Suyang Dai
Meta-Reflection: A Feedback-Free Reflection Learning Framework
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Despite the remarkable capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in natural language understanding and reasoning, they often display undesirable behaviors, such as generating hallucinations and unfaithful reasoning. A prevalent strategy to mitigate these issues is the use of reflection, which refines responses through an iterative process. However, while promising, reflection heavily relies on high-quality external feedback and requires iterative multi-agent inference processes, thus hindering its practical application. In this paper, we propose Meta-Reflection, a novel feedback-free reflection mechanism that necessitates only a single inference pass without external feedback. Motivated by the human ability to remember and retrieve reflections from past experiences when encountering similar problems, Meta-Reflection integrates reflective insights into a codebook, allowing the historical insights to be stored, retrieved, and used to guide LLMs in problem-solving. To thoroughly investigate and evaluate the practicality of Meta-Reflection in real-world scenarios, we introduce an industrial e-commerce benchmark named E-commerce Customer Intent Detection (ECID). Extensive experiments conducted on both public datasets and the ECID benchmark highlight the effectiveness and efficiency of our proposed approach.
AttentionXML: Extreme Multi-Label Text Classification with Multi-Label Attention Based Recurrent Neural Networks
Nov 01, 2018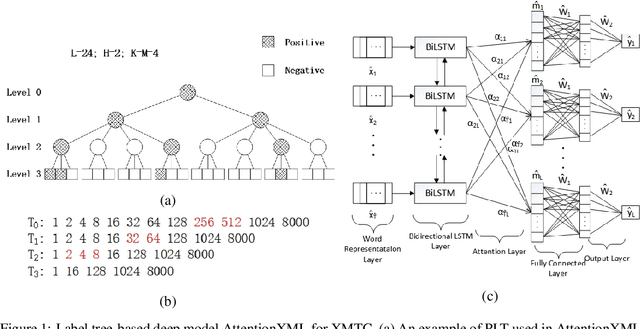
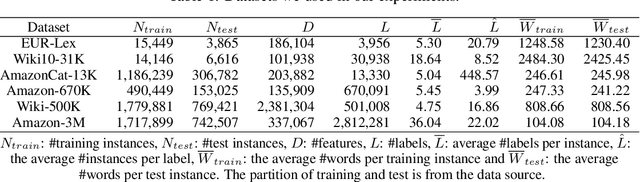
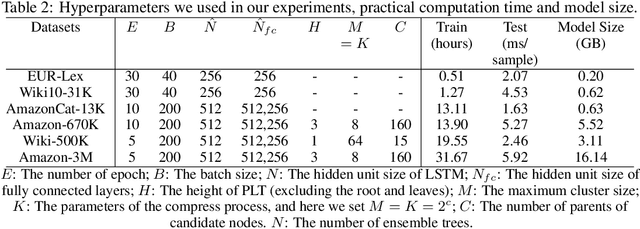
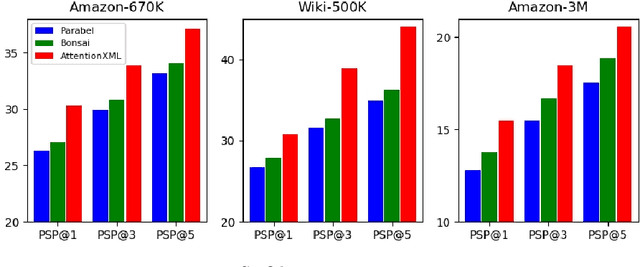
Abstract:Extreme multi-label text classification (XMTC) is a task for tagging each given text with the most relevant multiple labels from an extremely large-scale label set. This task can be found in many applications, such as product categorization,web page tagging, news annotation and so on. Many methods have been proposed so far for solving XMTC, while most of the existing methods use traditional bag-of-words (BOW) representation, ignoring word context as well as deep semantic information. XML-CNN, a state-of-the-art deep learning-based method, uses convolutional neural network (CNN) with dynamic pooling to process the text, going beyond the BOW-based appraoches but failing to capture 1) the long-distance dependency among words and 2) different levels of importance of a word for each label. We propose a new deep learning-based method, AttentionXML, which uses bidirectional long short-term memory (LSTM) and a multi-label attention mechanism for solving the above 1st and 2nd problems, respectively. We empirically compared AttentionXML with other six state-of-the-art methods over five benchmark datasets. AttentionXML outperformed all competing methods under all experimental settings except only a couple of cases. In addition, a consensus ensemble of AttentionXML with the second best method, Parabel, could further improve the performance over all five benchmark datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge