Sifat Muhammad Abdullah
Taming Data Challenges in ML-based Security Tasks: Lessons from Integrating Generative AI
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:Machine learning-based supervised classifiers are widely used for security tasks, and their improvement has been largely focused on algorithmic advancements. We argue that data challenges that negatively impact the performance of these classifiers have received limited attention. We address the following research question: Can developments in Generative AI (GenAI) address these data challenges and improve classifier performance? We propose augmenting training datasets with synthetic data generated using GenAI techniques to improve classifier generalization. We evaluate this approach across 7 diverse security tasks using 6 state-of-the-art GenAI methods and introduce a novel GenAI scheme called Nimai that enables highly controlled data synthesis. We find that GenAI techniques can significantly improve the performance of security classifiers, achieving improvements of up to 32.6% even in severely data-constrained settings (only ~180 training samples). Furthermore, we demonstrate that GenAI can facilitate rapid adaptation to concept drift post-deployment, requiring minimal labeling in the adjustment process. Despite successes, our study finds that some GenAI schemes struggle to initialize (train and produce data) on certain security tasks. We also identify characteristics of specific tasks, such as noisy labels, overlapping class distributions, and sparse feature vectors, which hinder performance boost using GenAI. We believe that our study will drive the development of future GenAI tools designed for security tasks.
An Analysis of Recent Advances in Deepfake Image Detection in an Evolving Threat Landscape
Apr 24, 2024Abstract:Deepfake or synthetic images produced using deep generative models pose serious risks to online platforms. This has triggered several research efforts to accurately detect deepfake images, achieving excellent performance on publicly available deepfake datasets. In this work, we study 8 state-of-the-art detectors and argue that they are far from being ready for deployment due to two recent developments. First, the emergence of lightweight methods to customize large generative models, can enable an attacker to create many customized generators (to create deepfakes), thereby substantially increasing the threat surface. We show that existing defenses fail to generalize well to such \emph{user-customized generative models} that are publicly available today. We discuss new machine learning approaches based on content-agnostic features, and ensemble modeling to improve generalization performance against user-customized models. Second, the emergence of \textit{vision foundation models} -- machine learning models trained on broad data that can be easily adapted to several downstream tasks -- can be misused by attackers to craft adversarial deepfakes that can evade existing defenses. We propose a simple adversarial attack that leverages existing foundation models to craft adversarial samples \textit{without adding any adversarial noise}, through careful semantic manipulation of the image content. We highlight the vulnerabilities of several defenses against our attack, and explore directions leveraging advanced foundation models and adversarial training to defend against this new threat.
Deepfake Text Detection: Limitations and Opportunities
Oct 17, 2022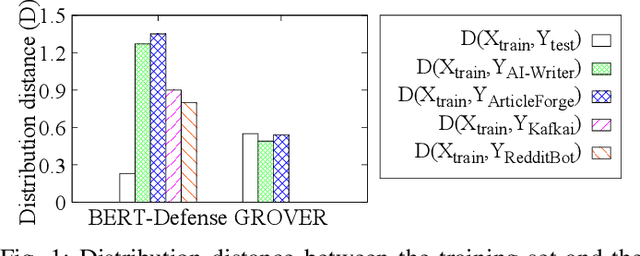
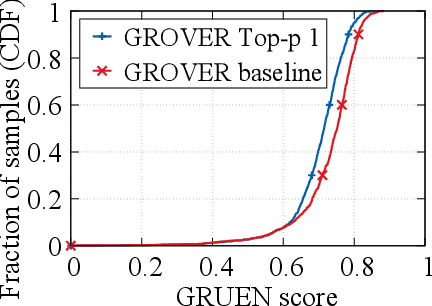
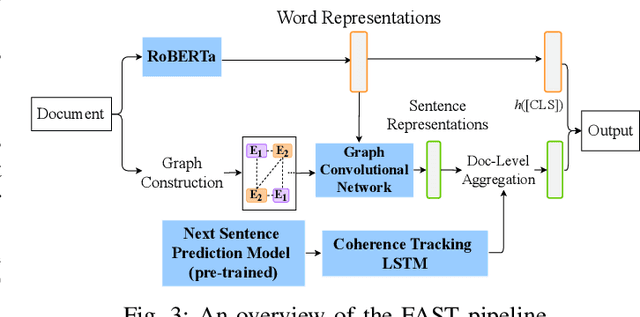
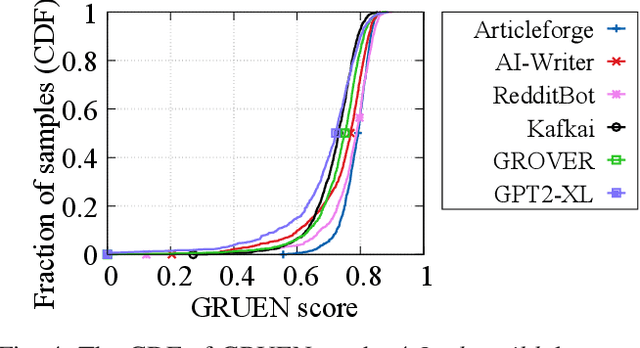
Abstract:Recent advances in generative models for language have enabled the creation of convincing synthetic text or deepfake text. Prior work has demonstrated the potential for misuse of deepfake text to mislead content consumers. Therefore, deepfake text detection, the task of discriminating between human and machine-generated text, is becoming increasingly critical. Several defenses have been proposed for deepfake text detection. However, we lack a thorough understanding of their real-world applicability. In this paper, we collect deepfake text from 4 online services powered by Transformer-based tools to evaluate the generalization ability of the defenses on content in the wild. We develop several low-cost adversarial attacks, and investigate the robustness of existing defenses against an adaptive attacker. We find that many defenses show significant degradation in performance under our evaluation scenarios compared to their original claimed performance. Our evaluation shows that tapping into the semantic information in the text content is a promising approach for improving the robustness and generalization performance of deepfake text detection schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge