Stefan Thater
MCScript: A Novel Dataset for Assessing Machine Comprehension Using Script Knowledge
Mar 14, 2018

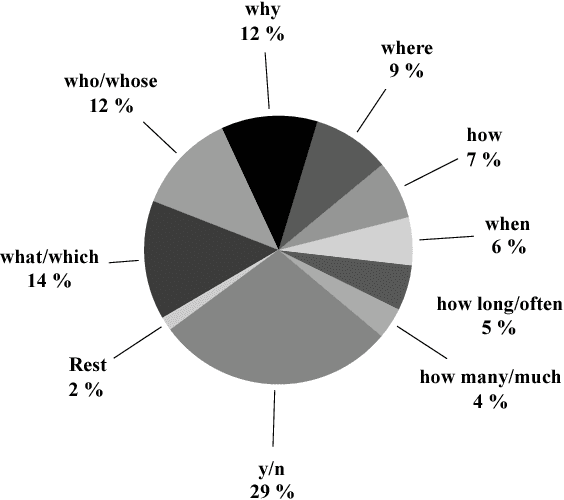

Abstract:We introduce a large dataset of narrative texts and questions about these texts, intended to be used in a machine comprehension task that requires reasoning using commonsense knowledge. Our dataset complements similar datasets in that we focus on stories about everyday activities, such as going to the movies or working in the garden, and that the questions require commonsense knowledge, or more specifically, script knowledge, to be answered. We show that our mode of data collection via crowdsourcing results in a substantial amount of such inference questions. The dataset forms the basis of a shared task on commonsense and script knowledge organized at SemEval 2018 and provides challenging test cases for the broader natural language understanding community.
Aligning Script Events with Narrative Texts
Oct 16, 2017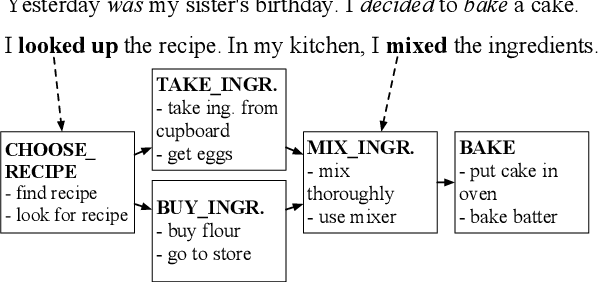



Abstract:Script knowledge plays a central role in text understanding and is relevant for a variety of downstream tasks. In this paper, we consider two recent datasets which provide a rich and general representation of script events in terms of paraphrase sets. We introduce the task of mapping event mentions in narrative texts to such script event types, and present a model for this task that exploits rich linguistic representations as well as information on temporal ordering. The results of our experiments demonstrate that this complex task is indeed feasible.
Sequence to Sequence Learning for Event Prediction
Sep 18, 2017



Abstract:This paper presents an approach to the task of predicting an event description from a preceding sentence in a text. Our approach explores sequence-to-sequence learning using a bidirectional multi-layer recurrent neural network. Our approach substantially outperforms previous work in terms of the BLEU score on two datasets derived from WikiHow and DeScript respectively. Since the BLEU score is not easy to interpret as a measure of event prediction, we complement our study with a second evaluation that exploits the rich linguistic annotation of gold paraphrase sets of events.
A Mixture Model for Learning Multi-Sense Word Embeddings
Jun 15, 2017



Abstract:Word embeddings are now a standard technique for inducing meaning representations for words. For getting good representations, it is important to take into account different senses of a word. In this paper, we propose a mixture model for learning multi-sense word embeddings. Our model generalizes the previous works in that it allows to induce different weights of different senses of a word. The experimental results show that our model outperforms previous models on standard evaluation tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge