Shlomi Laufer
RoHan: Robust Hand Detection in Operation Room
Jan 15, 2025Abstract:Hand-specific localization has garnered significant interest within the computer vision community. Although there are numerous datasets with hand annotations from various angles and settings, domain transfer techniques frequently struggle in surgical environments. This is mainly due to the limited availability of gloved hand instances and the unique challenges of operating rooms (ORs). Thus, hand-detection models tailored to OR settings require extensive training and expensive annotation processes. To overcome these challenges, we present "RoHan" - a novel approach for robust hand detection in the OR, leveraging advanced semi-supervised domain adaptation techniques to tackle the challenges of varying recording conditions, diverse glove colors, and occlusions common in surgical settings. Our methodology encompasses two main stages: (1) data augmentation strategy that utilizes "Artificial Gloves," a method for augmenting publicly available hand datasets with synthetic images of hands-wearing gloves; (2) semi-supervised domain adaptation pipeline that improves detection performance in real-world OR settings through iterative prediction refinement and efficient frame filtering. We evaluate our method using two datasets: simulated enterotomy repair and saphenous vein graft harvesting. "RoHan" substantially reduces the need for extensive labeling and model training, paving the way for the practical implementation of hand detection technologies in medical settings.
Monocular pose estimation of articulated surgical instruments in open surgery
Jul 16, 2024Abstract:This work presents a novel approach to monocular 6D pose estimation of surgical instruments in open surgery, addressing challenges such as object articulations, symmetries, occlusions, and lack of annotated real-world data. The method leverages synthetic data generation and domain adaptation techniques to overcome these obstacles. The proposed approach consists of three main components: (1) synthetic data generation using 3D modeling of surgical tools with articulation rigging and physically-based rendering; (2) a tailored pose estimation framework combining object detection with pose estimation and a hybrid geometric fusion strategy; and (3) a training strategy that utilizes both synthetic and real unannotated data, employing domain adaptation on real video data using automatically generated pseudo-labels. Evaluations conducted on videos of open surgery demonstrate the good performance and real-world applicability of the proposed method, highlighting its potential for integration into medical augmented reality and robotic systems. The approach eliminates the need for extensive manual annotation of real surgical data.
Robust Surgical Phase Recognition From Annotation Efficient Supervision
Jun 26, 2024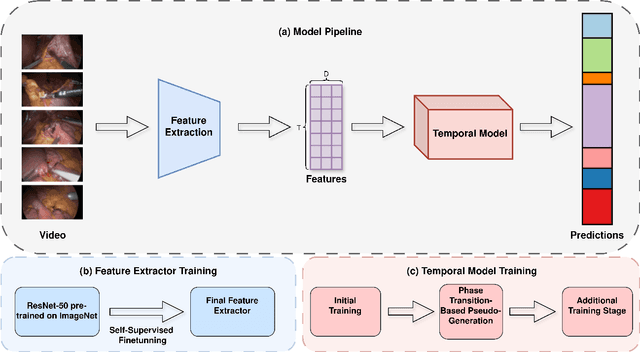

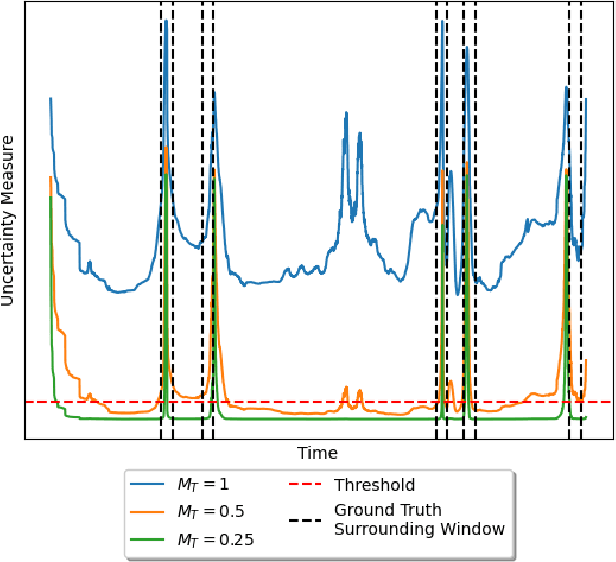

Abstract:Surgical phase recognition is a key task in computer-assisted surgery, aiming to automatically identify and categorize the different phases within a surgical procedure. Despite substantial advancements, most current approaches rely on fully supervised training, requiring expensive and time-consuming frame-level annotations. Timestamp supervision has recently emerged as a promising alternative, significantly reducing annotation costs while maintaining competitive performance. However, models trained on timestamp annotations can be negatively impacted by missing phase annotations, leading to a potential drawback in real-world scenarios. In this work, we address this issue by proposing a robust method for surgical phase recognition that can handle missing phase annotations effectively. Furthermore, we introduce the SkipTag@K annotation approach to the surgical domain, enabling a flexible balance between annotation effort and model performance. Our method achieves competitive results on two challenging datasets, demonstrating its efficacy in handling missing phase annotations and its potential for reducing annotation costs. Specifically, we achieve an accuracy of 85.1\% on the MultiBypass140 dataset using only 3 annotated frames per video, showcasing the effectiveness of our method and the potential of the SkipTag@K setup. We perform extensive experiments to validate the robustness of our method and provide valuable insights to guide future research in surgical phase recognition. Our work contributes to the advancement of surgical workflow recognition and paves the way for more efficient and reliable surgical phase recognition systems.
CuVLER: Enhanced Unsupervised Object Discoveries through Exhaustive Self-Supervised Transformers
Mar 12, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce VoteCut, an innovative method for unsupervised object discovery that leverages feature representations from multiple self-supervised models. VoteCut employs normalized-cut based graph partitioning, clustering and a pixel voting approach. Additionally, We present CuVLER (Cut-Vote-and-LEaRn), a zero-shot model, trained using pseudo-labels, generated by VoteCut, and a novel soft target loss to refine segmentation accuracy. Through rigorous evaluations across multiple datasets and several unsupervised setups, our methods demonstrate significant improvements in comparison to previous state-of-the-art models. Our ablation studies further highlight the contributions of each component, revealing the robustness and efficacy of our approach. Collectively, VoteCut and CuVLER pave the way for future advancements in image segmentation.
Depth Over RGB: Automatic Evaluation of Open Surgery Skills Using Depth Camera
Jan 18, 2024Abstract:Purpose: In this paper, we present a novel approach to the automatic evaluation of open surgery skills using depth cameras. This work is intended to show that depth cameras achieve similar results to RGB cameras, which is the common method in the automatic evaluation of open surgery skills. Moreover, depth cameras offer advantages such as robustness to lighting variations, camera positioning, simplified data compression, and enhanced privacy, making them a promising alternative to RGB cameras. Methods: Experts and novice surgeons completed two simulators of open suturing. We focused on hand and tool detection, and action segmentation in suturing procedures. YOLOv8 was used for tool detection in RGB and depth videos. Furthermore, UVAST and MSTCN++ were used for action segmentation. Our study includes the collection and annotation of a dataset recorded with Azure Kinect. Results: We demonstrated that using depth cameras in object detection and action segmentation achieves comparable results to RGB cameras. Furthermore, we analyzed 3D hand path length, revealing significant differences between experts and novice surgeons, emphasizing the potential of depth cameras in capturing surgical skills. We also investigated the influence of camera angles on measurement accuracy, highlighting the advantages of 3D cameras in providing a more accurate representation of hand movements. Conclusion: Our research contributes to advancing the field of surgical skill assessment by leveraging depth cameras for more reliable and privacy evaluations. The findings suggest that depth cameras can be valuable in assessing surgical skills and provide a foundation for future research in this area.
SFGANS Self-supervised Future Generator for human ActioN Segmentation
Dec 31, 2023Abstract:The ability to locate and classify action segments in long untrimmed video is of particular interest to many applications such as autonomous cars, robotics and healthcare applications. Today, the most popular pipeline for action segmentation is composed of encoding the frames into feature vectors, which are then processed by a temporal model for segmentation. In this paper we present a self-supervised method that comes in the middle of the standard pipeline and generated refined representations of the original feature vectors. Experiments show that this method improves the performance of existing models on different sub-tasks of action segmentation, even without additional hyper parameter tuning.
More Than Meets the Eye: Analyzing Anesthesiologists' Visual Attention in the Operating Room Using Deep Learning Models
Aug 10, 2023Abstract:Patient's vital signs, which are displayed on monitors, make the anesthesiologist's visual attention (VA) a key component in the safe management of patients under general anesthesia; moreover, the distribution of said VA and the ability to acquire specific cues throughout the anesthetic, may have a direct impact on patient's outcome. Currently, most studies employ wearable eye-tracking technologies to analyze anesthesiologists' visual patterns. Albeit being able to produce meticulous data, wearable devices are not a sustainable solution for large-scale or long-term use for data collection in the operating room (OR). Thus, by utilizing a novel eye-tracking method in the form of deep learning models that process monitor-mounted webcams, we collected continuous behavioral data and gained insight into the anesthesiologist's VA distribution with minimal disturbance to their natural workflow. In this study, we collected OR video recordings using the proposed framework and compared different visual behavioral patterns. We distinguished between baseline VA distribution during uneventful periods to patterns associated with active phases or during critical, unanticipated incidents. In the future, such a platform may serve as a crucial component of context-aware assistive technologies in the OR.
Kinematic Data-Based Action Segmentation for Surgical Applications
Mar 14, 2023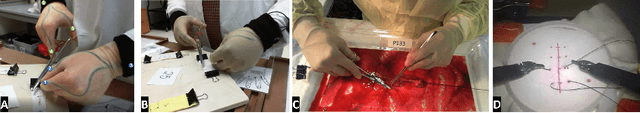
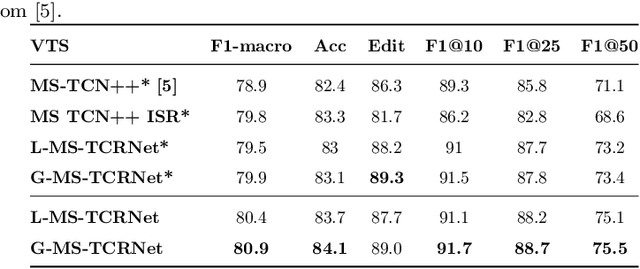
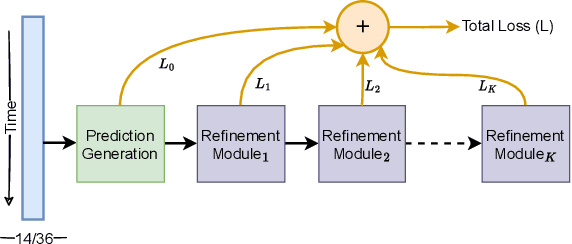
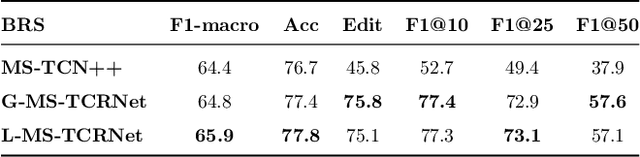
Abstract:Action segmentation is a challenging task in high-level process analysis, typically performed on video or kinematic data obtained from various sensors. In the context of surgical procedures, action segmentation is critical for workflow analysis algorithms. This work presents two contributions related to action segmentation on kinematic data. Firstly, we introduce two multi-stage architectures, MS-TCN-BiLSTM and MS-TCN-BiGRU, specifically designed for kinematic data. The architectures consist of a prediction generator with intra-stage regularization and Bidirectional LSTM or GRU-based refinement stages. Secondly, we propose two new data augmentation techniques, World Frame Rotation and Horizontal-Flip, which utilize the strong geometric structure of kinematic data to improve algorithm performance and robustness. We evaluate our models on three datasets of surgical suturing tasks: the Variable Tissue Simulation (VTS) Dataset and the newly introduced Bowel Repair Simulation (BRS) Dataset, both of which are open surgery simulation datasets collected by us, as well as the JHU-ISI Gesture and Skill Assessment Working Set (JIGSAWS), a well-known benchmark in robotic surgery. Our methods achieve state-of-the-art performance on all benchmark datasets and establish a strong baseline for the BRS dataset.
Pose Estimation For Surgical Training
Nov 13, 2022Abstract:Purpose: This research aims to facilitate the use of state-of-the-art computer vision algorithms for the automated training of surgeons and the analysis of surgical footage. By estimating 2D hand poses, we model the movement of the practitioner's hands, and their interaction with surgical instruments, to study their potential benefit for surgical training. Methods: We leverage pre-trained models on a publicly-available hands dataset to create our own in-house dataset of 100 open surgery simulation videos with 2D hand poses. We also assess the ability of pose estimations to segment surgical videos into gestures and tool-usage segments and compare them to kinematic sensors and I3D features. Furthermore, we introduce 6 novel surgical skill proxies stemming from domain experts' training advice, all of which our framework can automatically detect given raw video footage. Results: State-of-the-art gesture segmentation accuracy of 88.49% on the Open Surgery Simulation dataset is achieved with the fusion of 2D poses and I3D features from multiple angles. The introduced surgical skill proxies presented significant differences for novices compared to experts and produced actionable feedback for improvement. Conclusion: This research demonstrates the benefit of pose estimations for open surgery by analyzing their effectiveness in gesture segmentation and skill assessment. Gesture segmentation using pose estimations achieved comparable results to physical sensors while being remote and markerless. Surgical skill proxies that rely on pose estimation proved they can be used to work towards automated training feedback. We hope our findings encourage additional collaboration on novel skill proxies to make surgical training more efficient.
Bounded Future MS-TCN++ for surgical gesture recognition
Oct 05, 2022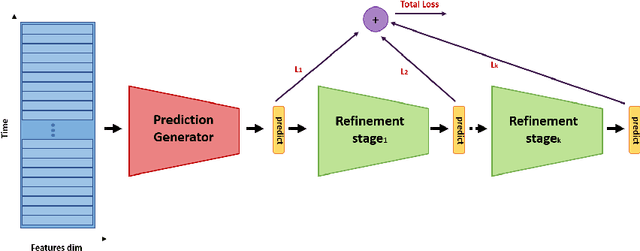

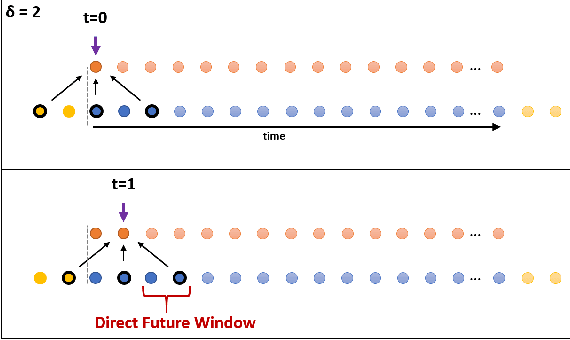
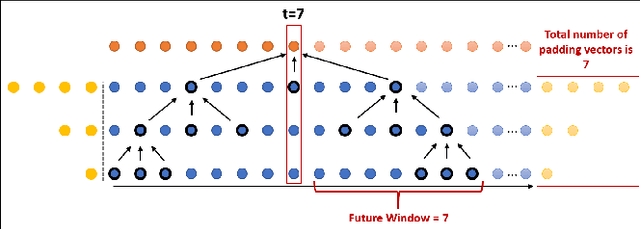
Abstract:In recent times there is a growing development of video based applications for surgical purposes. Part of these applications can work offline after the end of the procedure, other applications must react immediately. However, there are cases where the response should be done during the procedure but some delay is acceptable. In the literature, the online-offline performance gap is known. Our goal in this study was to learn the performance-delay trade-off and design an MS-TCN++-based algorithm that can utilize this trade-off. To this aim, we used our open surgery simulation data-set containing 96 videos of 24 participants that perform a suturing task on a variable tissue simulator. In this study, we used video data captured from the side view. The Networks were trained to identify the performed surgical gestures. The naive approach is to reduce the MS-TCN++ depth, as a result, the receptive field is reduced, and also the number of required future frames is also reduced. We showed that this method is sub-optimal, mainly in the small delay cases. The second method was to limit the accessible future in each temporal convolution. This way, we have flexibility in the network design and as a result, we achieve significantly better performance than in the naive approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge