Shangbo Zhou
Integrating Dependency Tree Into Self-attention for Sentence Representation
Mar 11, 2022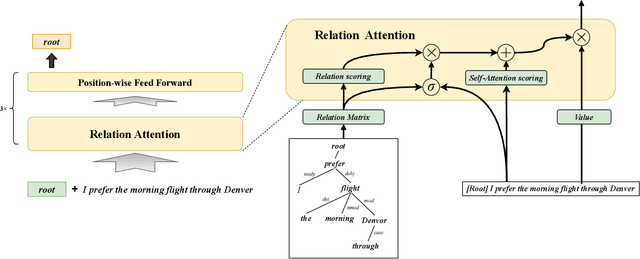



Abstract:Recent progress on parse tree encoder for sentence representation learning is notable. However, these works mainly encode tree structures recursively, which is not conducive to parallelization. On the other hand, these works rarely take into account the labels of arcs in dependency trees. To address both issues, we propose Dependency-Transformer, which applies a relation-attention mechanism that works in concert with the self-attention mechanism. This mechanism aims to encode the dependency and the spatial positional relations between nodes in the dependency tree of sentences. By a score-based method, we successfully inject the syntax information without affecting Transformer's parallelizability. Our model outperforms or is comparable to the state-of-the-art methods on four tasks for sentence representation and has obvious advantages in computational efficiency.
X-TREPAN: a multi class regression and adapted extraction of comprehensible decision tree in artificial neural networks
Aug 30, 2015



Abstract:In this work, the TREPAN algorithm is enhanced and extended for extracting decision trees from neural networks. We empirically evaluated the performance of the algorithm on a set of databases from real world events. This benchmark enhancement was achieved by adapting Single-test TREPAN and C4.5 decision tree induction algorithms to analyze the datasets. The models are then compared with X-TREPAN for comprehensibility and classification accuracy. Furthermore, we validate the experimentations by applying statistical methods. Finally, the modified algorithm is extended to work with multi-class regression problems and the ability to comprehend generalized feed forward networks is achieved.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge