Stephane Thiery
Combining pretrained CNN feature extractors to enhance clustering of complex natural images
Jan 07, 2021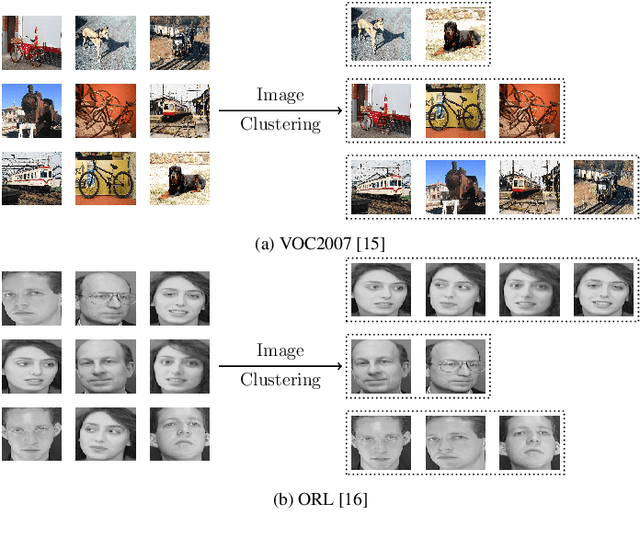
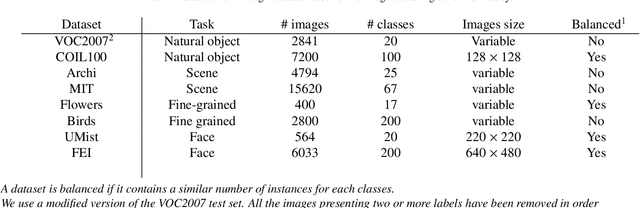
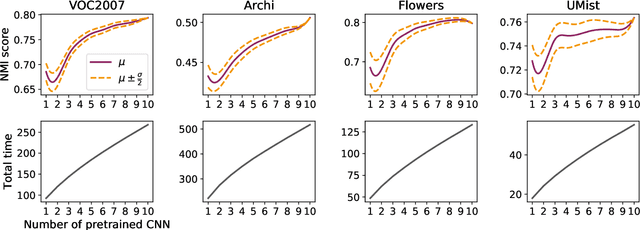
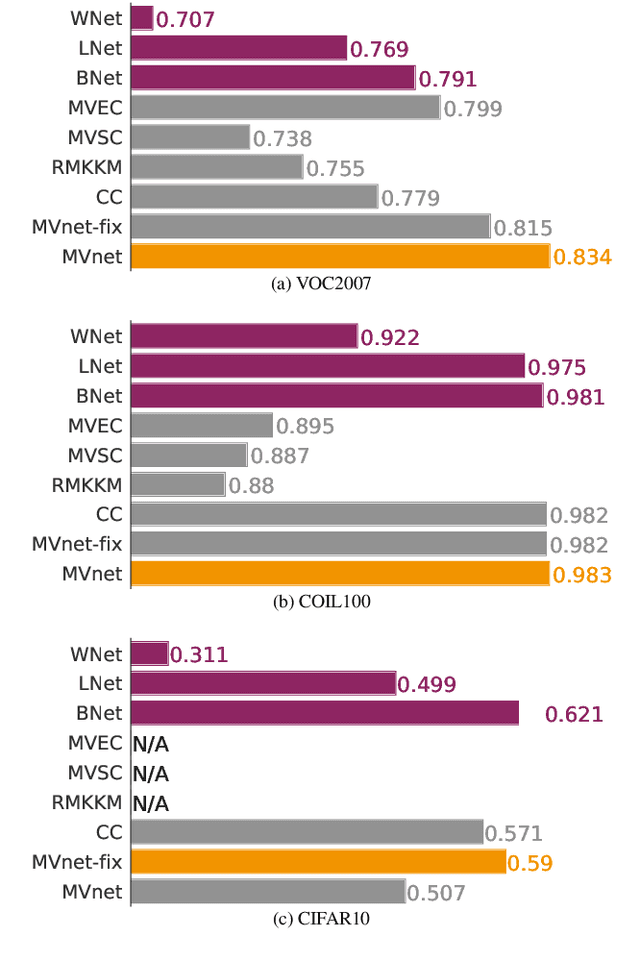
Abstract:Recently, a common starting point for solving complex unsupervised image classification tasks is to use generic features, extracted with deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) pretrained on a large and versatile dataset (ImageNet). However, in most research, the CNN architecture for feature extraction is chosen arbitrarily, without justification. This paper aims at providing insight on the use of pretrained CNN features for image clustering (IC). First, extensive experiments are conducted and show that, for a given dataset, the choice of the CNN architecture for feature extraction has a huge impact on the final clustering. These experiments also demonstrate that proper extractor selection for a given IC task is difficult. To solve this issue, we propose to rephrase the IC problem as a multi-view clustering (MVC) problem that considers features extracted from different architectures as different "views" of the same data. This approach is based on the assumption that information contained in the different CNN may be complementary, even when pretrained on the same data. We then propose a multi-input neural network architecture that is trained end-to-end to solve the MVC problem effectively. This approach is tested on nine natural image datasets, and produces state-of-the-art results for IC.
* 21 pages, 16 figures, 10 tables, preprint of our paper published in Neurocomputing
Learning local trajectories for high precision robotic tasks : application to KUKA LBR iiwa Cartesian positioning
Jan 05, 2017

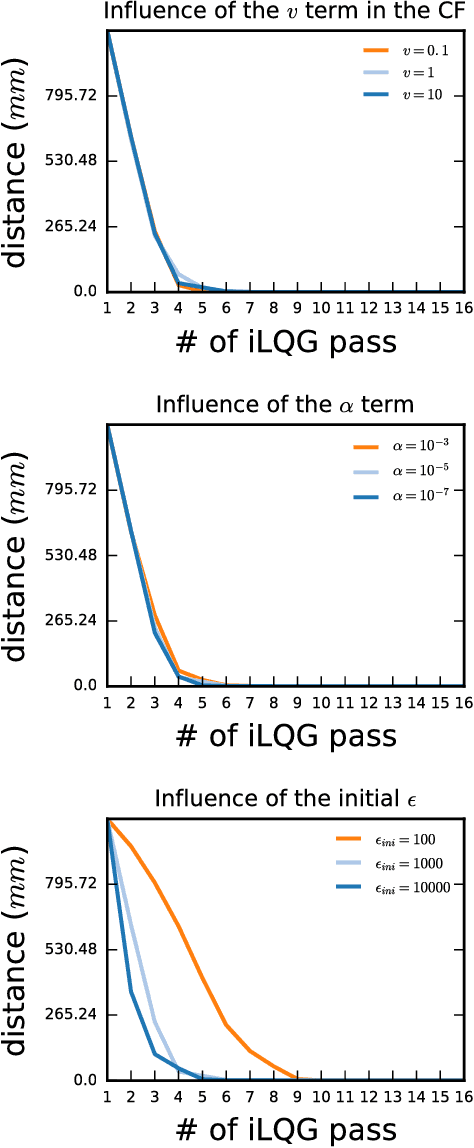
Abstract:To ease the development of robot learning in industry, two conditions need to be fulfilled. Manipulators must be able to learn high accuracy and precision tasks while being safe for workers in the factory. In this paper, we extend previously submitted work which consists in rapid learning of local high accuracy behaviors. By exploration and regression, linear and quadratic models are learnt for respectively the dynamics and cost function. Iterative Linear Quadratic Gaussian Regulator combined with cost quadratic regression can converge rapidly in the final stages towards high accuracy behavior as the cost function is modelled quite precisely. In this paper, both a different cost function and a second order improvement method are implemented within this framework. We also propose an analysis of the algorithm parameters through simulation for a positioning task. Finally, an experimental validation on a KUKA LBR iiwa robot is carried out. This collaborative robot manipulator can be easily programmed into safety mode, which makes it qualified for the second industry constraint stated above.
* 6 pages, double column, 6 figures and one table. Published in: Industrial Electronics Society , IECON 2016 - 42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge