Srivatsan Balaji
Torsion Resistant Strain Limiting Layers Enable High Grip Strength of Electrically-Driven Handed Shearing Auxetic Grippers
Dec 10, 2024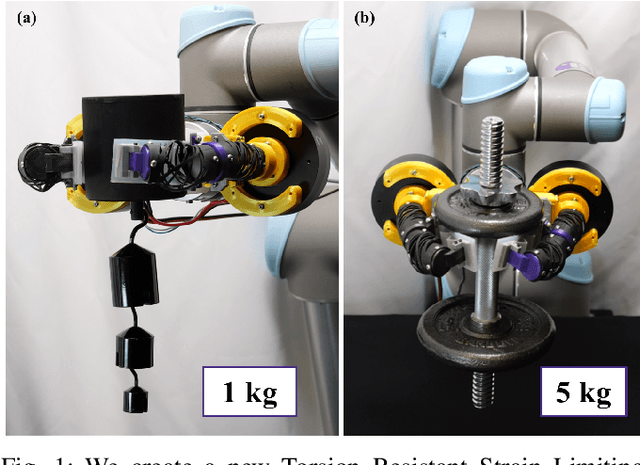



Abstract:Soft grippers have demonstrated a strong ability to successfully pick and manipulate many objects. A key limitation to their wider adoption is their inability to grasp larger payloads due to objects slipping out of grasps. We have overcome this limitation by introducing a torsionally rigid strain limiting layer (TR-SLL). This reduces out-of-plane bending while maintaining the gripper's softness and in-plane flexibility. We characterize the design space of the strain limiting layer and Handed Shearing Auxetic (HSA) actuators for a soft gripper using simulation and experiment. The inclusion of the TR-SLL with HSAs enables HSA grippers to be made with a single digit. We found that the use of our TR-SLL HSA gripper enabled pinch grasping of payloads over 1 kg. We demonstrate a lifting capacity of 5 kg when loading using the TR-SLL. We also demonstrate a peak pinch grasp force of 5.8 N, and a peak planar caging force of 14.5 N. Finally, we test the TR-SLL gripper on a suite of 43 YCB objects. We show success on 37 objects demonstrating significant capabilities.
Enhancing the Performance of Pneu-net Actuators Using a Torsion Resistant Strain Limiting Layer
Nov 04, 2023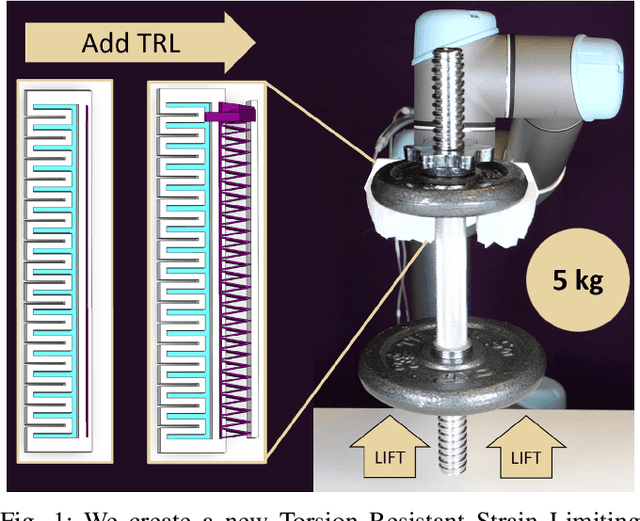

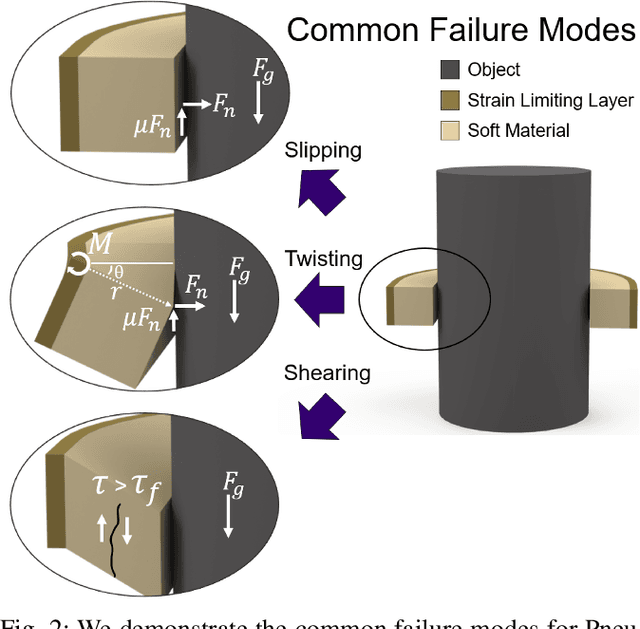
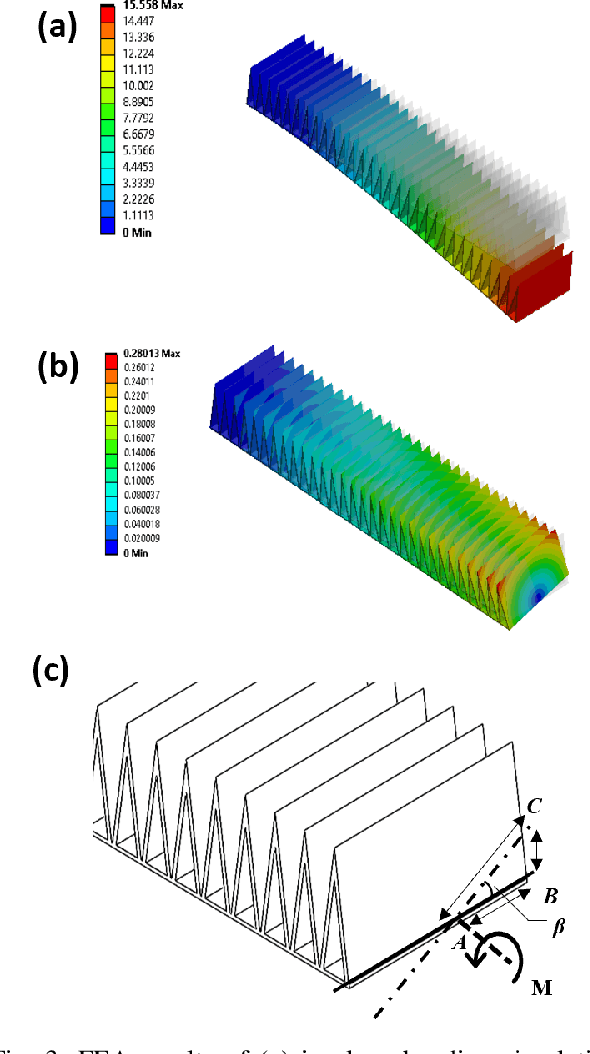
Abstract:Pneunets are the primary form of soft robotic grippers. A key limitation to their wider adoption is their inability to grasp larger payloads due to objects slipping out of grasps. We have overcome this limitation by introducing a torsionally rigid strain limiting layer (TRL). This reduces out-of-plane bending while maintaining the gripper's softness and in-plane flexibility. We characterize the design space of the strain limiting layer for a Pneu-net gripper using simulation and experiment and map bending angle and relative grip strength. We found that the use of our TRL reduced out-of-plane bending by up to 97.7% in testing compared to a benchmark Pneu-net gripper from the Soft Robotics Toolkit. We demonstrate a lifting capacity of 5kg when loading using the TRL. We also see a relative improvement in peak grip force of 3N and stiffness of 1200N/m compared to 1N and 150N/m for a Pneu-net gripper without our TRL at equal pressures. Finally, we test the TRL gripper on a suite of six YCB objects above the demonstrated capability of a traditional Pneu-net gripper. We show success on all but one demonstrating significant increased capabilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge