Shrabon Das
Exploring Learnability in Memory-Augmented Recurrent Neural Networks: Precision, Stability, and Empirical Insights
Oct 04, 2024Abstract:This study explores the learnability of memory-less and memory-augmented RNNs, which are theoretically equivalent to Pushdown Automata. Empirical results show that these models often fail to generalize on longer sequences, relying more on precision than mastering symbolic grammar. Experiments on fully trained and component-frozen models reveal that freezing the memory component significantly improves performance, achieving state-of-the-art results on the Penn Treebank dataset (test perplexity reduced from 123.5 to 120.5). Models with frozen memory retained up to 90% of initial performance on longer sequences, compared to a 60% drop in standard models. Theoretical analysis suggests that freezing memory stabilizes temporal dependencies, leading to robust convergence. These findings stress the need for stable memory designs and long-sequence evaluations to understand RNNs true learnability limits.
BanStereoSet: A Dataset to Measure Stereotypical Social Biases in LLMs for Bangla
Sep 18, 2024
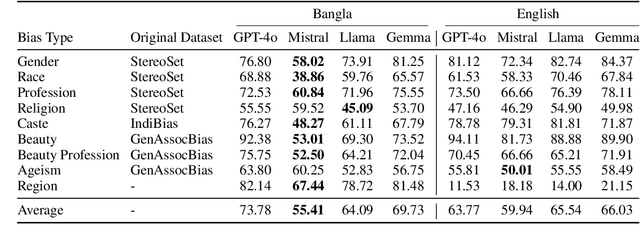


Abstract:This study presents BanStereoSet, a dataset designed to evaluate stereotypical social biases in multilingual LLMs for the Bangla language. In an effort to extend the focus of bias research beyond English-centric datasets, we have localized the content from the StereoSet, IndiBias, and Kamruzzaman et. al.'s datasets, producing a resource tailored to capture biases prevalent within the Bangla-speaking community. Our BanStereoSet dataset consists of 1,194 sentences spanning 9 categories of bias: race, profession, gender, ageism, beauty, beauty in profession, region, caste, and religion. This dataset not only serves as a crucial tool for measuring bias in multilingual LLMs but also facilitates the exploration of stereotypical bias across different social categories, potentially guiding the development of more equitable language technologies in Bangladeshi contexts. Our analysis of several language models using this dataset indicates significant biases, reinforcing the necessity for culturally and linguistically adapted datasets to develop more equitable language technologies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge