Or Rubin
Robust Surgical Phase Recognition From Annotation Efficient Supervision
Jun 26, 2024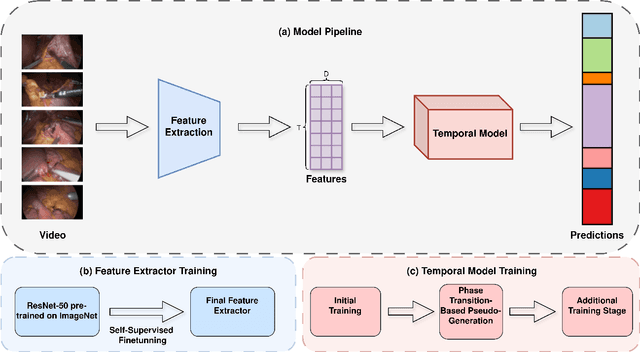

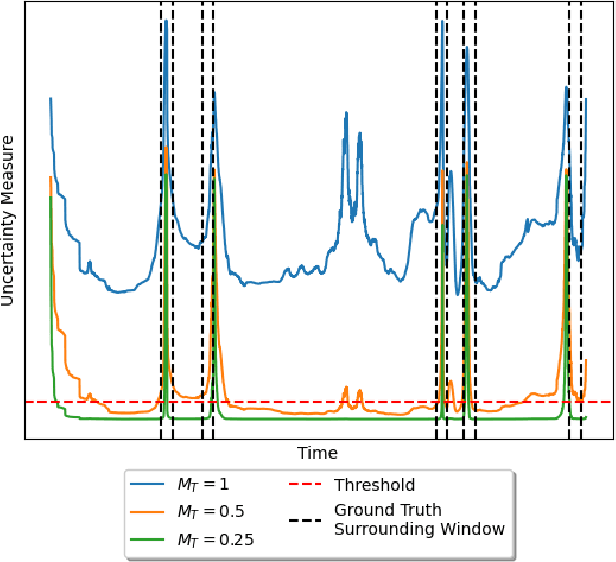

Abstract:Surgical phase recognition is a key task in computer-assisted surgery, aiming to automatically identify and categorize the different phases within a surgical procedure. Despite substantial advancements, most current approaches rely on fully supervised training, requiring expensive and time-consuming frame-level annotations. Timestamp supervision has recently emerged as a promising alternative, significantly reducing annotation costs while maintaining competitive performance. However, models trained on timestamp annotations can be negatively impacted by missing phase annotations, leading to a potential drawback in real-world scenarios. In this work, we address this issue by proposing a robust method for surgical phase recognition that can handle missing phase annotations effectively. Furthermore, we introduce the SkipTag@K annotation approach to the surgical domain, enabling a flexible balance between annotation effort and model performance. Our method achieves competitive results on two challenging datasets, demonstrating its efficacy in handling missing phase annotations and its potential for reducing annotation costs. Specifically, we achieve an accuracy of 85.1\% on the MultiBypass140 dataset using only 3 annotated frames per video, showcasing the effectiveness of our method and the potential of the SkipTag@K setup. We perform extensive experiments to validate the robustness of our method and provide valuable insights to guide future research in surgical phase recognition. Our work contributes to the advancement of surgical workflow recognition and paves the way for more efficient and reliable surgical phase recognition systems.
CuVLER: Enhanced Unsupervised Object Discoveries through Exhaustive Self-Supervised Transformers
Mar 12, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce VoteCut, an innovative method for unsupervised object discovery that leverages feature representations from multiple self-supervised models. VoteCut employs normalized-cut based graph partitioning, clustering and a pixel voting approach. Additionally, We present CuVLER (Cut-Vote-and-LEaRn), a zero-shot model, trained using pseudo-labels, generated by VoteCut, and a novel soft target loss to refine segmentation accuracy. Through rigorous evaluations across multiple datasets and several unsupervised setups, our methods demonstrate significant improvements in comparison to previous state-of-the-art models. Our ablation studies further highlight the contributions of each component, revealing the robustness and efficacy of our approach. Collectively, VoteCut and CuVLER pave the way for future advancements in image segmentation.
Kinematic Data-Based Action Segmentation for Surgical Applications
Mar 14, 2023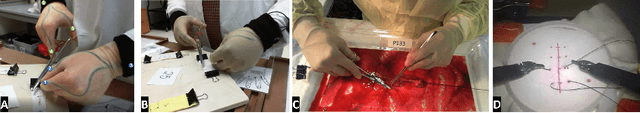
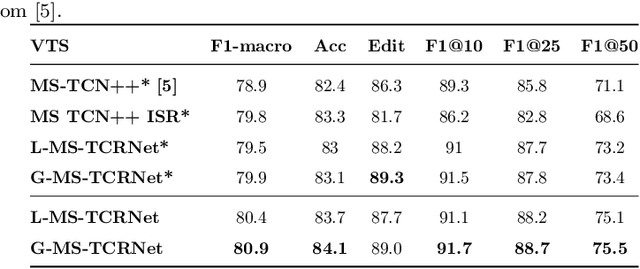
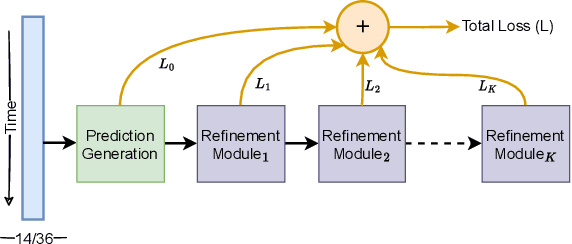
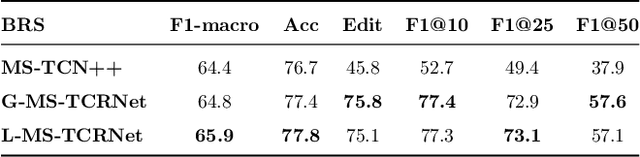
Abstract:Action segmentation is a challenging task in high-level process analysis, typically performed on video or kinematic data obtained from various sensors. In the context of surgical procedures, action segmentation is critical for workflow analysis algorithms. This work presents two contributions related to action segmentation on kinematic data. Firstly, we introduce two multi-stage architectures, MS-TCN-BiLSTM and MS-TCN-BiGRU, specifically designed for kinematic data. The architectures consist of a prediction generator with intra-stage regularization and Bidirectional LSTM or GRU-based refinement stages. Secondly, we propose two new data augmentation techniques, World Frame Rotation and Horizontal-Flip, which utilize the strong geometric structure of kinematic data to improve algorithm performance and robustness. We evaluate our models on three datasets of surgical suturing tasks: the Variable Tissue Simulation (VTS) Dataset and the newly introduced Bowel Repair Simulation (BRS) Dataset, both of which are open surgery simulation datasets collected by us, as well as the JHU-ISI Gesture and Skill Assessment Working Set (JIGSAWS), a well-known benchmark in robotic surgery. Our methods achieve state-of-the-art performance on all benchmark datasets and establish a strong baseline for the BRS dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge