Sophia Hager
Does Local News Stay Local?: Online Content Shifts in Sinclair-Acquired Stations
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Local news stations are often considered to be reliable sources of non-politicized information, particularly local concerns that residents care about. Because these stations are trusted news sources, viewers are particularly susceptible to the information they report. The Sinclair Broadcast group is a broadcasting company that has acquired many local news stations in the last decade. We investigate the effects of local news stations being acquired by Sinclair: how does coverage change? We use computational methods to investigate changes in internet content put out by local news stations before and after being acquired by Sinclair and in comparison to national news outlets. We find that there is clear evidence that local news stations report more frequently on national news at the expense of local topics, and that their coverage of polarizing national topics increases.
Learning Extrapolative Sequence Transformations from Markov Chains
May 26, 2025Abstract:Most successful applications of deep learning involve similar training and test conditions. However, tasks such as biological sequence design involve searching for sequences that improve desirable properties beyond previously known values, which requires novel hypotheses that \emph{extrapolate} beyond training data. In these settings, extrapolation may be achieved by using random search methods such as Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), which, given an initial state, sample local transformations to approximate a target density that rewards states with the desired properties. However, even with a well-designed proposal, MCMC may struggle to explore large structured state spaces efficiently. Rather than relying on stochastic search, it would be desirable to have a model that greedily optimizes the properties of interest, successfully extrapolating in as few steps as possible. We propose to learn such a model from the Markov chains resulting from MCMC search. Specifically, our approach uses selected states from Markov chains as a source of training data for an autoregressive model, which is then able to efficiently generate novel sequences that extrapolate along the sequence-level properties of interest. The proposed approach is validated on three problems: protein sequence design, text sentiment control, and text anonymization. We find that the autoregressive model can extrapolate as well or better than MCMC, but with the additional benefits of scalability and significantly higher sample efficiency.
Uncertainty Distillation: Teaching Language Models to Express Semantic Confidence
Mar 18, 2025
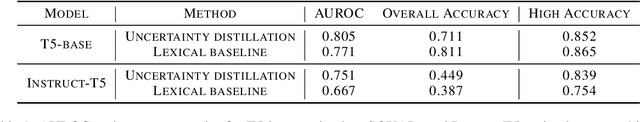
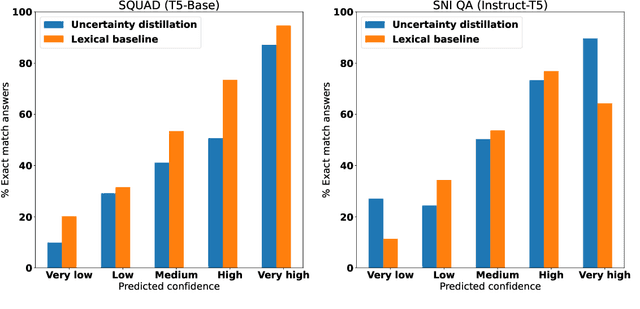
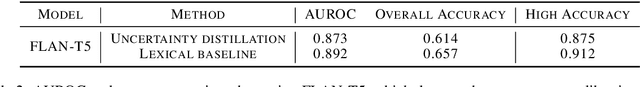
Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used for factual question-answering, it becomes more important for LLMs to have the capability to communicate the likelihood that their answer is correct. For these verbalized expressions of uncertainty to be meaningful, they should reflect the error rates at the expressed level of confidence. However, when prompted to express confidence, the error rates of current LLMs are inconsistent with their communicated confidences, highlighting the need for uncertainty quantification methods. Many prior methods calculate lexical uncertainty, estimating a model's confidence in the specific string it generated. In some cases, however, it may be more useful to estimate semantic uncertainty, or the model's confidence in the answer regardless of how it is verbalized. We propose a simple procedure, uncertainty distillation, to teach an LLM to verbalize calibrated semantic confidences. Using held-out data to map initial uncertainty estimates to meaningful probabilities, we create examples annotated with verbalized probabilities for supervised fine-tuning. We demonstrate our method yields verbalized confidences that correlate with observed error rates with a small fine-tuned language model as well as with larger instruction-tuned models, and find that our semantic uncertainty correlates well with lexical uncertainty on short answers.
Generating Music with Structure Using Self-Similarity as Attention
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Despite the innovations in deep learning and generative AI, creating long term structure as well as the layers of repeated structure common in musical works remains an open challenge in music generation. We propose an attention layer that uses a novel approach applying user-supplied self-similarity matrices to previous time steps, and demonstrate it in our Similarity Incentivized Neural Generator (SING) system, a deep learning autonomous music generation system with two layers. The first is a vanilla Long Short Term Memory layer, and the second is the proposed attention layer. During generation, this attention mechanism imposes a suggested structure from a template piece on the generated music. We train SING on the MAESTRO dataset using a novel variable batching method, and compare its performance to the same model without the attention mechanism. The addition of our proposed attention mechanism significantly improves the network's ability to replicate specific structures, and it performs better on an unseen test set than a model without the attention mechanism.
Learning to Generate Text in Arbitrary Writing Styles
Dec 28, 2023Abstract:Prior work in style-controlled text generation has focused on tasks such as emulating the style of prolific literary authors, producing formal or informal text, and the degree of toxicity of generated text. Plentiful demonstrations of these styles are available, and as a result modern language models are often able to emulate them, either via prompting or discriminative control. However, in applications such as writing assistants, it is desirable for language models to produce text in an author-specific style on the basis of a small writing sample. We find that instruction-tuned language models can struggle to reproduce author-specific style demonstrated in a prompt. Instead, we propose to guide a language model to generate text in a target style using contrastively-trained representations that capture stylometric features. A central challenge in doing so is that an author's writing is characterized by surprising token choices under a generic language model. To reconcile this tension, we combine generative re-scoring to achieve an author-specific model, with discriminative control to ensure style consistency at the sequence-level. The combination of these approaches is found to be particularly effective at adhering to an author-specific style in a variety of conditions, including unconditional generation and style transfer, and is applicable to any underlying language model without requiring fine-tuning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge