Songlin Fan
Consistent Video Editing as Flow-Driven Image-to-Video Generation
Jun 09, 2025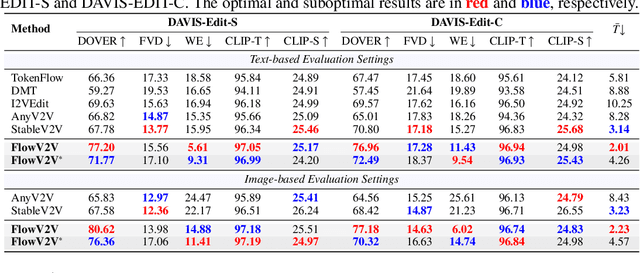
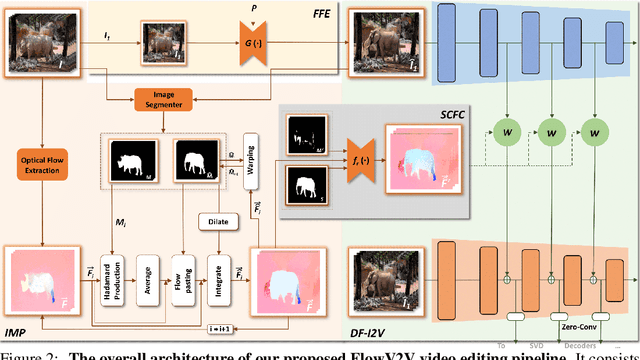


Abstract:With the prosper of video diffusion models, down-stream applications like video editing have been significantly promoted without consuming much computational cost. One particular challenge in this task lies at the motion transfer process from the source video to the edited one, where it requires the consideration of the shape deformation in between, meanwhile maintaining the temporal consistency in the generated video sequence. However, existing methods fail to model complicated motion patterns for video editing, and are fundamentally limited to object replacement, where tasks with non-rigid object motions like multi-object and portrait editing are largely neglected. In this paper, we observe that optical flows offer a promising alternative in complex motion modeling, and present FlowV2V to re-investigate video editing as a task of flow-driven Image-to-Video (I2V) generation. Specifically, FlowV2V decomposes the entire pipeline into first-frame editing and conditional I2V generation, and simulates pseudo flow sequence that aligns with the deformed shape, thus ensuring the consistency during editing. Experimental results on DAVIS-EDIT with improvements of 13.67% and 50.66% on DOVER and warping error illustrate the superior temporal consistency and sample quality of FlowV2V compared to existing state-of-the-art ones. Furthermore, we conduct comprehensive ablation studies to analyze the internal functionalities of the first-frame paradigm and flow alignment in the proposed method.
E-Bench: Subjective-Aligned Benchmark Suite for Text-Driven Video Editing Quality Assessment
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:Text-driven video editing has recently experienced rapid development. Despite this, evaluating edited videos remains a considerable challenge. Current metrics tend to fail to align with human perceptions, and effective quantitative metrics for video editing are still notably absent. To address this, we introduce E-Bench, a benchmark suite tailored to the assessment of text-driven video editing. This suite includes E-Bench DB, a video quality assessment (VQA) database for video editing. E-Bench DB encompasses a diverse set of source videos featuring various motions and subjects, along with multiple distinct editing prompts, editing results from 8 different models, and the corresponding Mean Opinion Scores (MOS) from 24 human annotators. Based on E-Bench DB, we further propose E-Bench QA, a quantitative human-aligned measurement for the text-driven video editing task. In addition to the aesthetic, distortion, and other visual quality indicators that traditional VQA methods emphasize, E-Bench QA focuses on the text-video alignment and the relevance modeling between source and edited videos. It proposes a new assessment network for video editing that attains superior performance in alignment with human preferences. To the best of our knowledge, E-Bench introduces the first quality assessment dataset for video editing and an effective subjective-aligned quantitative metric for this domain. All data and code will be publicly available at https://github.com/littlespray/E-Bench.
Uncertainty-aware No-Reference Point Cloud Quality Assessment
Jan 17, 2024
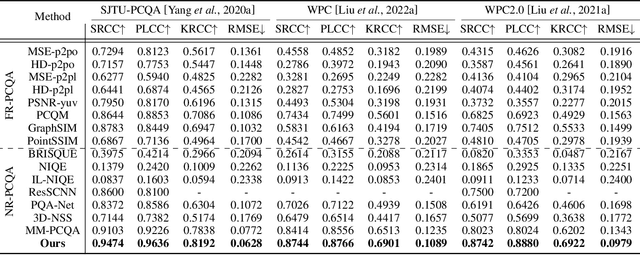

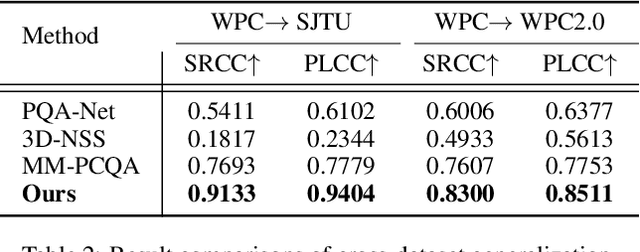
Abstract:The evolution of compression and enhancement algorithms necessitates an accurate quality assessment for point clouds. Previous works consistently regard point cloud quality assessment (PCQA) as a MOS regression problem and devise a deterministic mapping, ignoring the stochasticity in generating MOS from subjective tests. Besides, the viewpoint switching of 3D point clouds in subjective tests reinforces the judging stochasticity of different subjects compared with traditional images. This work presents the first probabilistic architecture for no-reference PCQA, motivated by the labeling process of existing datasets. The proposed method can model the quality judging stochasticity of subjects through a tailored conditional variational autoencoder (CVAE) and produces multiple intermediate quality ratings. These intermediate ratings simulate the judgments from different subjects and are then integrated into an accurate quality prediction, mimicking the generation process of a ground truth MOS. Specifically, our method incorporates a Prior Module, a Posterior Module, and a Quality Rating Generator, where the former two modules are introduced to model the judging stochasticity in subjective tests, while the latter is developed to generate diverse quality ratings. Extensive experiments indicate that our approach outperforms previous cutting-edge methods by a large margin and exhibits gratifying cross-dataset robustness.
Screen-based 3D Subjective Experiment Software
Aug 08, 2023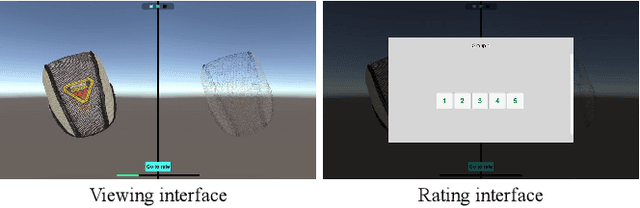

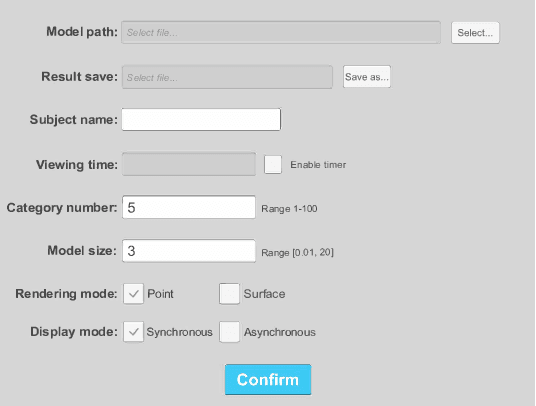

Abstract:Recently, widespread 3D graphics (e.g., point clouds and meshes) have drawn considerable efforts from academia and industry to assess their perceptual quality by conducting subjective experiments. However, lacking a handy software for 3D subjective experiments complicates the construction of 3D graphics quality assessment datasets, thus hindering the prosperity of relevant fields. In this paper, we develop a powerful platform with which users can flexibly design their 3D subjective methodologies and build high-quality datasets, easing a broad spectrum of 3D graphics subjective quality study. To accurately illustrate the perceptual quality differences of 3D stimuli, our software can simultaneously render the source stimulus and impaired stimulus and allows both stimuli to respond synchronously to viewer interactions. Compared with amateur 3D visualization tool-based or image/video rendering-based schemes, our approach embodies typical 3D applications while minimizing cognitive overload during subjective experiments. We organized a subjective experiment involving 40 participants to verify the validity of the proposed software. Experimental analyses demonstrate that subjective tests on our software can produce reasonable subjective quality scores of 3D models. All resources in this paper can be found at https://openi.pcl.ac.cn/OpenDatasets/3DQA.
Salient Object Detection for Point Clouds
Jul 25, 2022
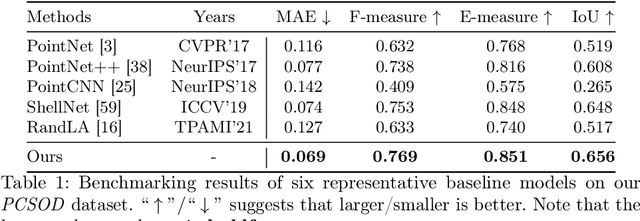

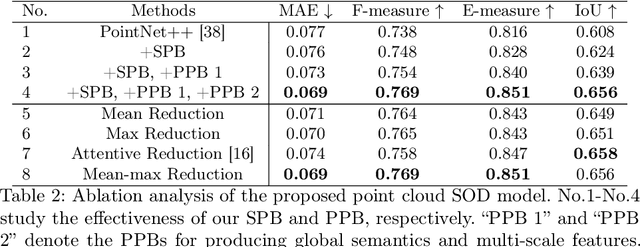
Abstract:This paper researches the unexplored task-point cloud salient object detection (SOD). Differing from SOD for images, we find the attention shift of point clouds may provoke saliency conflict, i.e., an object paradoxically belongs to salient and non-salient categories. To eschew this issue, we present a novel view-dependent perspective of salient objects, reasonably reflecting the most eye-catching objects in point cloud scenarios. Following this formulation, we introduce PCSOD, the first dataset proposed for point cloud SOD consisting of 2,872 in-/out-door 3D views. The samples in our dataset are labeled with hierarchical annotations, e.g., super-/sub-class, bounding box, and segmentation map, which endows the brilliant generalizability and broad applicability of our dataset verifying various conjectures. To evidence the feasibility of our solution, we further contribute a baseline model and benchmark five representative models for a comprehensive comparison. The proposed model can effectively analyze irregular and unordered points for detecting salient objects. Thanks to incorporating the task-tailored designs, our method shows visible superiority over other baselines, producing more satisfactory results. Extensive experiments and discussions reveal the promising potential of this research field, paving the way for further study.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge