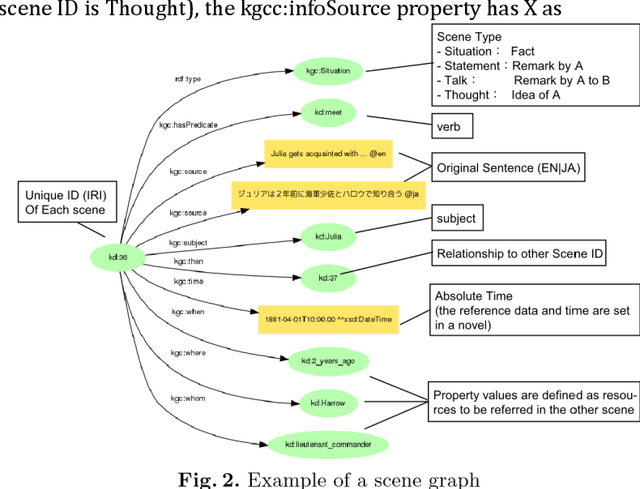
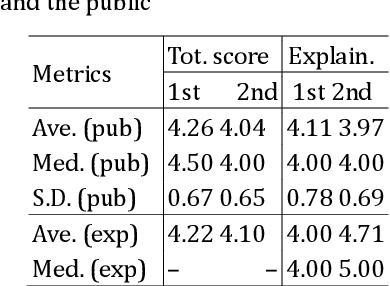
Abstract:A new challenge for knowledge graph reasoning started in 2018. Deep learning has promoted the application of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to a wide variety of social problems. Accordingly, being able to explain the reason for an AI decision is becoming important to ensure the secure and safe use of AI techniques. Thus, we, the Special Interest Group on Semantic Web and Ontology of the Japanese Society for AI, organized a challenge calling for techniques that reason and/or estimate which characters are criminals while providing a reasonable explanation based on an open knowledge graph of a well-known Sherlock Holmes mystery story. This paper presents a summary report of the first challenge held in 2018, including the knowledge graph construction, the techniques proposed for reasoning and/or estimation, the evaluation metrics, and the results. The first prize went to an approach that formalized the problem as a constraint satisfaction problem and solved it using a lightweight formal method; the second prize went to an approach that used SPARQL and rules; the best resource prize went to a submission that constructed word embedding of characters from all sentences of Sherlock Holmes novels; and the best idea prize went to a discussion multi-agents model. We conclude this paper with the plans and issues for the next challenge in 2019.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge