Shunyi Zhao
BioPIE: A Biomedical Protocol Information Extraction Dataset for High-Reasoning-Complexity Experiment Question Answer
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Question Answer (QA) systems for biomedical experiments facilitate cross-disciplinary communication, and serve as a foundation for downstream tasks, e.g., laboratory automation. High Information Density (HID) and Multi-Step Reasoning (MSR) pose unique challenges for biomedical experimental QA. While extracting structured knowledge, e.g., Knowledge Graphs (KGs), can substantially benefit biomedical experimental QA. Existing biomedical datasets focus on general or coarsegrained knowledge and thus fail to support the fine-grained experimental reasoning demanded by HID and MSR. To address this gap, we introduce Biomedical Protocol Information Extraction Dataset (BioPIE), a dataset that provides procedure-centric KGs of experimental entities, actions, and relations at a scale that supports reasoning over biomedical experiments across protocols. We evaluate information extraction methods on BioPIE, and implement a QA system that leverages BioPIE, showcasing performance gains on test, HID, and MSR question sets, showing that the structured experimental knowledge in BioPIE underpins both AI-assisted and more autonomous biomedical experimentation.
Real-Time AIoT for UAV Antenna Interference Detection via Edge-Cloud Collaboration
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:In the fifth-generation (5G) era, eliminating communication interference sources is crucial for maintaining network performance. Interference often originates from unauthorized or malfunctioning antennas, and radio monitoring agencies must address numerous sources of such antennas annually. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can improve inspection efficiency. However, the data transmission delay in the existing cloud-only (CO) artificial intelligence (AI) mode fails to meet the low latency requirements for real-time performance. Therefore, we propose a computer vision-based AI of Things (AIoT) system to detect antenna interference sources for UAVs. The system adopts an optimized edge-cloud collaboration (ECC+) mode, combining a keyframe selection algorithm (KSA), focusing on reducing end-to-end latency (E2EL) and ensuring reliable data transmission, which aligns with the core principles of ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC). At the core of our approach is an end-to-end antenna localization scheme based on the tracking-by-detection (TBD) paradigm, including a detector (EdgeAnt) and a tracker (AntSort). EdgeAnt achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance with a mean average precision (mAP) of 42.1% on our custom antenna interference source dataset, requiring only 3 million parameters and 14.7 GFLOPs. On the COCO dataset, EdgeAnt achieves 38.9% mAP with 5.4 GFLOPs. We deployed EdgeAnt on Jetson Xavier NX (TRT) and Raspberry Pi 4B (NCNN), achieving real-time inference speeds of 21.1 (1088) and 4.8 (640) frames per second (FPS), respectively. Compared with CO mode, the ECC+ mode reduces E2EL by 88.9%, increases accuracy by 28.2%. Additionally, the system offers excellent scalability for coordinated multiple UAVs inspections. The detector code is publicly available at https://github.com/SCNU-RISLAB/EdgeAnt.
An Illumination-Robust Feature Extractor Augmented by Relightable 3D Reconstruction
Oct 01, 2024
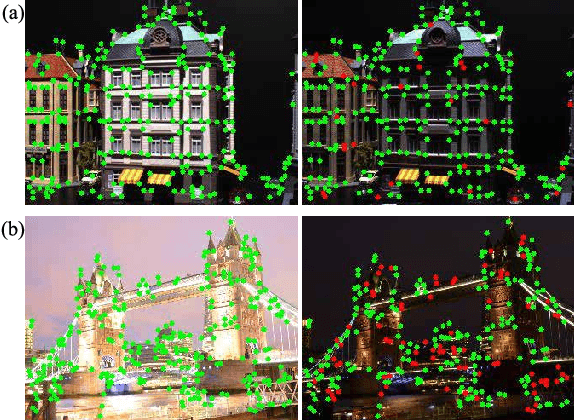
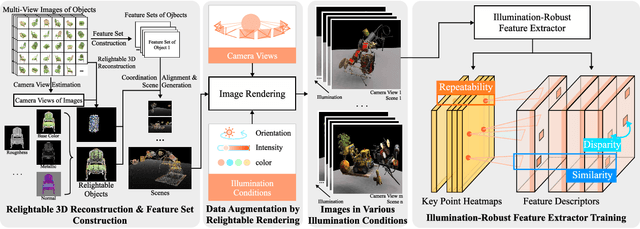


Abstract:Visual features, whose description often relies on the local intensity and gradient direction, have found wide applications in robot navigation and localization in recent years. However, the extraction of visual features is usually disturbed by the variation of illumination conditions, making it challenging for real-world applications. Previous works have addressed this issue by establishing datasets with variations in illumination conditions, but can be costly and time-consuming. This paper proposes a design procedure for an illumination-robust feature extractor, where the recently developed relightable 3D reconstruction techniques are adopted for rapid and direct data generation with varying illumination conditions. A self-supervised framework is proposed for extracting features with advantages in repeatability for key points and similarity for descriptors across good and bad illumination conditions. Experiments are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method for robust feature extraction. Ablation studies also indicate the effectiveness of the self-supervised framework design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge