Takaaki Tagawa
An Attention-based Recurrent Convolutional Network for Vehicle Taillight Recognition
Jun 09, 2019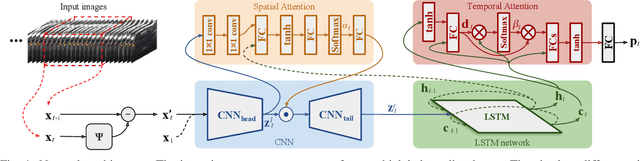

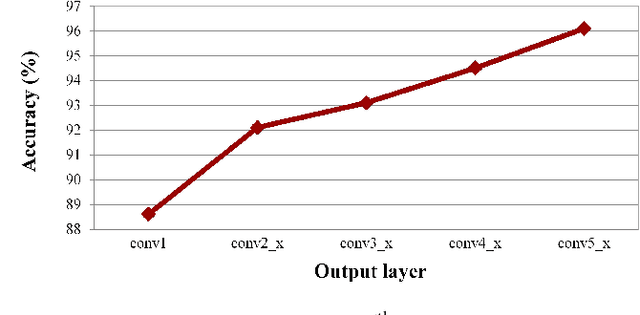
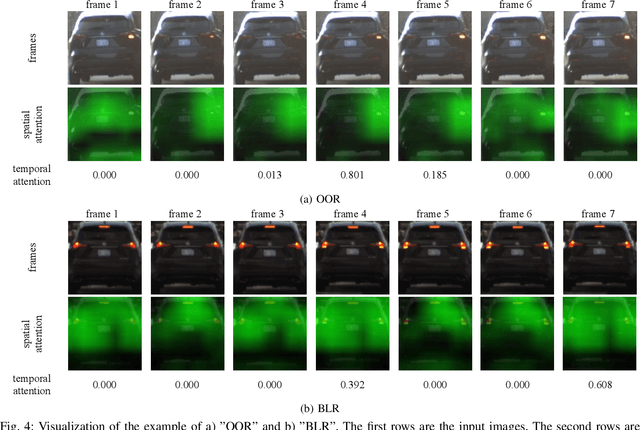
Abstract:Vehicle taillight recognition is an important application for automated driving, especially for intent prediction of ado vehicles and trajectory planning of the ego vehicle. In this work, we propose an end-to-end deep learning framework to recognize taillights, i.e. rear turn and brake signals, from a sequence of images. The proposed method starts with a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to extract spatial features, and then applies a Long Short-Term Memory network (LSTM) to learn temporal dependencies. Furthermore, we integrate attention models in both spatial and temporal domains, where the attention models learn to selectively focus on both spatial and temporal features. Our method is able to outperform the state of the art in terms of accuracy on the UC Merced Vehicle Rear Signal Dataset, demonstrating the effectiveness of attention models for vehicle taillight recognition.
Learning to Fuse Things and Stuff
Dec 04, 2018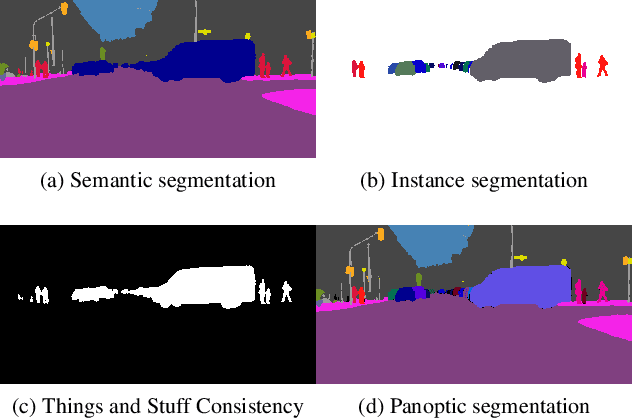
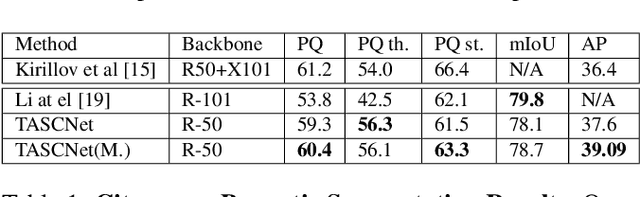
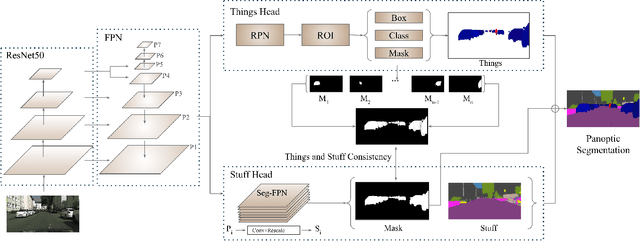
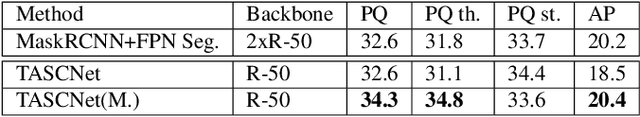
Abstract:We propose an end-to-end learning approach for panoptic segmentation, a novel task unifying instance (things) and semantic (stuff) segmentation. Our model, TASCNet, uses feature maps from a shared backbone network to predict in a single feed-forward pass both things and stuff segmentations. We explicitly constrain these two output distributions through a global things and stuff binary mask to enforce cross-task consistency. Our proposed unified network is competitive with the state of the art on several benchmarks for panoptic segmentation as well as on the individual semantic and instance segmentation tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge