Sidik Soleman
IndoNLU: Benchmark and Resources for Evaluating Indonesian Natural Language Understanding
Oct 08, 2020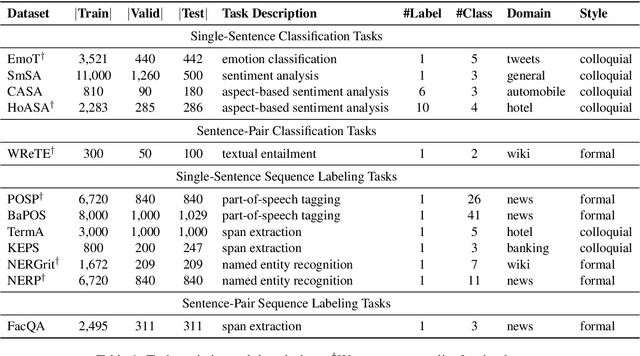
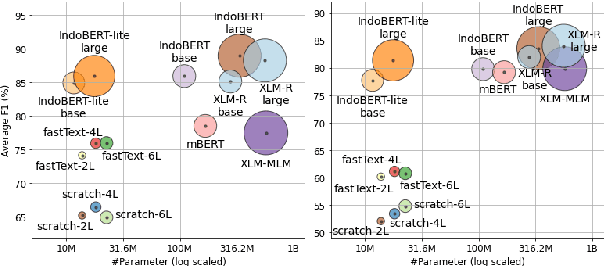
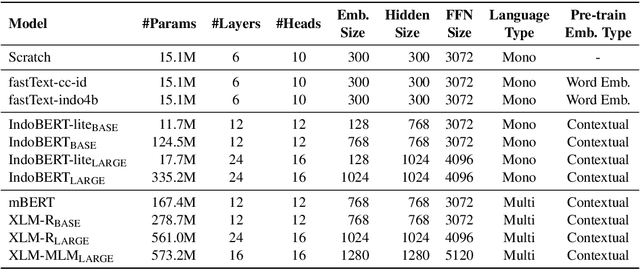
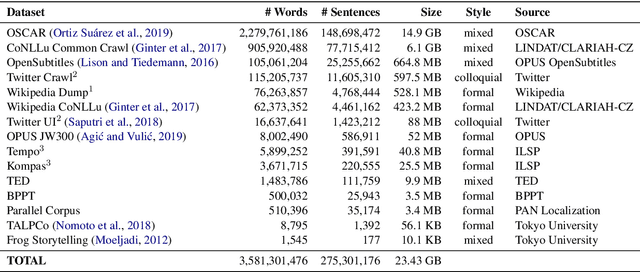
Abstract:Although Indonesian is known to be the fourth most frequently used language over the internet, the research progress on this language in the natural language processing (NLP) is slow-moving due to a lack of available resources. In response, we introduce the first-ever vast resource for the training, evaluating, and benchmarking on Indonesian natural language understanding (IndoNLU) tasks. IndoNLU includes twelve tasks, ranging from single sentence classification to pair-sentences sequence labeling with different levels of complexity. The datasets for the tasks lie in different domains and styles to ensure task diversity. We also provide a set of Indonesian pre-trained models (IndoBERT) trained from a large and clean Indonesian dataset Indo4B collected from publicly available sources such as social media texts, blogs, news, and websites. We release baseline models for all twelve tasks, as well as the framework for benchmark evaluation, and thus it enables everyone to benchmark their system performances.
Improving Joint Layer RNN based Keyphrase Extraction by Using Syntactical Features
Sep 15, 2020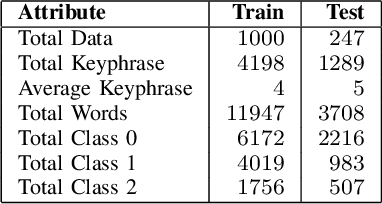
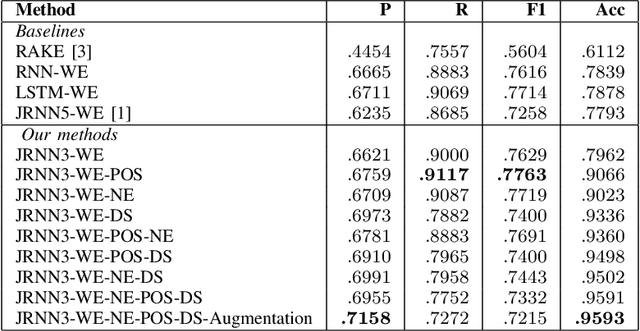
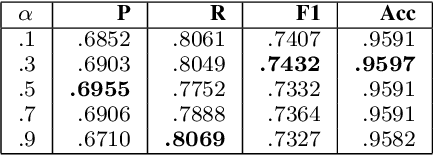
Abstract:Keyphrase extraction as a task to identify important words or phrases from a text, is a crucial process to identify main topics when analyzing texts from a social media platform. In our study, we focus on text written in Indonesia language taken from Twitter. Different from the original joint layer recurrent neural network (JRNN) with output of one sequence of keywords and using only word embedding, here we propose to modify the input layer of JRNN to extract more than one sequence of keywords by additional information of syntactical features, namely part of speech, named entity types, and dependency structures. Since JRNN in general requires a large amount of data as the training examples and creating those examples is expensive, we used a data augmentation method to increase the number of training examples. Our experiment had shown that our method outperformed the baseline methods. Our method achieved .9597 in accuracy and .7691 in F1.
* 6 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge