T. Y. S. S. Santosh
LeCoPCR: Legal Concept-guided Prior Case Retrieval for European Court of Human Rights cases
Jan 23, 2025


Abstract:Prior case retrieval (PCR) is crucial for legal practitioners to find relevant precedent cases given the facts of a query case. Existing approaches often overlook the underlying semantic intent in determining relevance with respect to the query case. In this work, we propose LeCoPCR, a novel approach that explicitly generate intents in the form of legal concepts from a given query case facts and then augments the query with these concepts to enhance models understanding of semantic intent that dictates relavance. To overcome the unavailability of annotated legal concepts, we employ a weak supervision approach to extract key legal concepts from the reasoning section using Determinantal Point Process (DPP) to balance quality and diversity. Experimental results on the ECtHR-PCR dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of leveraging legal concepts and DPP-based key concept extraction.
RELexED: Retrieval-Enhanced Legal Summarization with Exemplar Diversity
Jan 23, 2025

Abstract:This paper addresses the task of legal summarization, which involves distilling complex legal documents into concise, coherent summaries. Current approaches often struggle with content theme deviation and inconsistent writing styles due to their reliance solely on source documents. We propose RELexED, a retrieval-augmented framework that utilizes exemplar summaries along with the source document to guide the model. RELexED employs a two-stage exemplar selection strategy, leveraging a determinantal point process to balance the trade-off between similarity of exemplars to the query and diversity among exemplars, with scores computed via influence functions. Experimental results on two legal summarization datasets demonstrate that RELexED significantly outperforms models that do not utilize exemplars and those that rely solely on similarity-based exemplar selection.
CoPERLex: Content Planning with Event-based Representations for Legal Case Summarization
Jan 23, 2025Abstract:Legal professionals often struggle with lengthy judgments and require efficient summarization for quick comprehension. To address this challenge, we investigate the need for structured planning in legal case summarization, particularly through event-centric representations that reflect the narrative nature of legal case documents. We propose our framework, CoPERLex, which operates in three stages: first, it performs content selection to identify crucial information from the judgment; second, the selected content is utilized to generate intermediate plans through event-centric representations modeled as Subject-Verb-Object tuples; and finally, it generates coherent summaries based on both the content and the structured plan. Our experiments on four legal summarization datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of integrating content selection and planning components, highlighting the advantages of event-centric plans over traditional entity-centric approaches in the context of legal judgements.
QABISAR: Query-Article Bipartite Interactions for Statutory Article Retrieval
Dec 01, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce QABISAR, a novel framework for statutory article retrieval, to overcome the semantic mismatch problem when modeling each query-article pair in isolation, making it hard to learn representation that can effectively capture multi-faceted information. QABISAR leverages bipartite interactions between queries and articles to capture diverse aspects inherent in them. Further, we employ knowledge distillation to transfer enriched query representations from the graph network into the query bi-encoder, to capture the rich semantics present in the graph representations, despite absence of graph-based supervision for unseen queries during inference. Our experiments on a real-world expert-annotated dataset demonstrate its effectiveness.
LexSumm and LexT5: Benchmarking and Modeling Legal Summarization Tasks in English
Oct 12, 2024Abstract:In the evolving NLP landscape, benchmarks serve as yardsticks for gauging progress. However, existing Legal NLP benchmarks only focus on predictive tasks, overlooking generative tasks. This work curates LexSumm, a benchmark designed for evaluating legal summarization tasks in English. It comprises eight English legal summarization datasets, from diverse jurisdictions, such as the US, UK, EU and India. Additionally, we release LexT5, legal oriented sequence-to-sequence model, addressing the limitation of the existing BERT-style encoder-only models in the legal domain. We assess its capabilities through zero-shot probing on LegalLAMA and fine-tuning on LexSumm. Our analysis reveals abstraction and faithfulness errors even in summaries generated by zero-shot LLMs, indicating opportunities for further improvements. LexSumm benchmark and LexT5 model are available at https://github.com/TUMLegalTech/LexSumm-LexT5.
HiCuLR: Hierarchical Curriculum Learning for Rhetorical Role Labeling of Legal Documents
Sep 27, 2024
Abstract:Rhetorical Role Labeling (RRL) of legal documents is pivotal for various downstream tasks such as summarization, semantic case search and argument mining. Existing approaches often overlook the varying difficulty levels inherent in legal document discourse styles and rhetorical roles. In this work, we propose HiCuLR, a hierarchical curriculum learning framework for RRL. It nests two curricula: Rhetorical Role-level Curriculum (RC) on the outer layer and Document-level Curriculum (DC) on the inner layer. DC categorizes documents based on their difficulty, utilizing metrics like deviation from a standard discourse structure and exposes the model to them in an easy-to-difficult fashion. RC progressively strengthens the model to discern coarse-to-fine-grained distinctions between rhetorical roles. Our experiments on four RRL datasets demonstrate the efficacy of HiCuLR, highlighting the complementary nature of DC and RC.
The Craft of Selective Prediction: Towards Reliable Case Outcome Classification -- An Empirical Study on European Court of Human Rights Cases
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:In high-stakes decision-making tasks within legal NLP, such as Case Outcome Classification (COC), quantifying a model's predictive confidence is crucial. Confidence estimation enables humans to make more informed decisions, particularly when the model's certainty is low, or where the consequences of a mistake are significant. However, most existing COC works prioritize high task performance over model reliability. This paper conducts an empirical investigation into how various design choices including pre-training corpus, confidence estimator and fine-tuning loss affect the reliability of COC models within the framework of selective prediction. Our experiments on the multi-label COC task, focusing on European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR) cases, highlight the importance of a diverse yet domain-specific pre-training corpus for better calibration. Additionally, we demonstrate that larger models tend to exhibit overconfidence, Monte Carlo dropout methods produce reliable confidence estimates, and confident error regularization effectively mitigates overconfidence. To our knowledge, this is the first systematic exploration of selective prediction in legal NLP. Our findings underscore the need for further research on enhancing confidence measurement and improving the trustworthiness of models in the legal domain.
Incorporating Precedents for Legal Judgement Prediction on European Court of Human Rights Cases
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:Inspired by the legal doctrine of stare decisis, which leverages precedents (prior cases) for informed decision-making, we explore methods to integrate them into LJP models. To facilitate precedent retrieval, we train a retriever with a fine-grained relevance signal based on the overlap ratio of alleged articles between cases. We investigate two strategies to integrate precedents: direct incorporation at inference via label interpolation based on case proximity and during training via a precedent fusion module using a stacked-cross attention model. We employ joint training of the retriever and LJP models to address latent space divergence between them. Our experiments on LJP tasks from the ECHR jurisdiction reveal that integrating precedents during training coupled with joint training of the retriever and LJP model, outperforms models without precedents or with precedents incorporated only at inference, particularly benefiting sparser articles.
Joint Span Segmentation and Rhetorical Role Labeling with Data Augmentation for Legal Documents
Feb 13, 2023Abstract:Segmentation and Rhetorical Role Labeling of legal judgements play a crucial role in retrieval and adjacent tasks, including case summarization, semantic search, argument mining etc. Previous approaches have formulated this task either as independent classification or sequence labeling of sentences. In this work, we reformulate the task at span level as identifying spans of multiple consecutive sentences that share the same rhetorical role label to be assigned via classification. We employ semi-Markov Conditional Random Fields (CRF) to jointly learn span segmentation and span label assignment. We further explore three data augmentation strategies to mitigate the data scarcity in the specialized domain of law where individual documents tend to be very long and annotation cost is high. Our experiments demonstrate improvement of span-level prediction metrics with a semi-Markov CRF model over a CRF baseline. This benefit is contingent on the presence of multi sentence spans in the document.
Incorporating Domain Knowledge into Medical NLI using Knowledge Graphs
Aug 31, 2019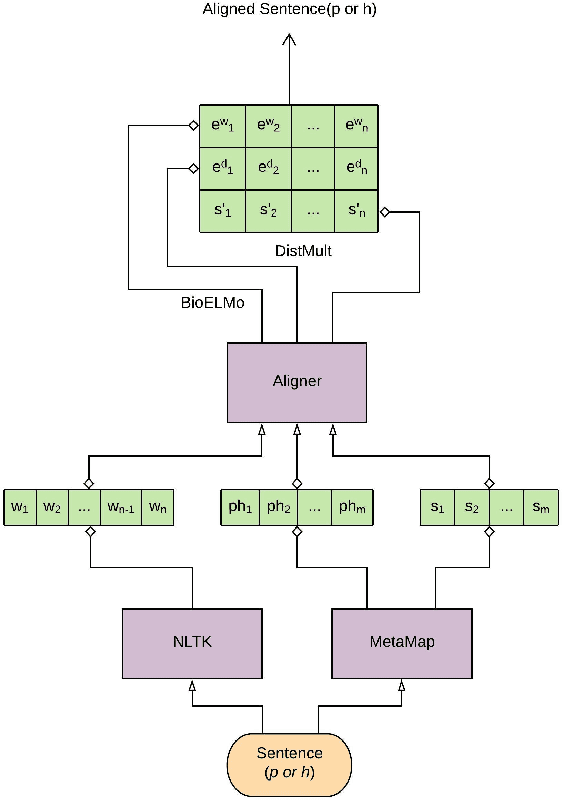
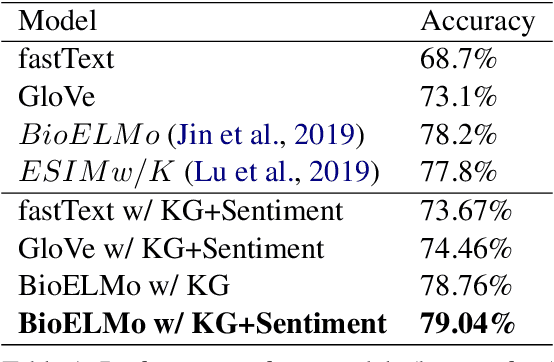
Abstract:Recently, biomedical version of embeddings obtained from language models such as BioELMo have shown state-of-the-art results for the textual inference task in the medical domain. In this paper, we explore how to incorporate structured domain knowledge, available in the form of a knowledge graph (UMLS), for the Medical NLI task. Specifically, we experiment with fusing embeddings obtained from knowledge graph with the state-of-the-art approaches for NLI task (ESIM model). We also experiment with fusing the domain-specific sentiment information for the task. Experiments conducted on MedNLI dataset clearly show that this strategy improves the baseline BioELMo architecture for the Medical NLI task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge