Sushant Mehta
HELM: A Human-Centered Evaluation Framework for LLM-Powered Recommender Systems
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into recommendation systems has introduced unprecedented capabilities for natural language understanding, explanation generation, and conversational interactions. However, existing evaluation methodologies focus predominantly on traditional accuracy metrics, failing to capture the multifaceted human-centered qualities that determine the real-world user experience. We introduce \framework{} (\textbf{H}uman-centered \textbf{E}valuation for \textbf{L}LM-powered reco\textbf{M}menders), a comprehensive evaluation framework that systematically assesses LLM-powered recommender systems across five human-centered dimensions: \textit{Intent Alignment}, \textit{Explanation Quality}, \textit{Interaction Naturalness}, \textit{Trust \& Transparency}, and \textit{Fairness \& Diversity}. Through extensive experiments involving three state-of-the-art LLM-based recommenders (GPT-4, LLaMA-3.1, and P5) across three domains (movies, books, and restaurants), and rigorous evaluation by 12 domain experts using 847 recommendation scenarios, we demonstrate that \framework{} reveals critical quality dimensions invisible to traditional metrics. Our results show that while GPT-4 achieves superior explanation quality (4.21/5.0) and interaction naturalness (4.35/5.0), it exhibits a significant popularity bias (Gini coefficient 0.73) compared to traditional collaborative filtering (0.58). We release \framework{} as an open-source toolkit to advance human-centered evaluation practices in the recommender systems community.
The Hierarchy of Agentic Capabilities: Evaluating Frontier Models on Realistic RL Environments
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:The advancement of large language model (LLM) based agents has shifted AI evaluation from single-turn response assessment to multi-step task completion in interactive environments. We present an empirical study evaluating frontier AI models on 150 workplace tasks within a realistic e-commerce RL environment from Surge. Our analysis reveals an empirically-derived \emph{hierarchy of agentic capabilities} that models must master for real-world deployment: (1) tool use, (2) planning and goal formation, (3) adaptability, (4) groundedness, and (5) common-sense reasoning. Even the best-performing models fail approximately 40\% of the tasks, with failures clustering predictably along this hierarchy. Weaker models struggle with fundamental tool use and planning, whereas stronger models primarily fail on tasks requiring contextual inference beyond explicit instructions. We introduce a task-centric design methodology for RL environments that emphasizes diversity and domain expert contributions, provide detailed failure analysis, and discuss implications for agent development. Our findings suggest that while current frontier models can demonstrate coherent multi-step behavior, substantial capability gaps remain before achieving human-level task completion in realistic workplace settings.
Beyond Accuracy: A Multi-Dimensional Framework for Evaluating Enterprise Agentic AI Systems
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Current agentic AI benchmarks predominantly evaluate task completion accuracy, while overlooking critical enterprise requirements such as cost-efficiency, reliability, and operational stability. Through systematic analysis of 12 main benchmarks and empirical evaluation of state-of-the-art agents, we identify three fundamental limitations: (1) absence of cost-controlled evaluation leading to 50x cost variations for similar precision, (2) inadequate reliability assessment where agent performance drops from 60\% (single run) to 25\% (8-run consistency), and (3) missing multidimensional metrics for security, latency, and policy compliance. We propose \textbf{CLEAR} (Cost, Latency, Efficacy, Assurance, Reliability), a holistic evaluation framework specifically designed for enterprise deployment. Evaluation of six leading agents on 300 enterprise tasks demonstrates that optimizing for accuracy alone yields agents 4.4-10.8x more expensive than cost-aware alternatives with comparable performance. Expert evaluation (N=15) confirms that CLEAR better predicts production success (correlation $ρ=0.83$) compared to accuracy-only evaluation ($ρ=0.41$).
Scaling Laws and In-Context Learning: A Unified Theoretical Framework
Nov 09, 2025



Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) enables large language models to adapt to new tasks from demonstrations without parameter updates. Despite extensive empirical studies, a principled understanding of ICL emergence at scale remains more elusive. We present a unified theoretical framework connecting scaling laws to ICL emergence in transformers. Our analysis establishes that ICL performance follows power-law relationships with model depth $L$, width $d$, context length $k$, and training data $D$, with exponents determined by task structure. We show that under specific conditions, transformers implement gradient-based metalearning in their forward pass, with an effective learning rate $η_{\text{eff}} = Θ(1/\sqrt{Ld})$. We demonstrate sharp phase transitions at critical scales and derive optimal depth-width allocations favoring $L^* \propto N^{2/3}$, $d^* \propto N^{1/3}$ for the fixed parameter budget $N = Ld$. Systematic experiments on synthetic tasks validate our predictions, with measured scaling exponents closely matching theory. This work provides both necessary and sufficient conditions for the emergence of ICLs and establishes fundamental computational limits on what transformers can learn in-context.
When Are Learning Biases Equivalent? A Unifying Framework for Fairness, Robustness, and Distribution Shift
Nov 09, 2025



Abstract:Machine learning systems exhibit diverse failure modes: unfairness toward protected groups, brittleness to spurious correlations, poor performance on minority sub-populations, which are typically studied in isolation by distinct research communities. We propose a unifying theoretical framework that characterizes when different bias mechanisms produce quantitatively equivalent effects on model performance. By formalizing biases as violations of conditional independence through information-theoretic measures, we prove formal equivalence conditions relating spurious correlations, subpopulation shift, class imbalance, and fairness violations. Our theory predicts that a spurious correlation of strength $α$ produces equivalent worst-group accuracy degradation as a sub-population imbalance ratio $r \approx (1+α)/(1-α)$ under feature overlap assumptions. Empirical validation in six datasets and three architectures confirms that predicted equivalences hold within the accuracy of the worst group 3\%, enabling the principled transfer of debiasing methods across problem domains. This work bridges the literature on fairness, robustness, and distribution shifts under a common perspective.
Latent Multi-Head Attention for Small Language Models
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:We present the first comprehensive study of latent multi-head attention (MLA) for small language models, revealing interesting efficiency-quality trade-offs. Training 30M-parameter GPT models on 100,000 synthetic stories, we benchmark three architectural variants: standard multi-head attention (MHA), MLA, and MLA with rotary positional embeddings (MLA+RoPE). Our key finding is that MLA+RoPE with half-rank latent dimensions (r = d/2) achieves a 45% KV-cache memory reduction while incurring only a 0.3% increase in validation loss (essentially matching MHA quality)- a Pareto improvement for memory constrained deployment. We further show that RoPE is crucial for MLA in small models: without it, MLA underperforms vanilla attention by 3-5%, but with RoPE, it surpasses vanilla by 2%. Inference benchmarks on NVIDIA A100 GPUs reveal that MLA with r=d/2 achieves a 1.4 times speedup over full-rank MLA while maintaining the memory savings. GPT-4 evaluations corroborate perplexity results, with ours achieving the highest quality scores (7.4/10) across grammar, creativity, and consistency metrics. Code and models will be released upon acceptance.
Interactive Image Generation Using Scene Graphs
May 09, 2019

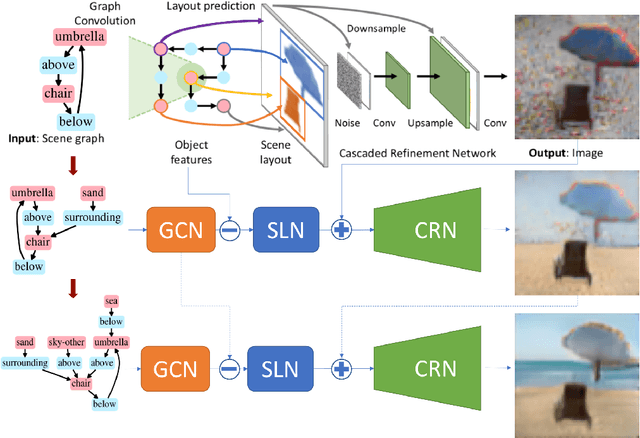

Abstract:Recent years have witnessed some exciting developments in the domain of generating images from scene-based text descriptions. These approaches have primarily focused on generating images from a static text description and are limited to generating images in a single pass. They are unable to generate an image interactively based on an incrementally additive text description (something that is more intuitive and similar to the way we describe an image). We propose a method to generate an image incrementally based on a sequence of graphs of scene descriptions (scene-graphs). We propose a recurrent network architecture that preserves the image content generated in previous steps and modifies the cumulative image as per the newly provided scene information. Our model utilizes Graph Convolutional Networks (GCN) to cater to variable-sized scene graphs along with Generative Adversarial image translation networks to generate realistic multi-object images without needing any intermediate supervision during training. We experiment with Coco-Stuff dataset which has multi-object images along with annotations describing the visual scene and show that our model significantly outperforms other approaches on the same dataset in generating visually consistent images for incrementally growing scene graphs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge