Syed Arbaaz Qureshi
Assessing the Effectiveness of Syntactic Structure to Learn Code Edit Representations
Jun 11, 2021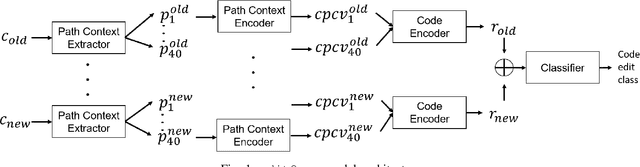
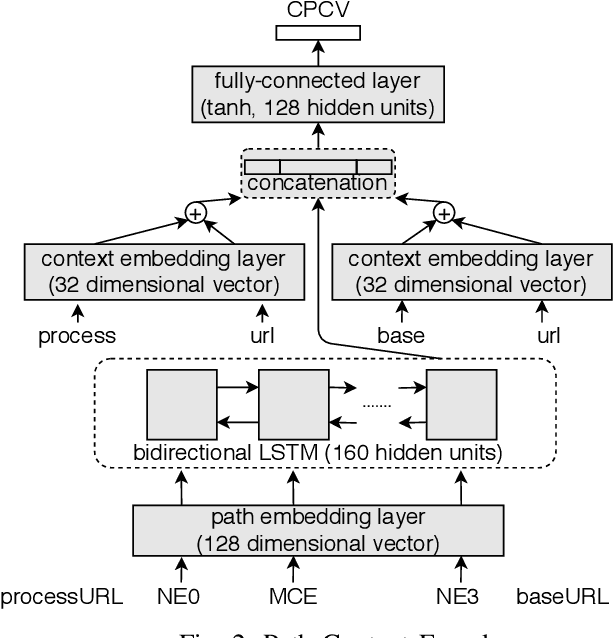
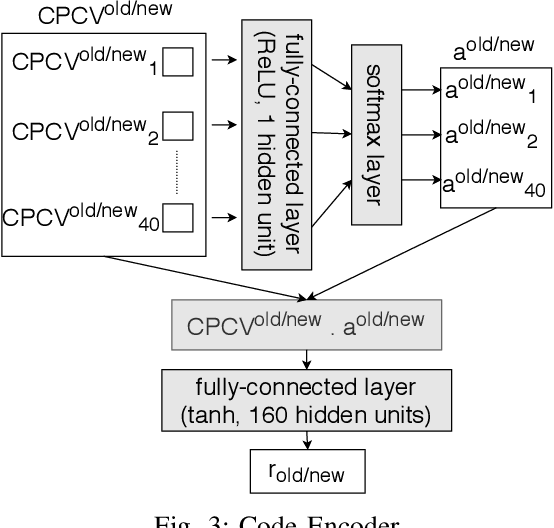
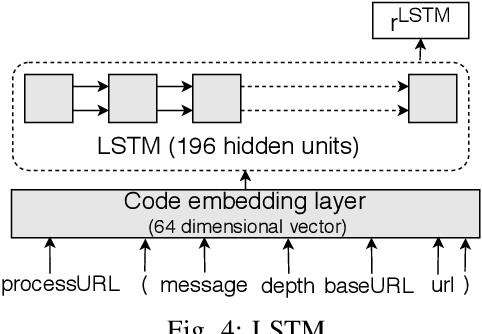
Abstract:In recent times, it has been shown that one can use code as data to aid various applications such as automatic commit message generation, automatic generation of pull request descriptions and automatic program repair. Take for instance the problem of commit message generation. Treating source code as a sequence of tokens, state of the art techniques generate commit messages using neural machine translation models. However, they tend to ignore the syntactic structure of programming languages. Previous work, i.e., code2seq has used structural information from Abstract Syntax Tree (AST) to represent source code and they use it to automatically generate method names. In this paper, we elaborate upon this state of the art approach and modify it to represent source code edits. We determine the effect of using such syntactic structure for the problem of classifying code edits. Inspired by the code2seq approach, we evaluate how using structural information from AST, i.e., paths between AST leaf nodes can help with the task of code edit classification on two datasets of fine-grained syntactic edits. Our experiments shows that attempts of adding syntactic structure does not result in any improvements over less sophisticated methods. The results suggest that techniques such as code2seq, while promising, have a long way to go before they can be generically applied to learning code edit representations. We hope that these results will benefit other researchers and inspire them to work further on this problem.
The Verbal and Non Verbal Signals of Depression -- Combining Acoustics, Text and Visuals for Estimating Depression Level
Apr 02, 2019
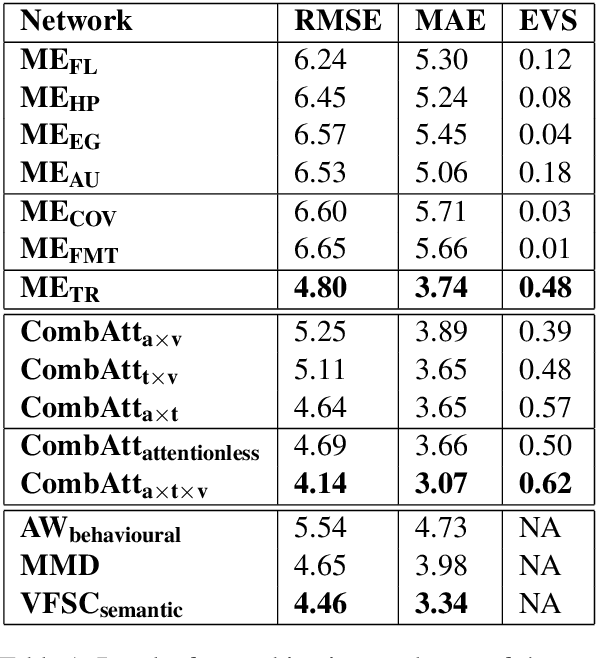
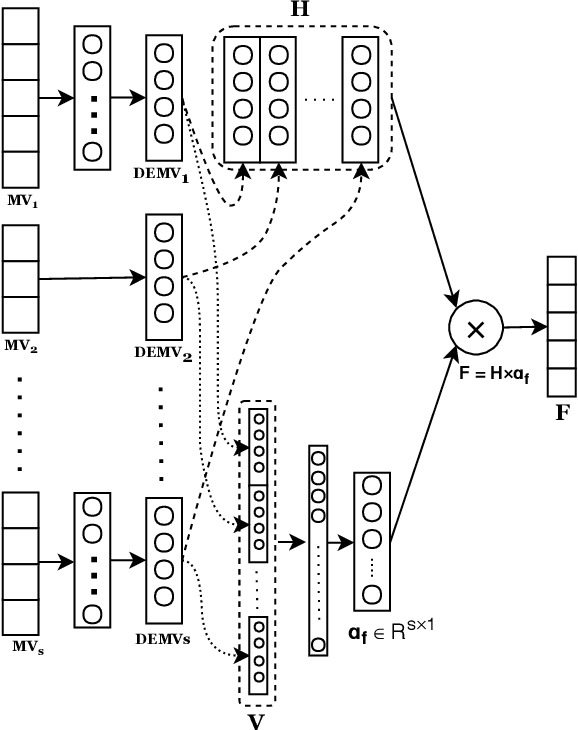
Abstract:Depression is a serious medical condition that is suffered by a large number of people around the world. It significantly affects the way one feels, causing a persistent lowering of mood. In this paper, we propose a novel attention-based deep neural network which facilitates the fusion of various modalities. We use this network to regress the depression level. Acoustic, text and visual modalities have been used to train our proposed network. Various experiments have been carried out on the benchmark dataset, namely, Distress Analysis Interview Corpus - a Wizard of Oz (DAIC-WOZ). From the results, we empirically justify that the fusion of all three modalities helps in giving the most accurate estimation of depression level. Our proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art by 7.17% on root mean squared error (RMSE) and 8.08% on mean absolute error (MAE).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge