Shreyas Vasawanala
Neural Proximal Gradient Descent for Compressive Imaging
Jun 01, 2018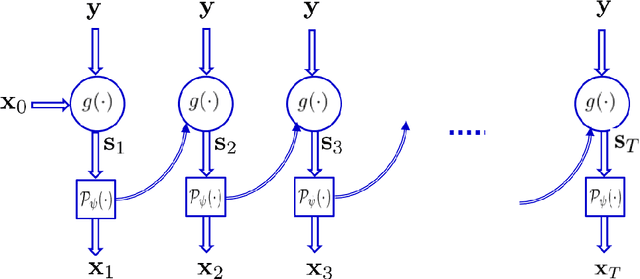
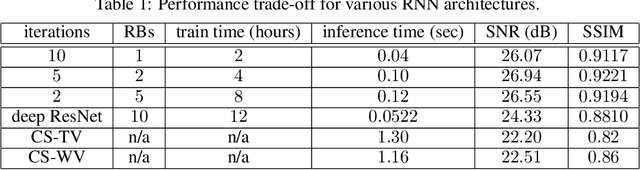
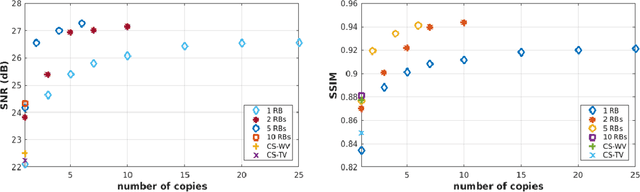
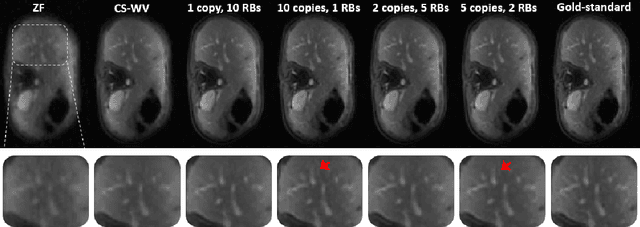
Abstract:Recovering high-resolution images from limited sensory data typically leads to a serious ill-posed inverse problem, demanding inversion algorithms that effectively capture the prior information. Learning a good inverse mapping from training data faces severe challenges, including: (i) scarcity of training data; (ii) need for plausible reconstructions that are physically feasible; (iii) need for fast reconstruction, especially in real-time applications. We develop a successful system solving all these challenges, using as basic architecture the recurrent application of proximal gradient algorithm. We learn a proximal map that works well with real images based on residual networks. Contraction of the resulting map is analyzed, and incoherence conditions are investigated that drive the convergence of the iterates. Extensive experiments are carried out under different settings: (a) reconstructing abdominal MRI of pediatric patients from highly undersampled Fourier-space data and (b) superresolving natural face images. Our key findings include: 1. a recurrent ResNet with a single residual block unrolled from an iterative algorithm yields an effective proximal which accurately reveals MR image details. 2. Our architecture significantly outperforms conventional non-recurrent deep ResNets by 2dB SNR; it is also trained much more rapidly. 3. It outperforms state-of-the-art compressed-sensing Wavelet-based methods by 4dB SNR, with 100x speedups in reconstruction time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge