Simon Donné
Foley Control: Aligning a Frozen Latent Text-to-Audio Model to Video
Oct 24, 2025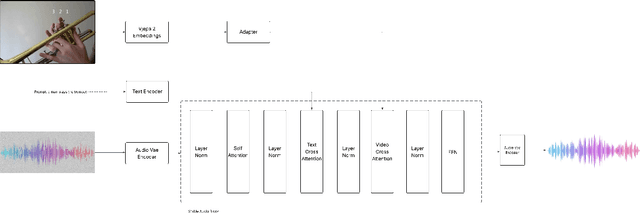
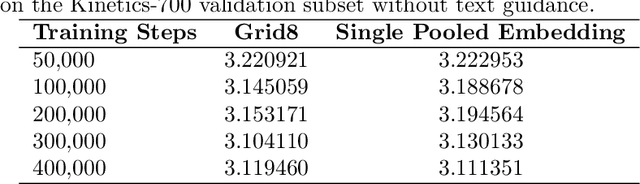
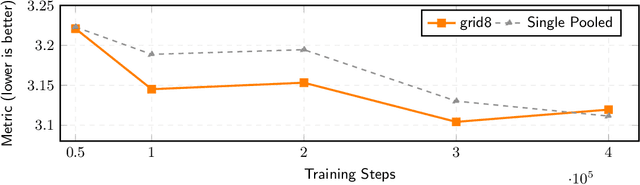
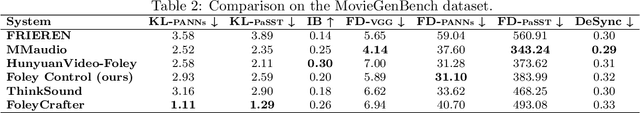
Abstract:Foley Control is a lightweight approach to video-guided Foley that keeps pretrained single-modality models frozen and learns only a small cross-attention bridge between them. We connect V-JEPA2 video embeddings to a frozen Stable Audio Open DiT text-to-audio (T2A) model by inserting compact video cross-attention after the model's existing text cross-attention, so prompts set global semantics while video refines timing and local dynamics. The frozen backbones retain strong marginals (video; audio given text) and the bridge learns the audio-video dependency needed for synchronization -- without retraining the audio prior. To cut memory and stabilize training, we pool video tokens before conditioning. On curated video-audio benchmarks, Foley Control delivers competitive temporal and semantic alignment with far fewer trainable parameters than recent multi-modal systems, while preserving prompt-driven controllability and production-friendly modularity (swap/upgrade encoders or the T2A backbone without end-to-end retraining). Although we focus on Video-to-Foley, the same bridge design can potentially extend to other audio modalities (e.g., speech).
Jointly Generating Multi-view Consistent PBR Textures using Collaborative Control
Oct 09, 2024Abstract:Multi-view consistency remains a challenge for image diffusion models. Even within the Text-to-Texture problem, where perfect geometric correspondences are known a priori, many methods fail to yield aligned predictions across views, necessitating non-trivial fusion methods to incorporate the results onto the original mesh. We explore this issue for a Collaborative Control workflow specifically in PBR Text-to-Texture. Collaborative Control directly models PBR image probability distributions, including normal bump maps; to our knowledge, the only diffusion model to directly output full PBR stacks. We discuss the design decisions involved in making this model multi-view consistent, and demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in ablation studies, as well as practical applications.
Geometry Image Diffusion: Fast and Data-Efficient Text-to-3D with Image-Based Surface Representation
Sep 05, 2024Abstract:Generating high-quality 3D objects from textual descriptions remains a challenging problem due to computational cost, the scarcity of 3D data, and complex 3D representations. We introduce Geometry Image Diffusion (GIMDiffusion), a novel Text-to-3D model that utilizes geometry images to efficiently represent 3D shapes using 2D images, thereby avoiding the need for complex 3D-aware architectures. By integrating a Collaborative Control mechanism, we exploit the rich 2D priors of existing Text-to-Image models such as Stable Diffusion. This enables strong generalization even with limited 3D training data (allowing us to use only high-quality training data) as well as retaining compatibility with guidance techniques such as IPAdapter. In short, GIMDiffusion enables the generation of 3D assets at speeds comparable to current Text-to-Image models. The generated objects consist of semantically meaningful, separate parts and include internal structures, enhancing both usability and versatility.
IPAdapter-Instruct: Resolving Ambiguity in Image-based Conditioning using Instruct Prompts
Aug 06, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models continuously push the boundary of state-of-the-art image generation, but the process is hard to control with any nuance: practice proves that textual prompts are inadequate for accurately describing image style or fine structural details (such as faces). ControlNet and IPAdapter address this shortcoming by conditioning the generative process on imagery instead, but each individual instance is limited to modeling a single conditional posterior: for practical use-cases, where multiple different posteriors are desired within the same workflow, training and using multiple adapters is cumbersome. We propose IPAdapter-Instruct, which combines natural-image conditioning with ``Instruct'' prompts to swap between interpretations for the same conditioning image: style transfer, object extraction, both, or something else still? IPAdapterInstruct efficiently learns multiple tasks with minimal loss in quality compared to dedicated per-task models.
Collaborative Control for Geometry-Conditioned PBR Image Generation
Feb 20, 2024Abstract:Current 3D content generation approaches build on diffusion models that output RGB images. Modern graphics pipelines, however, require physically-based rendering (PBR) material properties. We propose to model the PBR image distribution directly, avoiding photometric inaccuracies in RGB generation and the inherent ambiguity in extracting PBR from RGB. Existing paradigms for cross-modal fine-tuning are not suited for PBR generation due to both a lack of data and the high dimensionality of the output modalities: we overcome both challenges by retaining a frozen RGB model and tightly linking a newly trained PBR model using a novel cross-network communication paradigm. As the base RGB model is fully frozen, the proposed method does not risk catastrophic forgetting during fine-tuning and remains compatible with techniques such as IPAdapter pretrained for the base RGB model. We validate our design choices, robustness to data sparsity, and compare against existing paradigms with an extensive experimental section.
PointFlowNet: Learning Representations for 3D Scene Flow Estimation from Point Clouds
Sep 17, 2018



Abstract:Despite significant progress in image-based 3D scene flow estimation, the performance of such approaches has not yet reached the fidelity required by many applications. Simultaneously, these applications are often not restricted to image-based estimation: laser scanners provide a popular alternative to traditional cameras, for example in the context of self-driving cars, as they directly yield a 3D point cloud. In this paper, we propose to estimate 3D scene flow from such unstructured point clouds using a deep neural network. In a single forward pass, our model jointly predicts 3D scene flow as well as the 3D bounding box and rigid body motion of objects in the scene. While the prospect of estimating 3D scene flow from unstructured point clouds is promising, it is also a challenging task. We show that the traditional global representation of rigid body motion prohibits inference by CNNs, and propose a translation equivariant representation to circumvent this problem. For training our deep network, a large dataset is required. Because of this, we augment real scans from KITTI with virtual objects, realistically modeling occlusions and simulating sensor noise. A thorough comparison with classic and learning-based techniques highlights the robustness of the proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge