Shaodong Li
Learning the Generalizable Manipulation Skills on Soft-body Tasks via Guided Self-attention Behavior Cloning Policy
Oct 08, 2024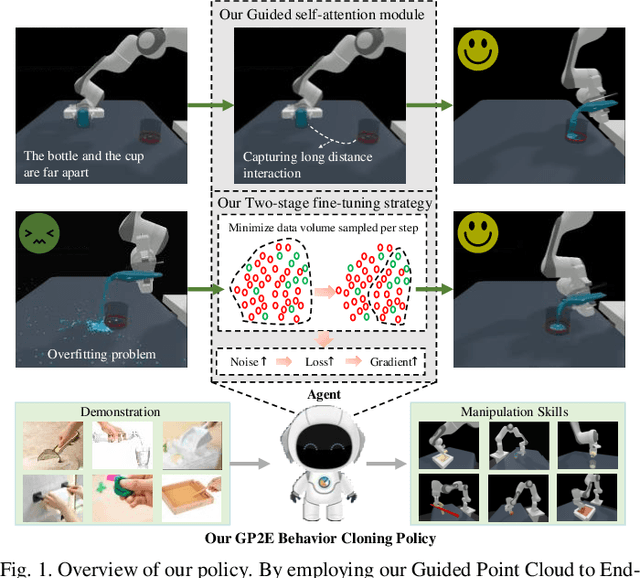
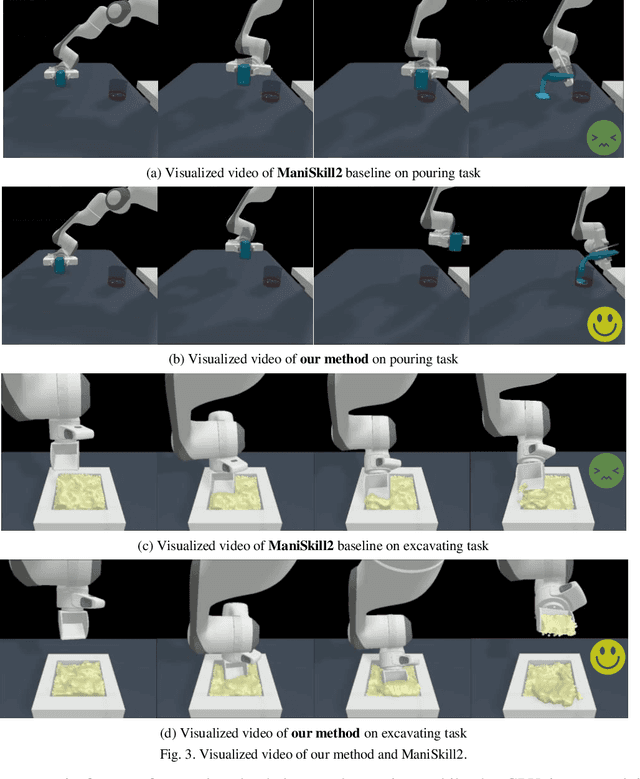
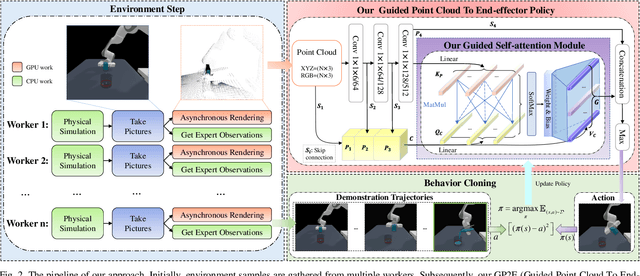

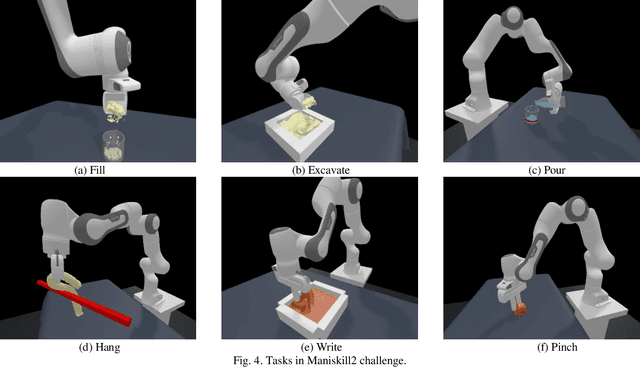
Abstract:Embodied AI represents a paradigm in AI research where artificial agents are situated within and interact with physical or virtual environments. Despite the recent progress in Embodied AI, it is still very challenging to learn the generalizable manipulation skills that can handle large deformation and topological changes on soft-body objects, such as clay, water, and soil. In this work, we proposed an effective policy, namely GP2E behavior cloning policy, which can guide the agent to learn the generalizable manipulation skills from soft-body tasks, including pouring, filling, hanging, excavating, pinching, and writing. Concretely, we build our policy from three insights:(1) Extracting intricate semantic features from point cloud data and seamlessly integrating them into the robot's end-effector frame; (2) Capturing long-distance interactions in long-horizon tasks through the incorporation of our guided self-attention module; (3) Mitigating overfitting concerns and facilitating model convergence to higher accuracy levels via the introduction of our two-stage fine-tuning strategy. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach by achieving the 1st prize in the soft-body track of the ManiSkill2 Challenge at the CVPR 2023 4th Embodied AI workshop. Our findings highlight the potential of our method to improve the generalization abilities of Embodied AI models and pave the way for their practical applications in real-world scenarios.
HyperCLOVA X Technical Report
Apr 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce HyperCLOVA X, a family of large language models (LLMs) tailored to the Korean language and culture, along with competitive capabilities in English, math, and coding. HyperCLOVA X was trained on a balanced mix of Korean, English, and code data, followed by instruction-tuning with high-quality human-annotated datasets while abiding by strict safety guidelines reflecting our commitment to responsible AI. The model is evaluated across various benchmarks, including comprehensive reasoning, knowledge, commonsense, factuality, coding, math, chatting, instruction-following, and harmlessness, in both Korean and English. HyperCLOVA X exhibits strong reasoning capabilities in Korean backed by a deep understanding of the language and cultural nuances. Further analysis of the inherent bilingual nature and its extension to multilingualism highlights the model's cross-lingual proficiency and strong generalization ability to untargeted languages, including machine translation between several language pairs and cross-lingual inference tasks. We believe that HyperCLOVA X can provide helpful guidance for regions or countries in developing their sovereign LLMs.
3D Hand Reconstruction via Aggregating Intra and Inter Graphs Guided by Prior Knowledge for Hand-Object Interaction Scenario
Mar 04, 2024Abstract:Recently, 3D hand reconstruction has gained more attention in human-computer cooperation, especially for hand-object interaction scenario. However, it still remains huge challenge due to severe hand-occlusion caused by interaction, which contain the balance of accuracy and physical plausibility, highly nonlinear mapping of model parameters and occlusion feature enhancement. To overcome these issues, we propose a 3D hand reconstruction network combining the benefits of model-based and model-free approaches to balance accuracy and physical plausibility for hand-object interaction scenario. Firstly, we present a novel MANO pose parameters regression module from 2D joints directly, which avoids the process of highly nonlinear mapping from abstract image feature and no longer depends on accurate 3D joints. Moreover, we further propose a vertex-joint mutual graph-attention model guided by MANO to jointly refine hand meshes and joints, which model the dependencies of vertex-vertex and joint-joint and capture the correlation of vertex-joint for aggregating intra-graph and inter-graph node features respectively. The experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves a competitive performance on recently benchmark datasets HO3DV2 and Dex-YCB, and outperforms all only model-base approaches and model-free approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge