Sukhbinder Singh
Tensorization is a powerful but underexplored tool for compression and interpretability of neural networks
May 26, 2025Abstract:Tensorizing a neural network involves reshaping some or all of its dense weight matrices into higher-order tensors and approximating them using low-rank tensor network decompositions. This technique has shown promise as a model compression strategy for large-scale neural networks. However, despite encouraging empirical results, tensorized neural networks (TNNs) remain underutilized in mainstream deep learning. In this position paper, we offer a perspective on both the potential and current limitations of TNNs. We argue that TNNs represent a powerful yet underexplored framework for deep learning--one that deserves greater attention from both engineering and theoretical communities. Beyond compression, we highlight the value of TNNs as a flexible class of architectures with distinctive scaling properties and increased interpretability. A central feature of TNNs is the presence of bond indices, which introduce new latent spaces not found in conventional networks. These internal representations may provide deeper insight into the evolution of features across layers, potentially advancing the goals of mechanistic interpretability. We conclude by outlining several key research directions aimed at overcoming the practical barriers to scaling and adopting TNNs in modern deep learning workflows.
Quantum Large Language Models via Tensor Network Disentanglers
Oct 22, 2024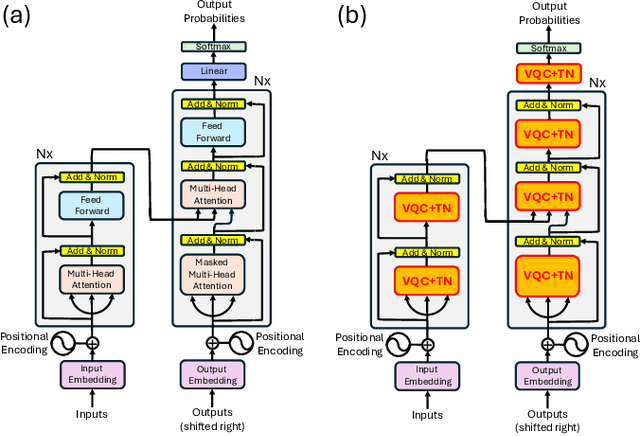
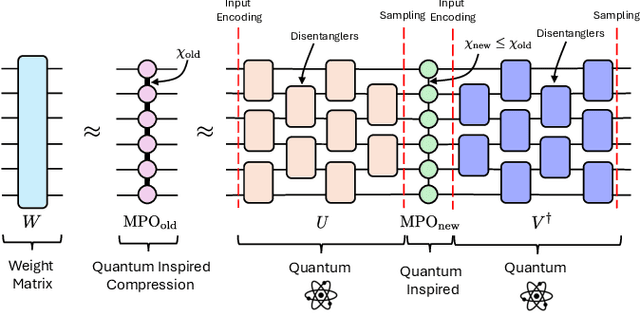
Abstract:We propose a method to enhance the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) by integrating quantum computing and quantum-inspired techniques. Specifically, our approach involves replacing the weight matrices in the Self-Attention and Multi-layer Perceptron layers with a combination of two variational quantum circuits and a quantum-inspired tensor network, such as a Matrix Product Operator (MPO). This substitution enables the reproduction of classical LLM functionality by decomposing weight matrices through the application of tensor network disentanglers and MPOs, leveraging well-established tensor network techniques. By incorporating more complex and deeper quantum circuits, along with increasing the bond dimensions of the MPOs, our method captures additional correlations within the quantum-enhanced LLM, leading to improved accuracy beyond classical models while maintaining low memory overhead.
Tensor network compressibility of convolutional models
Mar 21, 2024Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) represent one of the most widely used neural network architectures, showcasing state-of-the-art performance in computer vision tasks. Although larger CNNs generally exhibit higher accuracy, their size can be effectively reduced by "tensorization" while maintaining accuracy. Tensorization consists of replacing the convolution kernels with compact decompositions such as Tucker, Canonical Polyadic decompositions, or quantum-inspired decompositions such as matrix product states, and directly training the factors in the decompositions to bias the learning towards low-rank decompositions. But why doesn't tensorization seem to impact the accuracy adversely? We explore this by assessing how truncating the convolution kernels of dense (untensorized) CNNs impact their accuracy. Specifically, we truncated the kernels of (i) a vanilla four-layer CNN and (ii) ResNet-50 pre-trained for image classification on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets. We found that kernels (especially those inside deeper layers) could often be truncated along several cuts resulting in significant loss in kernel norm but not in classification accuracy. This suggests that such ``correlation compression'' (underlying tensorization) is an intrinsic feature of how information is encoded in dense CNNs. We also found that aggressively truncated models could often recover the pre-truncation accuracy after only a few epochs of re-training, suggesting that compressing the internal correlations of convolution layers does not often transport the model to a worse minimum. Our results can be applied to tensorize and compress CNN models more effectively.
CompactifAI: Extreme Compression of Large Language Models using Quantum-Inspired Tensor Networks
Jan 25, 2024


Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and LlaMA are advancing rapidly in generative Artificial Intelligence (AI), but their immense size poses significant challenges, such as huge training and inference costs, substantial energy demands, and limitations for on-site deployment. Traditional compression methods such as pruning, distillation, and low-rank approximation focus on reducing the effective number of neurons in the network, while quantization focuses on reducing the numerical precision of individual weights to reduce the model size while keeping the number of neurons fixed. While these compression methods have been relatively successful in practice, there's no compelling reason to believe that truncating the number of neurons is an optimal strategy. In this context, this paper introduces CompactifAI, an innovative LLM compression approach using quantum-inspired Tensor Networks that focuses on the model's correlation space instead, allowing for a more controlled, refined and interpretable model compression. Our method is versatile and can be implemented with - or on top of - other compression techniques. As a benchmark, we demonstrate that CompactifAI alone enables compression of the LlaMA-2 7B model to only $30\%$ of its original size while recovering over $90\%$ of the original accuracy after a brief distributed retraining.
Efficient tensor network simulation of IBM's largest quantum processors
Oct 16, 2023



Abstract:We show how quantum-inspired 2d tensor networks can be used to efficiently and accurately simulate the largest quantum processors from IBM, namely Eagle (127 qubits), Osprey (433 qubits) and Condor (1121 qubits). We simulate the dynamics of a complex quantum many-body system -- specifically, the kicked Ising experiment considered recently by IBM in Nature 618, p. 500-505 (2023) -- using graph-based Projected Entangled Pair States (gPEPS), which was proposed by some of us in PRB 99, 195105 (2019). Our results show that simple tensor updates are already sufficient to achieve very large unprecedented accuracy with remarkably low computational resources for this model. Apart from simulating the original experiment for 127 qubits, we also extend our results to 433 and 1121 qubits, and for evolution times around 8 times longer, thus setting a benchmark for the newest IBM quantum machines. We also report accurate simulations for infinitely-many qubits. Our results show that gPEPS are a natural tool to efficiently simulate quantum computers with an underlying lattice-based qubit connectivity, such as all quantum processors based on superconducting qubits.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge