Swathi Kiran
How the Stroop Effect Arises from Optimal Response Times in Laterally Connected Self-Organizing Maps
Feb 05, 2025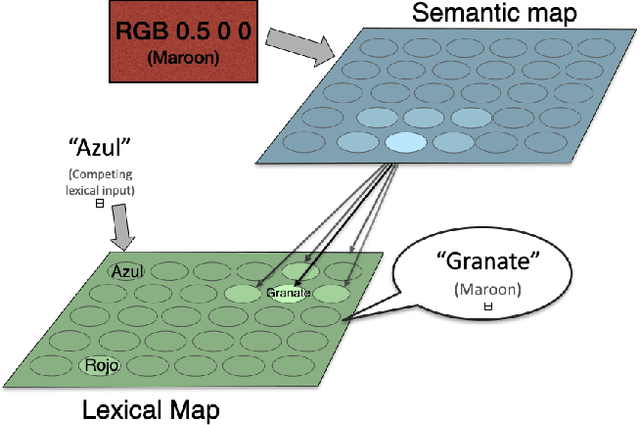
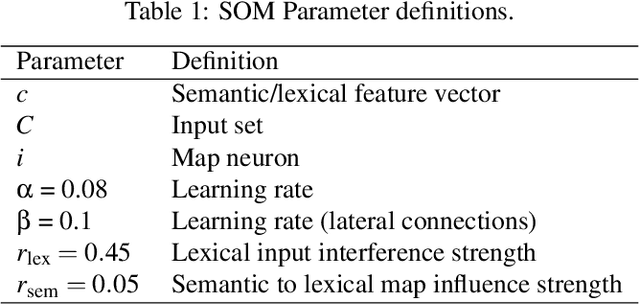
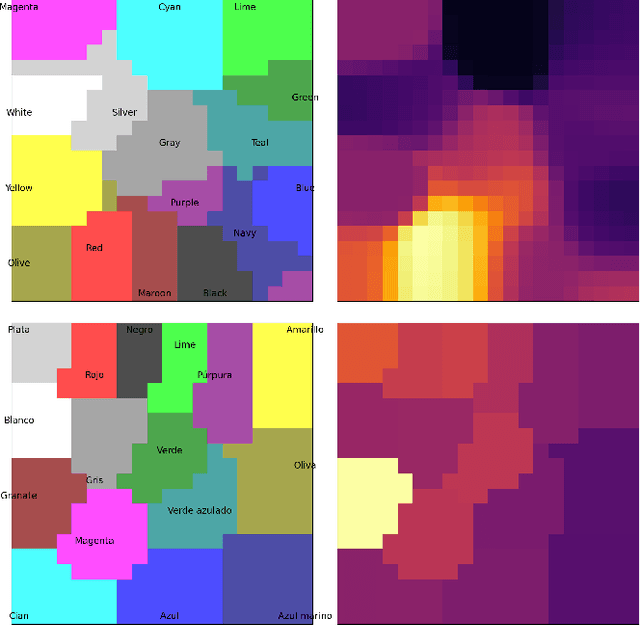
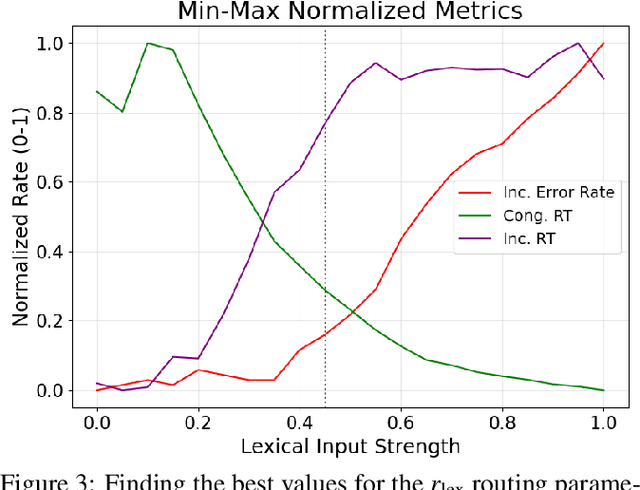
Abstract:The Stroop effect refers to cognitive interference in a color-naming task: When the color and the word do not match, the response is slower and more likely to be incorrect. The Stroop task is used to assess cognitive flexibility, selective attention, and executive function. This paper implements the Stroop task with self-organizing maps (SOMs): Target color and the competing word are inputs for the semantic and lexical maps, associative connections bring color information to the lexical map, and lateral connections combine their effects over time. The model achieved an overall accuracy of 84.2%, with significantly fewer errors and faster responses in congruent compared to no-input and incongruent conditions. The model's effect is a side effect of optimizing response times, and can thus be seen as a cost associated with overall efficient performance. The model can further serve studying neurologically-inspired cognitive control and related phenomena.
A Lesion-aware Edge-based Graph Neural Network for Predicting Language Ability in Patients with Post-stroke Aphasia
Sep 03, 2024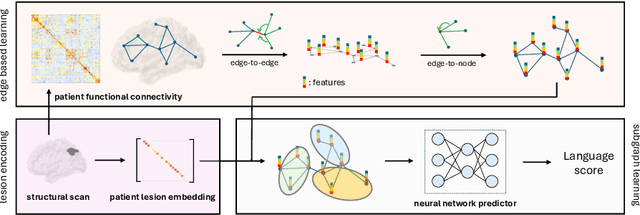



Abstract:We propose a lesion-aware graph neural network (LEGNet) to predict language ability from resting-state fMRI (rs-fMRI) connectivity in patients with post-stroke aphasia. Our model integrates three components: an edge-based learning module that encodes functional connectivity between brain regions, a lesion encoding module, and a subgraph learning module that leverages functional similarities for prediction. We use synthetic data derived from the Human Connectome Project (HCP) for hyperparameter tuning and model pretraining. We then evaluate the performance using repeated 10-fold cross-validation on an in-house neuroimaging dataset of post-stroke aphasia. Our results demonstrate that LEGNet outperforms baseline deep learning methods in predicting language ability. LEGNet also exhibits superior generalization ability when tested on a second in-house dataset that was acquired under a slightly different neuroimaging protocol. Taken together, the results of this study highlight the potential of LEGNet in effectively learning the relationships between rs-fMRI connectivity and language ability in a patient cohort with brain lesions for improved post-stroke aphasia evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge