Chih-Chuan Wang
BADGE: BADminton report Generation and Evaluation with LLM
Jun 26, 2024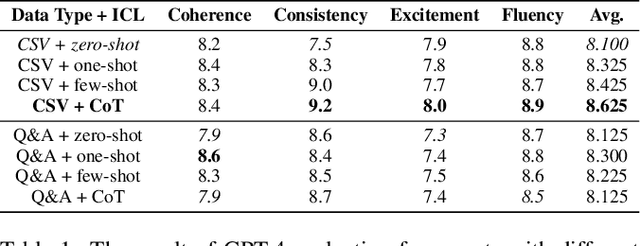
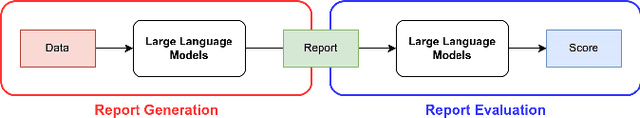
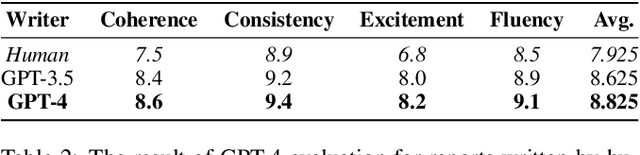
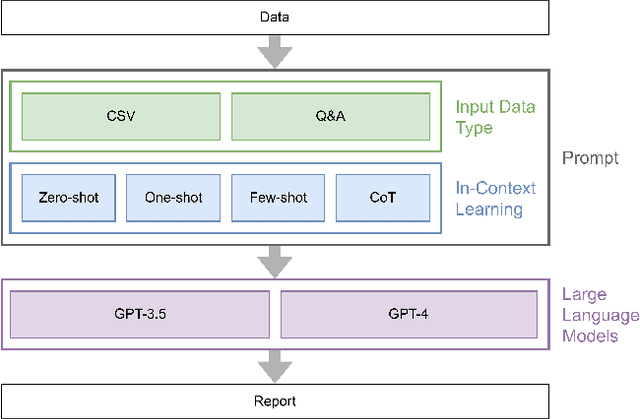
Abstract:Badminton enjoys widespread popularity, and reports on matches generally include details such as player names, game scores, and ball types, providing audiences with a comprehensive view of the games. However, writing these reports can be a time-consuming task. This challenge led us to explore whether a Large Language Model (LLM) could automate the generation and evaluation of badminton reports. We introduce a novel framework named BADGE, designed for this purpose using LLM. Our method consists of two main phases: Report Generation and Report Evaluation. Initially, badminton-related data is processed by the LLM, which then generates a detailed report of the match. We tested different Input Data Types, In-Context Learning (ICL), and LLM, finding that GPT-4 performs best when using CSV data type and the Chain of Thought prompting. Following report generation, the LLM evaluates and scores the reports to assess their quality. Our comparisons between the scores evaluated by GPT-4 and human judges show a tendency to prefer GPT-4 generated reports. Since the application of LLM in badminton reporting remains largely unexplored, our research serves as a foundational step for future advancements in this area. Moreover, our method can be extended to other sports games, thereby enhancing sports promotion. For more details, please refer to https://github.com/AndyChiangSH/BADGE.
Exploring the Long Short-Term Dependencies to Infer Shot Influence in Badminton Matches
Sep 14, 2021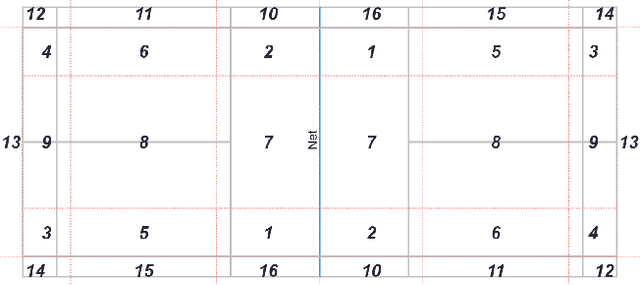
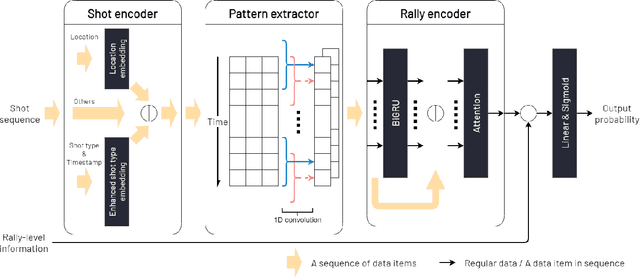
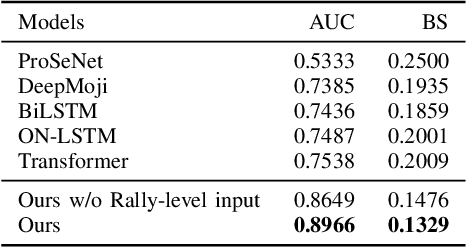

Abstract:Identifying significant shots in a rally is important for evaluating players' performance in badminton matches. While there are several studies that have quantified player performance in other sports, analyzing badminton data is remained untouched. In this paper, we introduce a badminton language to fully describe the process of the shot and propose a deep learning model composed of a novel short-term extractor and a long-term encoder for capturing a shot-by-shot sequence in a badminton rally by framing the problem as predicting a rally result. Our model incorporates an attention mechanism to enable the transparency of the action sequence to the rally result, which is essential for badminton experts to gain interpretable predictions. Experimental evaluation based on a real-world dataset demonstrates that our proposed model outperforms the strong baselines. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/yao0510/Shot-Influence.
CoachAI: A Project for Microscopic Badminton Match Data Collection and Tactical Analysis
Jul 12, 2019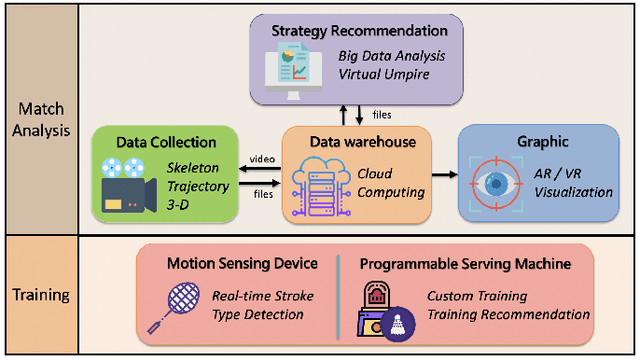
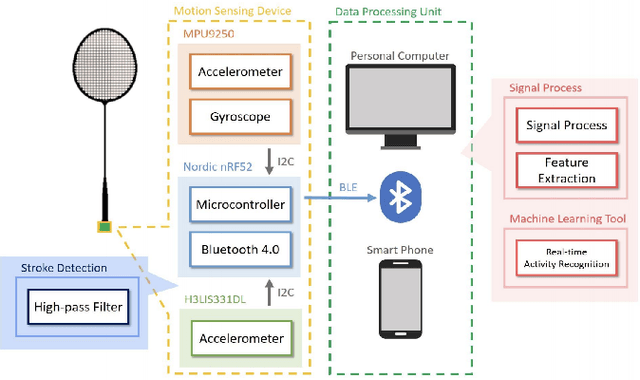
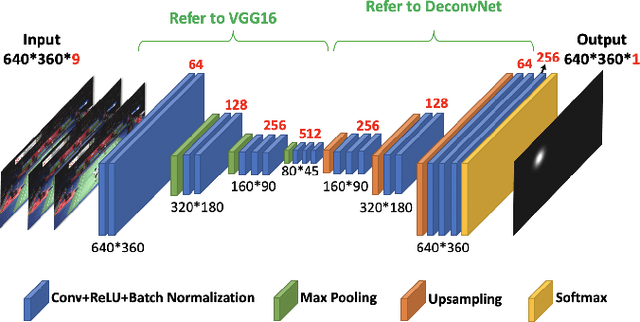
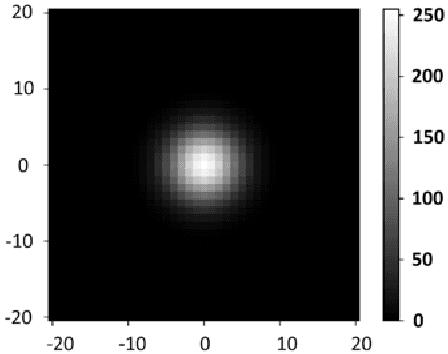
Abstract:Computer vision based object tracking has been used to annotate and augment sports video. For sports learning and training, video replay is often used in post-match review and training review for tactical analysis and movement analysis. For automatically and systematically competition data collection and tactical analysis, a project called CoachAI has been supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan. The proposed project also includes research of data visualization, connected training auxiliary devices, and data warehouse. Deep learning techniques will be used to develop video-based real-time microscopic competition data collection based on broadcast competition video. Machine learning techniques will be used to develop a tactical analysis. To reveal data in more understandable forms and to help in pre-match training, AR/VR techniques will be used to visualize data, tactics, and so on. In addition, training auxiliary devices including smart badminton rackets and connected serving machines will be developed based on the IoT technology to further utilize competition data and tactical data and boost training efficiency. Especially, the connected serving machines will be developed to perform specified tactics and to interact with players in their training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge