Shaoju Wang
CurveLane-NAS: Unifying Lane-Sensitive Architecture Search and Adaptive Point Blending
Jul 23, 2020

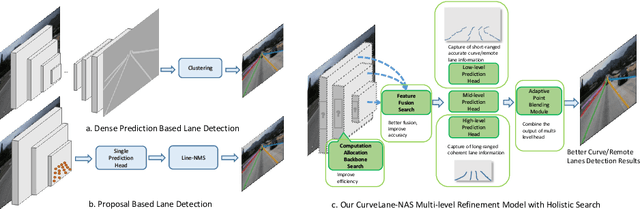
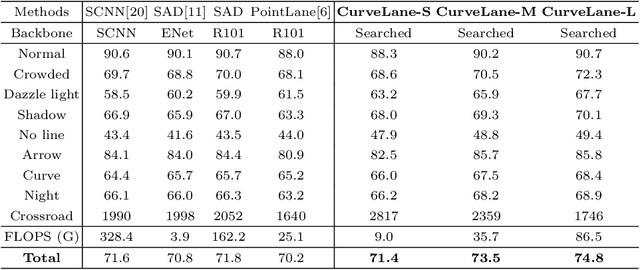
Abstract:We address the curve lane detection problem which poses more realistic challenges than conventional lane detection for better facilitating modern assisted/autonomous driving systems. Current hand-designed lane detection methods are not robust enough to capture the curve lanes especially the remote parts due to the lack of modeling both long-range contextual information and detailed curve trajectory. In this paper, we propose a novel lane-sensitive architecture search framework named CurveLane-NAS to automatically capture both long-ranged coherent and accurate short-range curve information while unifying both architecture search and post-processing on curve lane predictions via point blending. It consists of three search modules: a) a feature fusion search module to find a better fusion of the local and global context for multi-level hierarchy features; b) an elastic backbone search module to explore an efficient feature extractor with good semantics and latency; c) an adaptive point blending module to search a multi-level post-processing refinement strategy to combine multi-scale head prediction. The unified framework ensures lane-sensitive predictions by the mutual guidance between NAS and adaptive point blending. Furthermore, we also steer forward to release a more challenging benchmark named CurveLanes for addressing the most difficult curve lanes. It consists of 150K images with 680K labels.The new dataset can be downloaded at github.com/xbjxh/CurveLanes (already anonymized for this submission). Experiments on the new CurveLanes show that the SOTA lane detection methods suffer substantial performance drop while our model can still reach an 80+% F1-score. Extensive experiments on traditional lane benchmarks such as CULane also demonstrate the superiority of our CurveLane-NAS, e.g. achieving a new SOTA 74.8% F1-score on CULane.
ElixirNet: Relation-aware Network Architecture Adaptation for Medical Lesion Detection
Mar 03, 2020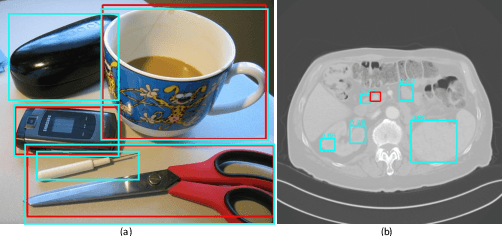
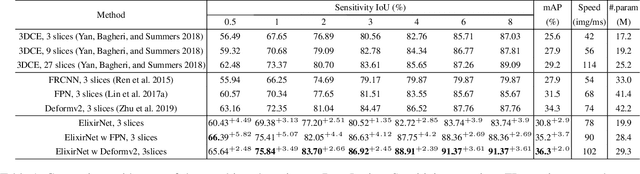
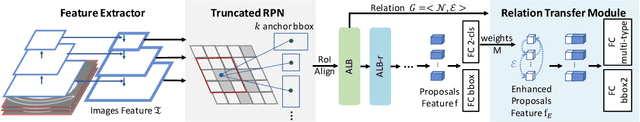
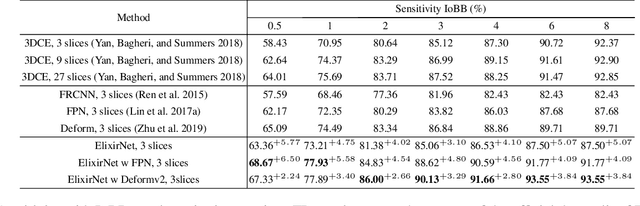
Abstract:Most advances in medical lesion detection network are limited to subtle modification on the conventional detection network designed for natural images. However, there exists a vast domain gap between medical images and natural images where the medical image detection often suffers from several domain-specific challenges, such as high lesion/background similarity, dominant tiny lesions, and severe class imbalance. Is a hand-crafted detection network tailored for natural image undoubtedly good enough over a discrepant medical lesion domain? Is there more powerful operations, filters, and sub-networks that better fit the medical lesion detection problem to be discovered? In this paper, we introduce a novel ElixirNet that includes three components: 1) TruncatedRPN balances positive and negative data for false positive reduction; 2) Auto-lesion Block is automatically customized for medical images to incorporate relation-aware operations among region proposals, and leads to more suitable and efficient classification and localization. 3) Relation transfer module incorporates the semantic relationship and transfers the relevant contextual information with an interpretable the graph thus alleviates the problem of lack of annotations for all types of lesions. Experiments on DeepLesion and Kits19 prove the effectiveness of ElixirNet, achieving improvement of both sensitivity and precision over FPN with fewer parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge