Sneha Bhattacharya
LEGAN: Disentangled Manipulation of Directional Lighting and Facial Expressions by Leveraging Human Perceptual Judgements
Oct 04, 2020
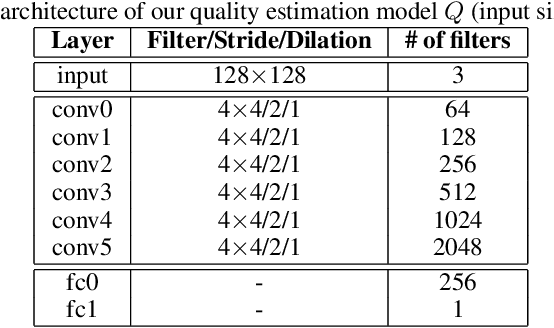

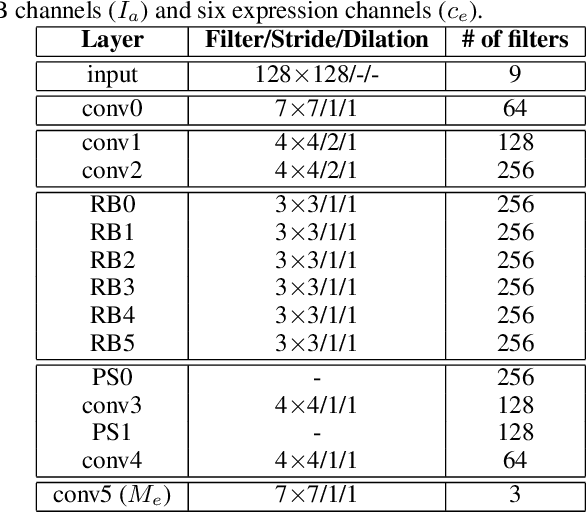
Abstract:Building facial analysis systems that generalize to extreme variations in lighting and facial expressions is a challenging problem that can potentially be alleviated using natural-looking synthetic data. Towards that, we propose LEGAN, a novel synthesis framework that leverages perceptual quality judgments for jointly manipulating lighting and expressions in face images, without requiring paired training data. LEGAN disentangles the lighting and expression subspaces and performs transformations in the feature space before upscaling to the desired output image. The fidelity of the synthetic image is further refined by integrating a perceptual quality estimation model into the LEGAN framework as an auxiliary discriminator. The quality estimation model is learned from face images rendered using multiple synthesis methods and their crowd-sourced naturalness ratings using a margin-based regression loss. Using objective metrics like FID and LPIPS, LEGAN is shown to generate higher quality face images when compared with popular GAN models like pix2pix, CycleGAN and StarGAN for lighting and expression synthesis. We also conduct a perceptual study using images synthesized by LEGAN and other GAN models, trained with and without the quality based auxiliary discriminator, and show the correlation between our quality estimation and visual fidelity. Finally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of LEGAN as training data augmenter for expression recognition and face verification tasks.
Pedestrian Detection in Thermal Images using Saliency Maps
Apr 15, 2019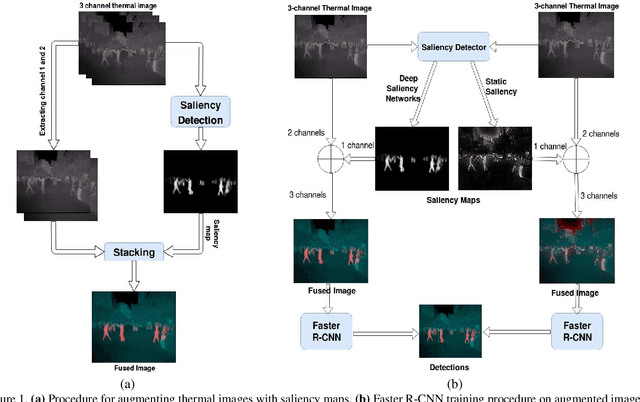
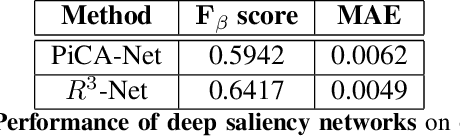
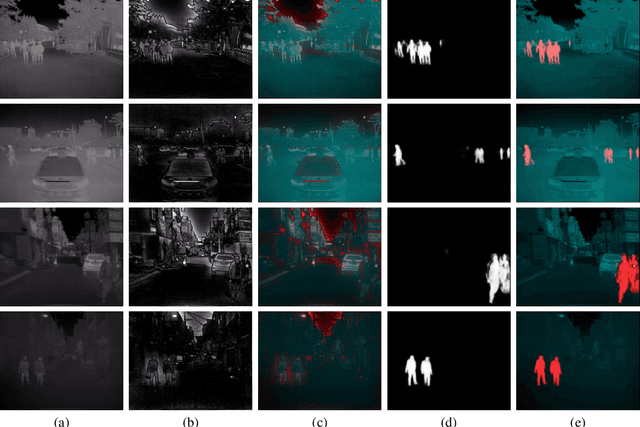

Abstract:Thermal images are mainly used to detect the presence of people at night or in bad lighting conditions, but perform poorly at daytime. To solve this problem, most state-of-the-art techniques employ a fusion network that uses features from paired thermal and color images. Instead, we propose to augment thermal images with their saliency maps, to serve as an attention mechanism for the pedestrian detector especially during daytime. We investigate how such an approach results in improved performance for pedestrian detection using only thermal images, eliminating the need for paired color images. For our experiments, we train the Faster R-CNN for pedestrian detection and report the added effect of saliency maps generated using static and deep methods (PiCA-Net and R3-Net). Our best performing model results in an absolute reduction of miss rate by 13.4% and 19.4% over the baseline in day and night images respectively. We also annotate and release pixel level masks of pedestrians on a subset of the KAIST Multispectral Pedestrian Detection dataset, which is a first publicly available dataset for salient pedestrian detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge