Sudipto Ghosh
Disentangling Causal Importance from Emergent Structure in Multi-Expert Orchestration
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Multi-expert systems, where multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) collaborate to solve complex tasks, are increasingly adopted for high-performance reasoning and generation. However, the orchestration policies governing expert interaction and sequencing remain largely opaque. We introduce INFORM, an interpretability analysis that treats orchestration as an explicit, analyzable computation, enabling the decoupling of expert interaction structure, execution order, and causal attribution. We use INFORM to evaluate an orchestrator on GSM8K, HumanEval, and MMLU using a homogeneous consortium of ten instruction-tuned experts drawn from LLaMA-3.1 8B, Qwen-3 8B, and DeepSeek-R1 8B, with controlled decoding-temperature variation, and a secondary heterogeneous consortium spanning 1B-7B parameter models. Across tasks, routing dominance is a poor proxy for functional necessity. We reveal a divergence between relational importance, captured by routing mass and interaction topology, and intrinsic importance, measured via gradient-based causal attribution: frequently selected experts often act as interaction hubs with limited causal influence, while sparsely routed experts can be structurally critical. Orchestration behaviors emerge asynchronously, with expert centralization preceding stable routing confidence and expert ordering remaining non-deterministic. Targeted ablations show that masking intrinsically important experts induces disproportionate collapse in interaction structure compared to masking frequent peers, confirming that INFORM exposes causal and structural dependencies beyond accuracy metrics alone.
Impact of White-Box Adversarial Attacks on Convolutional Neural Networks
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous vehicle navigation and healthcare diagnostics are among the many fields where the reliability and security of machine learning models for image data are critical. We conduct a comprehensive investigation into the susceptibility of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), which are widely used for image data, to white-box adversarial attacks. We investigate the effects of various sophisticated attacks -- Fast Gradient Sign Method, Basic Iterative Method, Jacobian-based Saliency Map Attack, Carlini & Wagner, Projected Gradient Descent, and DeepFool -- on CNN performance metrics, (e.g., loss, accuracy), the differential efficacy of adversarial techniques in increasing error rates, the relationship between perceived image quality metrics (e.g., ERGAS, PSNR, SSIM, and SAM) and classification performance, and the comparative effectiveness of iterative versus single-step attacks. Using the MNIST, CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and Fashio_MNIST datasets, we explore the effect of different attacks on the CNNs performance metrics by varying the hyperparameters of CNNs. Our study provides insights into the robustness of CNNs against adversarial threats, pinpoints vulnerabilities, and underscores the urgent need for developing robust defense mechanisms to protect CNNs and ensuring their trustworthy deployment in real-world scenarios.
Human Centered AI for Indian Legal Text Analytics
Mar 16, 2024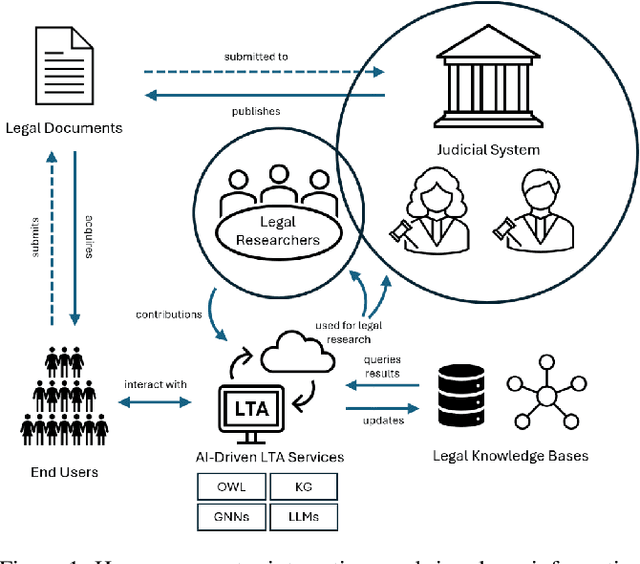
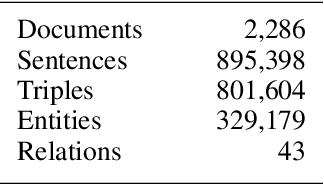


Abstract:Legal research is a crucial task in the practice of law. It requires intense human effort and intellectual prudence to research a legal case and prepare arguments. Recent boom in generative AI has not translated to proportionate rise in impactful legal applications, because of low trustworthiness and and the scarcity of specialized datasets for training Large Language Models (LLMs). This position paper explores the potential of LLMs within Legal Text Analytics (LTA), highlighting specific areas where the integration of human expertise can significantly enhance their performance to match that of experts. We introduce a novel dataset and describe a human centered, compound AI system that principally incorporates human inputs for performing LTA tasks with LLMs.
Link Prediction for Social Networks using Representation Learning and Heuristic-based Features
Mar 13, 2024



Abstract:The exponential growth in scale and relevance of social networks enable them to provide expansive insights. Predicting missing links in social networks efficiently can help in various modern-day business applications ranging from generating recommendations to influence analysis. Several categories of solutions exist for the same. Here, we explore various feature extraction techniques to generate representations of nodes and edges in a social network that allow us to predict missing links. We compare the results of using ten feature extraction techniques categorized across Structural embeddings, Neighborhood-based embeddings, Graph Neural Networks, and Graph Heuristics, followed by modeling with ensemble classifiers and custom Neural Networks. Further, we propose combining heuristic-based features and learned representations that demonstrate improved performance for the link prediction task on social network datasets. Using this method to generate accurate recommendations for many applications is a matter of further study that appears very promising. The code for all the experiments has been made public.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge