Sijuan Huang
Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center
A Subabdominal MRI Image Segmentation Algorithm Based on Multi-Scale Feature Pyramid Network and Dual Attention Mechanism
May 19, 2023Abstract:This study aimed to solve the semantic gap and misalignment issue between encoding and decoding because of multiple convolutional and pooling operations in U-Net when segmenting subabdominal MRI images during rectal cancer treatment. A MRI Image Segmentation is proposed based on a multi-scale feature pyramid network and dual attention mechanism. Our innovation is the design of two modules: 1) a dilated convolution and multi-scale feature pyramid network are used in the encoding to avoid the semantic gap. 2) a dual attention mechanism is designed to maintain spatial information of U-Net and reduce misalignment. Experiments on a subabdominal MRI image dataset show the proposed method achieves better performance than others methods. In conclusion, a multi-scale feature pyramid network can reduce the semantic gap, and the dual attention mechanism can make an alignment of features between encoding and decoding.
SECP-Net: SE-Connection Pyramid Network of Organ At Risk Segmentation for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Dec 28, 2021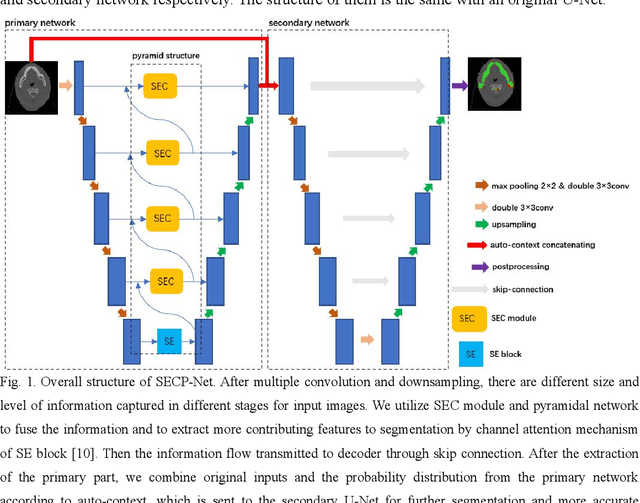
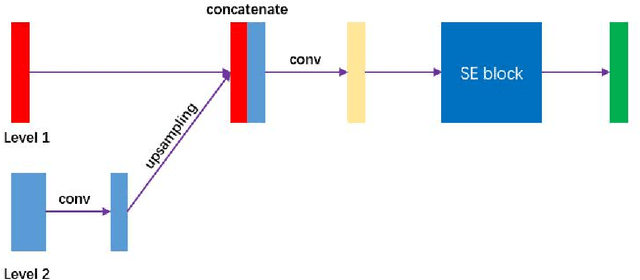
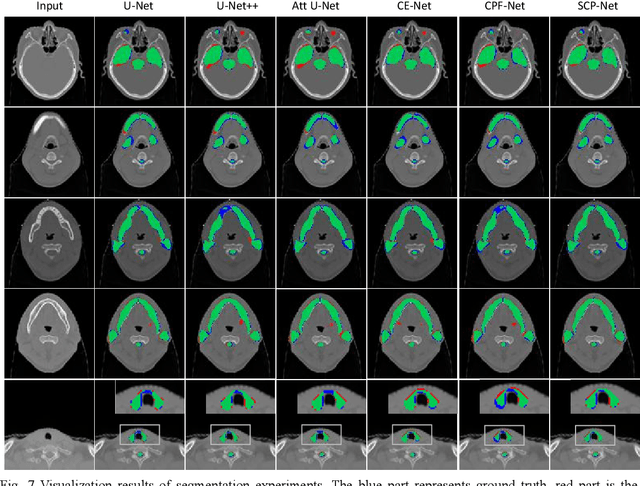
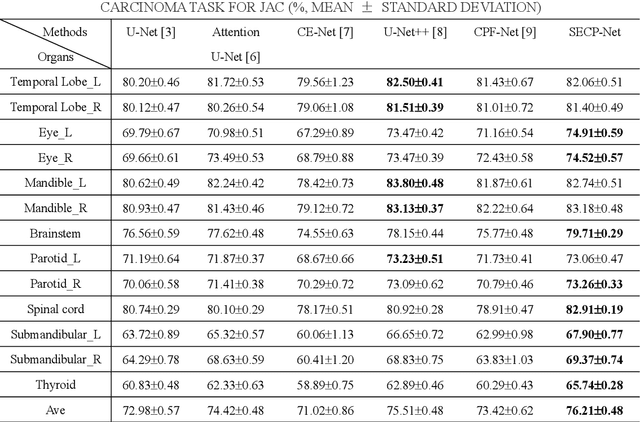
Abstract:Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a kind of malignant tumor. Accurate and automatic segmentation of organs at risk (OAR) of computed tomography (CT) images is clinically significant. In recent years, deep learning models represented by U-Net have been widely applied in medical image segmentation tasks, which can help doctors with reduction of workload and get accurate results more quickly. In OAR segmentation of NPC, the sizes of OAR are variable, especially, some of them are small. Traditional deep neural networks underperform during segmentation due to the lack use of global and multi-size information. This paper proposes a new SE-Connection Pyramid Network (SECP-Net). SECP-Net extracts global and multi-size information flow with se connection (SEC) modules and a pyramid structure of network for improving the segmentation performance, especially that of small organs. SECP-Net also designs an auto-context cascaded network to further improve the segmentation performance. Comparative experiments are conducted between SECP-Net and other recently methods on a dataset with CT images of head and neck. Five-fold cross validation is used to evaluate the performance based on two metrics, i.e., Dice and Jaccard similarity. Experimental results show that SECP-Net can achieve SOTA performance in this challenging task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge