Shang-Hsuan Chiang
Team NYCU at Defactify4: Robust Detection and Source Identification of AI-Generated Images Using CNN and CLIP-Based Models
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:With the rapid advancement of generative AI, AI-generated images have become increasingly realistic, raising concerns about creativity, misinformation, and content authenticity. Detecting such images and identifying their source models has become a critical challenge in ensuring the integrity of digital media. This paper tackles the detection of AI-generated images and identifying their source models using CNN and CLIP-ViT classifiers. For the CNN-based classifier, we leverage EfficientNet-B0 as the backbone and feed with RGB channels, frequency features, and reconstruction errors, while for CLIP-ViT, we adopt a pretrained CLIP image encoder to extract image features and SVM to perform classification. Evaluated on the Defactify 4 dataset, our methods demonstrate strong performance in both tasks, with CLIP-ViT showing superior robustness to image perturbations. Compared to baselines like AEROBLADE and OCC-CLIP, our approach achieves competitive results. Notably, our method ranked Top-3 overall in the Defactify 4 competition, highlighting its effectiveness and generalizability. All of our implementations can be found in https://github.com/uuugaga/Defactify_4
BADGE: BADminton report Generation and Evaluation with LLM
Jun 26, 2024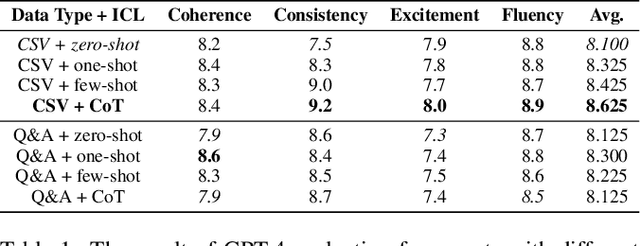
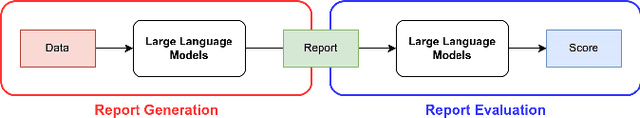
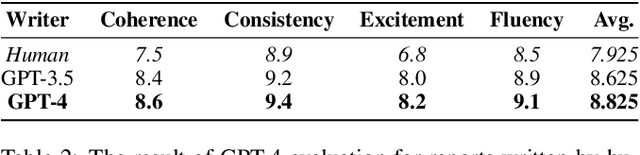
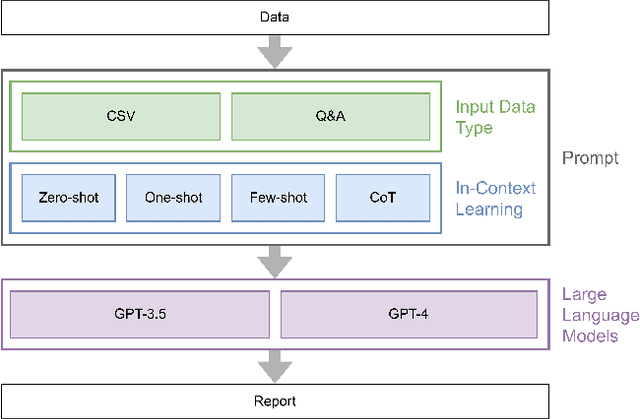
Abstract:Badminton enjoys widespread popularity, and reports on matches generally include details such as player names, game scores, and ball types, providing audiences with a comprehensive view of the games. However, writing these reports can be a time-consuming task. This challenge led us to explore whether a Large Language Model (LLM) could automate the generation and evaluation of badminton reports. We introduce a novel framework named BADGE, designed for this purpose using LLM. Our method consists of two main phases: Report Generation and Report Evaluation. Initially, badminton-related data is processed by the LLM, which then generates a detailed report of the match. We tested different Input Data Types, In-Context Learning (ICL), and LLM, finding that GPT-4 performs best when using CSV data type and the Chain of Thought prompting. Following report generation, the LLM evaluates and scores the reports to assess their quality. Our comparisons between the scores evaluated by GPT-4 and human judges show a tendency to prefer GPT-4 generated reports. Since the application of LLM in badminton reporting remains largely unexplored, our research serves as a foundational step for future advancements in this area. Moreover, our method can be extended to other sports games, thereby enhancing sports promotion. For more details, please refer to https://github.com/AndyChiangSH/BADGE.
Team Trifecta at Factify5WQA: Setting the Standard in Fact Verification with Fine-Tuning
Mar 15, 2024
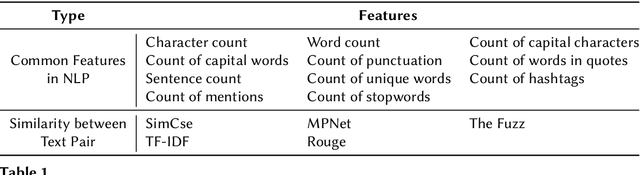
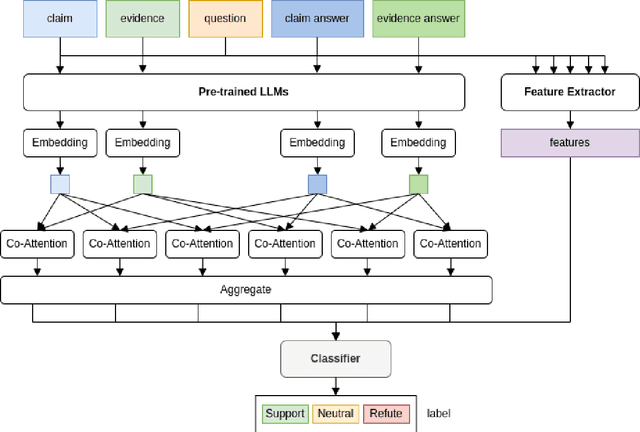
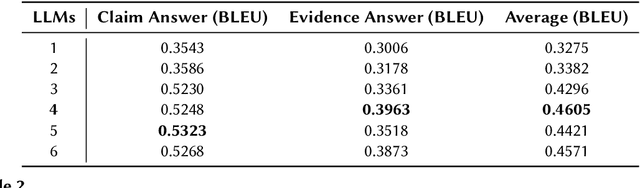
Abstract:In this paper, we present Pre-CoFactv3, a comprehensive framework comprised of Question Answering and Text Classification components for fact verification. Leveraging In-Context Learning, Fine-tuned Large Language Models (LLMs), and the FakeNet model, we address the challenges of fact verification. Our experiments explore diverse approaches, comparing different Pre-trained LLMs, introducing FakeNet, and implementing various ensemble methods. Notably, our team, Trifecta, secured first place in the AAAI-24 Factify 3.0 Workshop, surpassing the baseline accuracy by 103% and maintaining a 70% lead over the second competitor. This success underscores the efficacy of our approach and its potential contributions to advancing fact verification research.
CDGP: Automatic Cloze Distractor Generation based on Pre-trained Language Model
Mar 15, 2024



Abstract:Manually designing cloze test consumes enormous time and efforts. The major challenge lies in wrong option (distractor) selection. Having carefully-design distractors improves the effectiveness of learner ability assessment. As a result, the idea of automatically generating cloze distractor is motivated. In this paper, we investigate cloze distractor generation by exploring the employment of pre-trained language models (PLMs) as an alternative for candidate distractor generation. Experiments show that the PLM-enhanced model brings a substantial performance improvement. Our best performing model advances the state-of-the-art result from 14.94 to 34.17 (NDCG@10 score). Our code and dataset is available at https://github.com/AndyChiangSH/CDGP.
* Findings of short paper, EMNLP 2022
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge