Simone Cerrato
PIC4rl-gym: a ROS2 modular framework for Robots Autonomous Navigation with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Nov 19, 2022



Abstract:Learning agents can optimize standard autonomous navigation improving flexibility, efficiency, and computational cost of the system by adopting a wide variety of approaches. This work introduces the \textit{PIC4rl-gym}, a fundamental modular framework to enhance navigation and learning research by mixing ROS2 and Gazebo, the standard tools of the robotics community, with Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL). The paper describes the whole structure of the PIC4rl-gym, which fully integrates DRL agent's training and testing in several indoor and outdoor navigation scenarios and tasks. A modular approach is adopted to easily customize the simulation by selecting new platforms, sensors, or models. We demonstrate the potential of our novel gym by benchmarking the resulting policies, trained for different navigation tasks, with a complete set of metrics.
Position-Agnostic Autonomous Navigation in Vineyards with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jun 28, 2022



Abstract:Precision agriculture is rapidly attracting research to efficiently introduce automation and robotics solutions to support agricultural activities. Robotic navigation in vineyards and orchards offers competitive advantages in autonomously monitoring and easily accessing crops for harvesting, spraying and performing time-consuming necessary tasks. Nowadays, autonomous navigation algorithms exploit expensive sensors which also require heavy computational cost for data processing. Nonetheless, vineyard rows represent a challenging outdoor scenario where GPS and Visual Odometry techniques often struggle to provide reliable positioning information. In this work, we combine Edge AI with Deep Reinforcement Learning to propose a cutting-edge lightweight solution to tackle the problem of autonomous vineyard navigation without exploiting precise localization data and overcoming task-tailored algorithms with a flexible learning-based approach. We train an end-to-end sensorimotor agent which directly maps noisy depth images and position-agnostic robot state information to velocity commands and guides the robot to the end of a row, continuously adjusting its heading for a collision-free central trajectory. Our extensive experimentation in realistic simulated vineyards demonstrates the effectiveness of our solution and the generalization capabilities of our agent.
Waypoint Generation in Row-based Crops with Deep Learning and Contrastive Clustering
Jun 23, 2022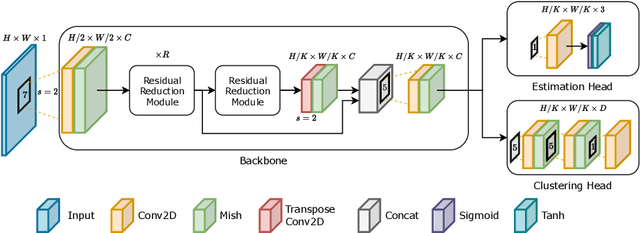


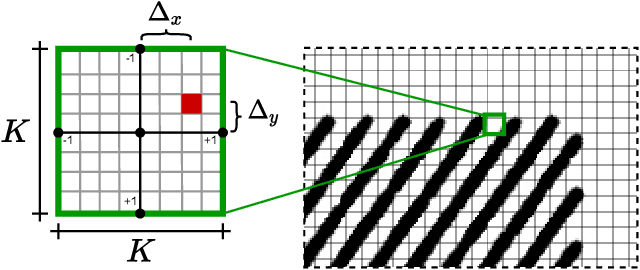
Abstract:The development of precision agriculture has gradually introduced automation in the agricultural process to support and rationalize all the activities related to field management. In particular, service robotics plays a predominant role in this evolution by deploying autonomous agents able to navigate in fields while executing different tasks without the need for human intervention, such as monitoring, spraying and harvesting. In this context, global path planning is the first necessary step for every robotic mission and ensures that the navigation is performed efficiently and with complete field coverage. In this paper, we propose a learning-based approach to tackle waypoint generation for planning a navigation path for row-based crops, starting from a top-view map of the region-of-interest. We present a novel methodology for waypoint clustering based on a contrastive loss, able to project the points to a separable latent space. The proposed deep neural network can simultaneously predict the waypoint position and cluster assignment with two specialized heads in a single forward pass. The extensive experimentation on simulated and real-world images demonstrates that the proposed approach effectively solves the waypoint generation problem for both straight and curved row-based crops, overcoming the limitations of previous state-of-the-art methodologies.
A Deep Learning Driven Algorithmic Pipeline for Autonomous Navigation in Row-Based Crops
Dec 07, 2021
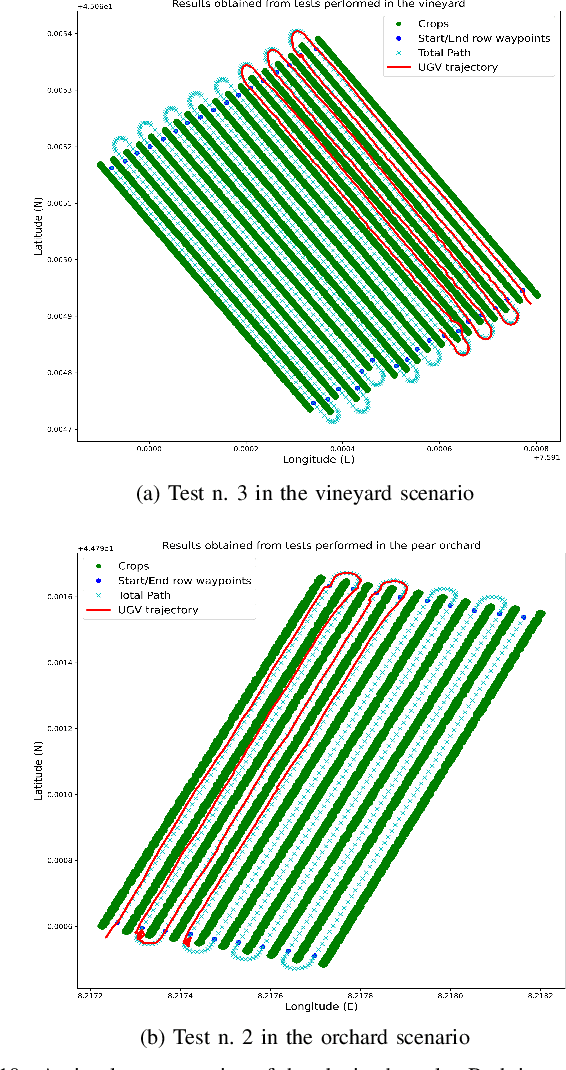


Abstract:Expensive sensors and inefficient algorithmic pipelines significantly affect the overall cost of autonomous machines. However, affordable robotic solutions are essential to practical usage, and their financial impact constitutes a fundamental requirement to employ service robotics in most fields of application. Among all, researchers in the precision agriculture domain strive to devise robust and cost-effective autonomous platforms in order to provide genuinely large-scale competitive solutions. In this article, we present a complete algorithmic pipeline for row-based crops autonomous navigation, specifically designed to cope with low-range sensors and seasonal variations. Firstly, we build on a robust data-driven methodology to generate a viable path for the autonomous machine, covering the full extension of the crop with only the occupancy grid map information of the field. Moreover, our solution leverages on latest advancement of deep learning optimization techniques and synthetic generation of data to provide an affordable solution that efficiently tackles the well-known Global Navigation Satellite System unreliability and degradation due to vegetation growing inside rows. Extensive experimentation and simulations against computer-generated environments and real-world crops demonstrated the robustness and intrinsic generalizability of our methodology that opens the possibility of highly affordable and fully autonomous machines.
Deep Semantic Segmentation at the Edge for Autonomous Navigation in Vineyard Rows
Jul 01, 2021
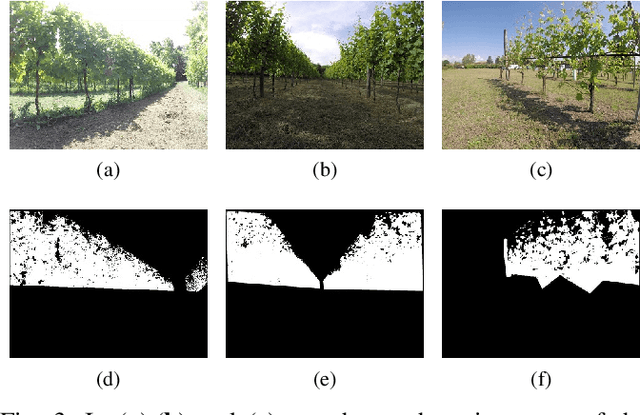
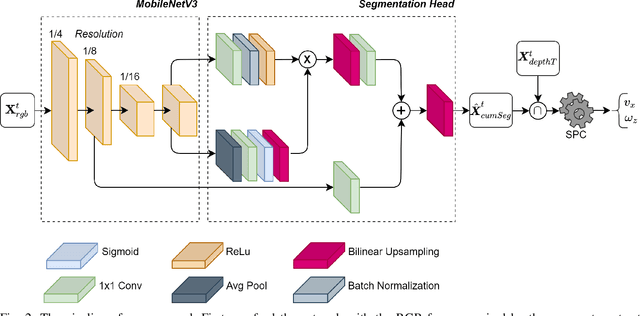

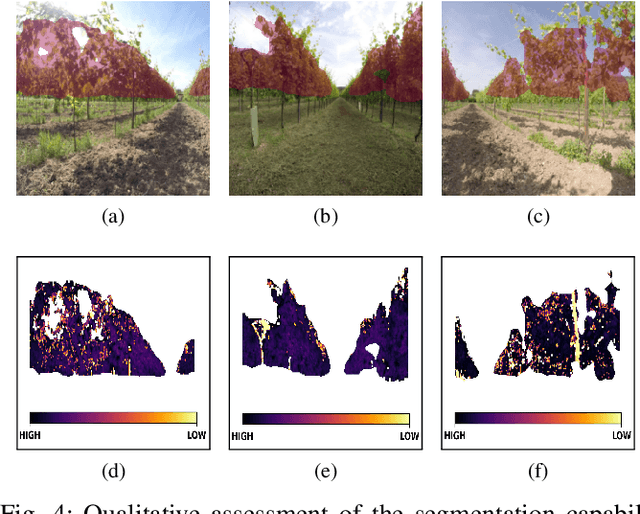
Abstract:Precision agriculture is a fast-growing field that aims at introducing affordable and effective automation into agricultural processes. Nowadays, algorithmic solutions for navigation in vineyards require expensive sensors and high computational workloads that preclude large-scale applicability of autonomous robotic platforms in real business case scenarios. From this perspective, our novel proposed control leverages the latest advancement in machine perception and edge AI techniques to achieve highly affordable and reliable navigation inside vineyard rows with low computational and power consumption. Indeed, using a custom-trained segmentation network and a low-range RGB-D camera, we are able to take advantage of the semantic information of the environment to produce smooth trajectories and stable control in different vineyards scenarios. Moreover, the segmentation maps generated by the control algorithm itself could be directly exploited as filters for a vegetative assessment of the crop status. Extensive experimentations and evaluations against real-world data and simulated environments demonstrated the effectiveness and intrinsic robustness of our methodology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge