Srijoni Majumdar
Fair Compromises in Participatory Budgeting: a Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Participatory budgeting is a method of collectively understanding and addressing spending priorities where citizens vote on how a budget is spent, it is regularly run to improve the fairness of the distribution of public funds. Participatory budgeting requires voters to make decisions on projects which can lead to ``choice overload". A multi-agent reinforcement learning approach to decision support can make decision making easier for voters by identifying voting strategies that increase the winning proportion of their vote. This novel approach can also support policymakers by highlighting aspects of election design that enable fair compromise on projects. This paper presents a novel, ethically aligned approach to decision support using multi-agent deep reinforcement learning modelling. This paper introduces a novel use of a branching neural network architecture to overcome scalability challenges of multi-agent reinforcement learning in a decentralized way. Fair compromises are found through optimising voter actions towards greater representation of voter preferences in the winning set. Experimental evaluation with real-world participatory budgeting data reveals a pattern in fair compromise: that it is achievable through projects with smaller cost.
Upgrading Democracies with Fairer Voting Methods
May 20, 2025
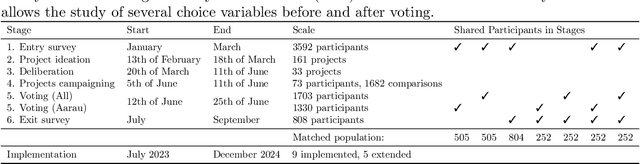
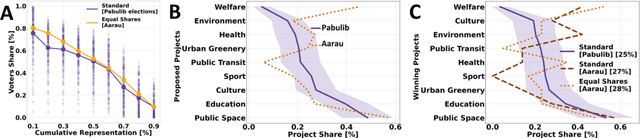

Abstract:Voting methods are instrumental design element of democracies. Citizens use them to express and aggregate their preferences to reach a collective decision. However, voting outcomes can be as sensitive to voting rules as they are to people's voting choices. Despite the significance and inter-disciplinary scientific progress on voting methods, several democracies keep relying on outdated voting methods that do not fit modern, pluralistic societies well, while lacking social innovation. Here, we demonstrate how one can upgrade real-world democracies, namely by using alternative preferential voting methods such as cumulative voting and the method of equal shares designed for a proportional representation of voters' preferences. By rigorously assessing a new participatory budgeting approach applied in the city of Aarau, Switzerland, we unravel the striking voting outcomes of fair voting methods: more winning projects with the same budget and broader geographic and preference representation of citizens by the elected projects, in particular for voters who used to be under-represented, while promoting novel project ideas. We provide profound causal evidence showing that citizens prefer proportional voting methods, which possess strong legitimacy without the need of very technical specialized explanations. We also reveal strong underlying democratic values exhibited by citizens who support fair voting methods such as altruism and compromise. These findings come with a global momentum to unleash a new and long-awaited participation blueprint of how to upgrade democracies.
Generative AI for Software Metadata: Overview of the Information Retrieval in Software Engineering Track at FIRE 2023
Oct 27, 2023Abstract:The Information Retrieval in Software Engineering (IRSE) track aims to develop solutions for automated evaluation of code comments in a machine learning framework based on human and large language model generated labels. In this track, there is a binary classification task to classify comments as useful and not useful. The dataset consists of 9048 code comments and surrounding code snippet pairs extracted from open source github C based projects and an additional dataset generated individually by teams using large language models. Overall 56 experiments have been submitted by 17 teams from various universities and software companies. The submissions have been evaluated quantitatively using the F1-Score and qualitatively based on the type of features developed, the supervised learning model used and their corresponding hyper-parameters. The labels generated from large language models increase the bias in the prediction model but lead to less over-fitted results.
Smart Knowledge Transfer using Google-like Search
Aug 12, 2023Abstract:To address the issue of rising software maintenance cost due to program comprehension challenges, we propose SMARTKT (Smart Knowledge Transfer), a search framework, which extracts and integrates knowledge related to various aspects of an application in form of a semantic graph. This graph supports syntax and semantic queries and converts the process of program comprehension into a {\em google-like} search problem.
Consensus-based Participatory Budgeting for Legitimacy: Decision Support via Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning
Jul 24, 2023



Abstract:The legitimacy of bottom-up democratic processes for the distribution of public funds by policy-makers is challenging and complex. Participatory budgeting is such a process, where voting outcomes may not always be fair or inclusive. Deliberation for which project ideas to put for voting and choose for implementation lack systematization and do not scale. This paper addresses these grand challenges by introducing a novel and legitimate iterative consensus-based participatory budgeting process. Consensus is designed to be a result of decision support via an innovative multi-agent reinforcement learning approach. Voters are assisted to interact with each other to make viable compromises. Extensive experimental evaluation with real-world participatory budgeting data from Poland reveal striking findings: Consensus is reachable, efficient and robust. Compromise is required, which is though comparable to the one of existing voting aggregation methods that promote fairness and inclusion without though attaining consensus.
* 13 Pages, 8 Figures, 3 Tables, Accepted in International Conference on Machine Learning, Optimization, and Data Science, 2023
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge