Sifan Zhang
More Pictures Say More: Visual Intersection Network for Open Set Object Detection
Aug 26, 2024Abstract:Open Set Object Detection has seen rapid development recently, but it continues to pose significant challenges. Language-based methods, grappling with the substantial modal disparity between textual and visual modalities, require extensive computational resources to bridge this gap. Although integrating visual prompts into these frameworks shows promise for enhancing performance, it always comes with constraints related to textual semantics. In contrast, viusal-only methods suffer from the low-quality fusion of multiple visual prompts. In response, we introduce a strong DETR-based model, Visual Intersection Network for Open Set Object Detection (VINO), which constructs a multi-image visual bank to preserve the semantic intersections of each category across all time steps. Our innovative multi-image visual updating mechanism learns to identify the semantic intersections from various visual prompts, enabling the flexible incorporation of new information and continuous optimization of feature representations. Our approach guarantees a more precise alignment between target category semantics and region semantics, while significantly reducing pre-training time and resource demands compared to language-based methods. Furthermore, the integration of a segmentation head illustrates the broad applicability of visual intersection in various visual tasks. VINO, which requires only 7 RTX4090 GPU days to complete one epoch on the Objects365v1 dataset, achieves competitive performance on par with vision-language models on benchmarks such as LVIS and ODinW35.
GMSR:Gradient-Guided Mamba for Spectral Reconstruction from RGB Images
May 13, 2024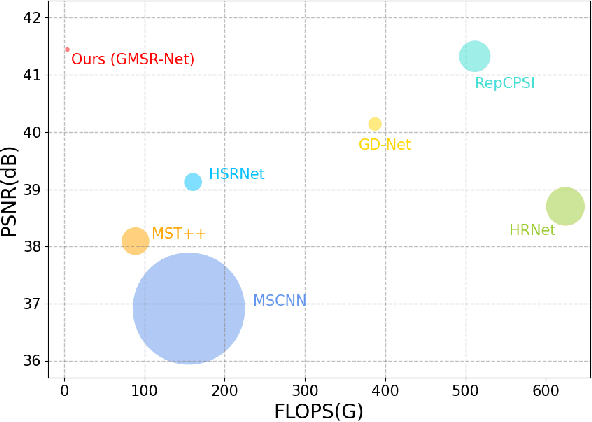
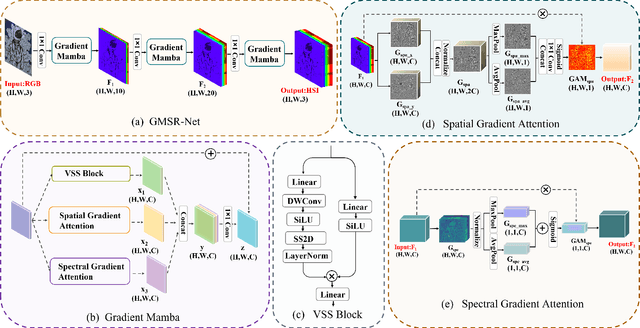
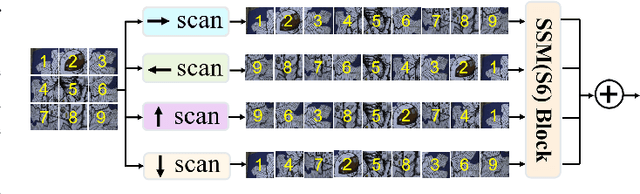
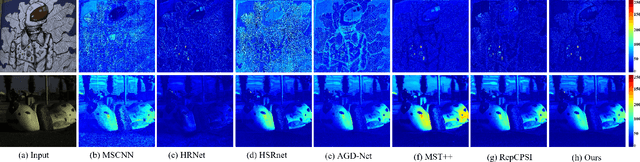
Abstract:Mainstream approaches to spectral reconstruction (SR) primarily focus on designing Convolution- and Transformer-based architectures. However, CNN methods often face challenges in handling long-range dependencies, whereas Transformers are constrained by computational efficiency limitations. Recent breakthroughs in state-space model (e.g., Mamba) has attracted significant attention due to its near-linear computational efficiency and superior performance, prompting our investigation into its potential for SR problem. To this end, we propose the Gradient-guided Mamba for Spectral Reconstruction from RGB Images, dubbed GMSR-Net. GMSR-Net is a lightweight model characterized by a global receptive field and linear computational complexity. Its core comprises multiple stacked Gradient Mamba (GM) blocks, each featuring a tri-branch structure. In addition to benefiting from efficient global feature representation by Mamba block, we further innovatively introduce spatial gradient attention and spectral gradient attention to guide the reconstruction of spatial and spectral cues. GMSR-Net demonstrates a significant accuracy-efficiency trade-off, achieving state-of-the-art performance while markedly reducing the number of parameters and computational burdens. Compared to existing approaches, GMSR-Net slashes parameters and FLOPS by substantial margins of 10 times and 20 times, respectively. Code is available at https://github.com/wxy11-27/GMSR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge