Faysal Ishtiaq
CompactifAI: Extreme Compression of Large Language Models using Quantum-Inspired Tensor Networks
Jan 25, 2024


Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and LlaMA are advancing rapidly in generative Artificial Intelligence (AI), but their immense size poses significant challenges, such as huge training and inference costs, substantial energy demands, and limitations for on-site deployment. Traditional compression methods such as pruning, distillation, and low-rank approximation focus on reducing the effective number of neurons in the network, while quantization focuses on reducing the numerical precision of individual weights to reduce the model size while keeping the number of neurons fixed. While these compression methods have been relatively successful in practice, there's no compelling reason to believe that truncating the number of neurons is an optimal strategy. In this context, this paper introduces CompactifAI, an innovative LLM compression approach using quantum-inspired Tensor Networks that focuses on the model's correlation space instead, allowing for a more controlled, refined and interpretable model compression. Our method is versatile and can be implemented with - or on top of - other compression techniques. As a benchmark, we demonstrate that CompactifAI alone enables compression of the LlaMA-2 7B model to only $30\%$ of its original size while recovering over $90\%$ of the original accuracy after a brief distributed retraining.
Financial Risk Management on a Neutral Atom Quantum Processor
Dec 06, 2022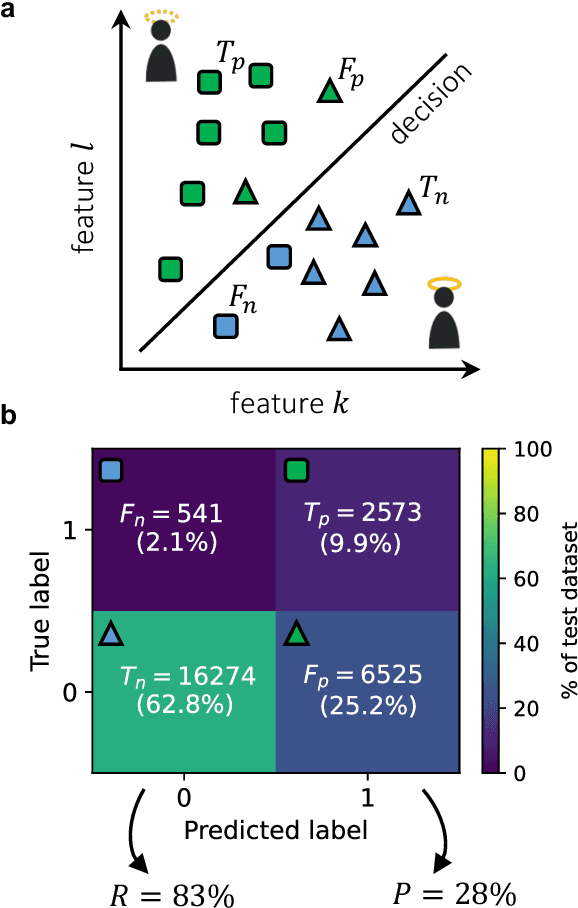
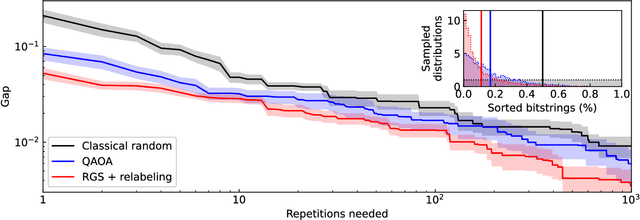
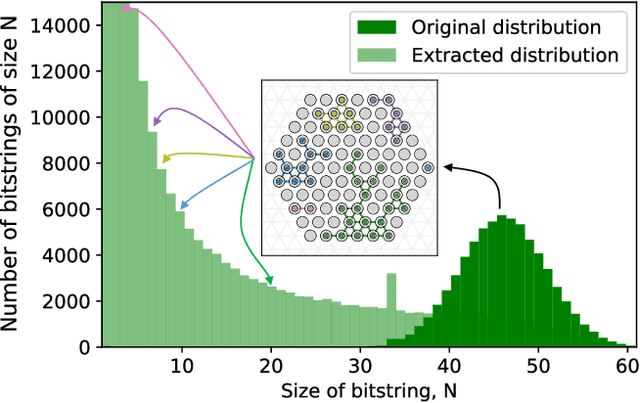
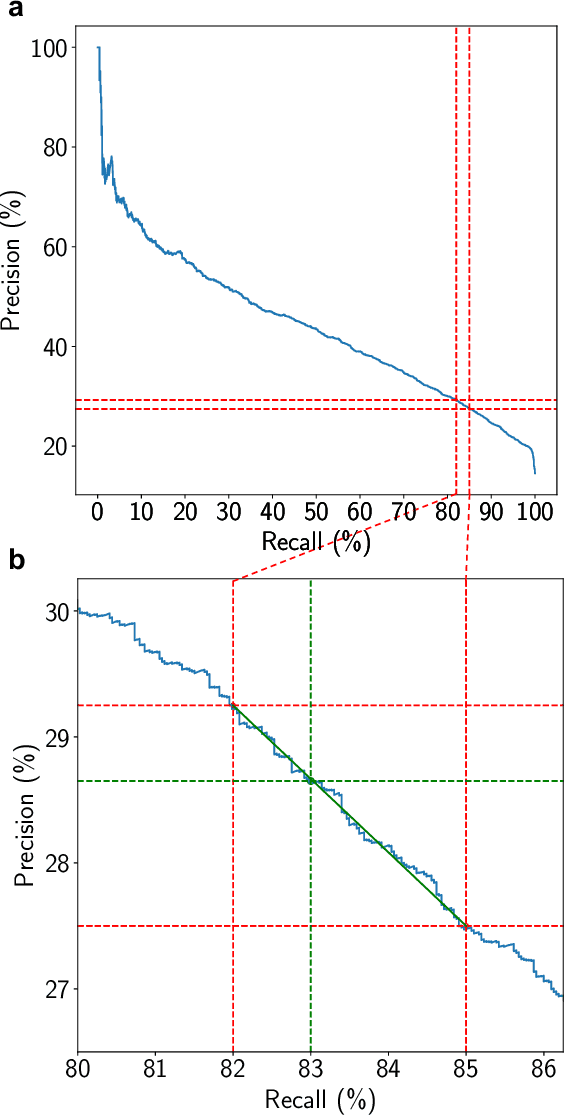
Abstract:Machine Learning models capable of handling the large datasets collected in the financial world can often become black boxes expensive to run. The quantum computing paradigm suggests new optimization techniques, that combined with classical algorithms, may deliver competitive, faster and more interpretable models. In this work we propose a quantum-enhanced machine learning solution for the prediction of credit rating downgrades, also known as fallen-angels forecasting in the financial risk management field. We implement this solution on a neutral atom Quantum Processing Unit with up to 60 qubits on a real-life dataset. We report competitive performances against the state-of-the-art Random Forest benchmark whilst our model achieves better interpretability and comparable training times. We examine how to improve performance in the near-term validating our ideas with Tensor Networks-based numerical simulations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge