Seyed Hossein Khasteh
Influence Maximization (IM) in Complex Networks with Limited Visibility Using Statistical Methods
Aug 28, 2022



Abstract:A social network (SN) is a social structure consisting of a group representing the interaction between them. SNs have recently been widely used and, subsequently, have become suitable and popular platforms for product promotion and information diffusion. People in an SN directly influence each other's interests and behavior. One of the most important problems in SNs is to find people who can have the maximum influence on other nodes in the network in a cascade manner if they are chosen as the seed nodes of a network diffusion scenario. Influential diffusers are people who, if they are chosen as the seed set in a publishing issue in the network, that network will have the most people who have learned about that diffused entity. This is a well-known problem in literature known as influence maximization (IM) problem. Although it has been proven that this is an NP-complete problem and does not have a solution in polynomial time, it has been argued that it has the properties of sub modular functions and, therefore, can be solved using a greedy algorithm. Most of the methods proposed to improve this complexity are based on the assumption that the entire graph is visible. However, this assumption does not hold for many real-world graphs. This study is conducted to extend current maximization methods with link prediction techniques to pseudo-visibility graphs. To this end, a graph generation method called the exponential random graph model (ERGM) is used for link prediction. The proposed method is tested using the data from the Snap dataset of Stanford University. According to the experimental tests, the proposed method is efficient on real-world graphs.
Opinion Leader Detection in Online Social Networks Based on Output and Input Links
Aug 28, 2022



Abstract:The understanding of how users in a network update their opinions based on their neighbours opinions has attracted a great deal of interest in the field of network science, and a growing body of literature recognises the significance of this issue. In this research paper, we propose a new dynamic model of opinion formation in directed networks. In this model, the opinion of each node is updated as the weighted average of its neighbours opinions, where the weights represent social influence. We define a new centrality measure as a social influence metric based on both influence and conformity. We measure this new approach using two opinion formation models: (i) the Degroot model and (ii) our own proposed model. Previously published research studies have not considered conformity, and have only considered the influence of the nodes when computing the social influence. In our definition, nodes with low in-degree and high out-degree that were connected to nodes with high out-degree and low in-degree had higher centrality. As the main contribution of this research, we propose an algorithm for finding a small subset of nodes in a social network that can have a significant impact on the opinions of other nodes. Experiments on real-world data demonstrate that the proposed algorithm significantly outperforms previously published state-of-the-art methods.
Profitable Strategy Design by Using Deep Reinforcement Learning for Trades on Cryptocurrency Markets
Jan 15, 2022



Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning solutions have been applied to different control problems with outperforming and promising results. In this research work we have applied Proximal Policy Optimization, Soft Actor-Critic and Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning to strategy design problem of three cryptocurrency markets. Our input data includes price data and technical indicators. We have implemented a Gym environment based on cryptocurrency markets to be used with the algorithms. Our test results on unseen data shows a great potential for this approach in helping investors with an expert system to exploit the market and gain profit. Our highest gain for an unseen 66 day span is 4850 US dollars per 10000 US dollars investment. We also discuss on how a specific hyperparameter in the environment design can be used to adjust risk in the generated strategies.
Text as Environment: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Text Readability Assessment Model
Dec 15, 2019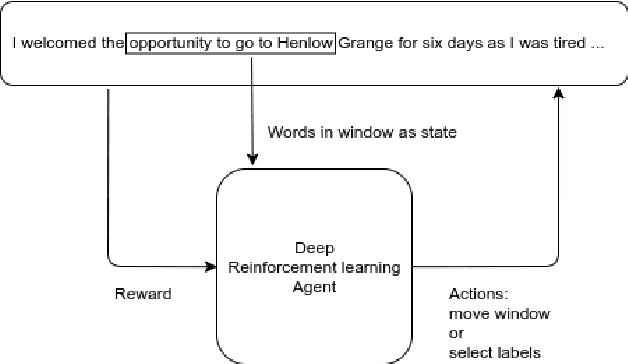
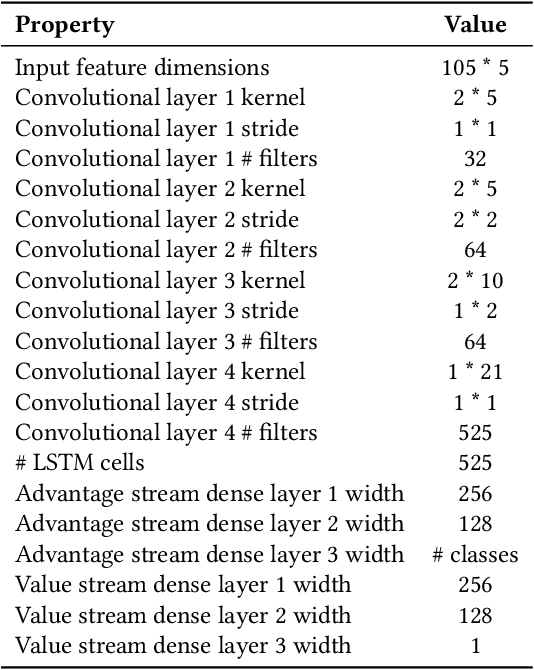
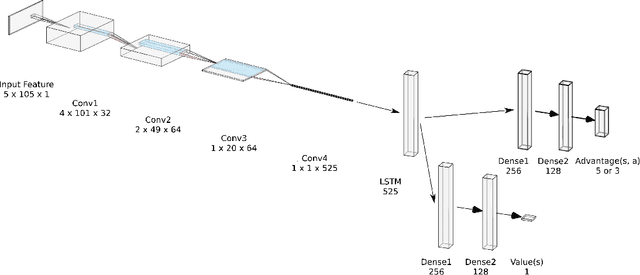
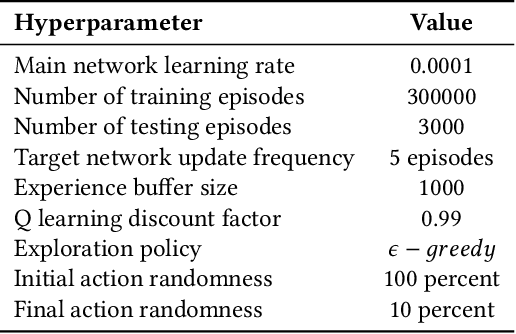
Abstract:Evaluating the readability of a text can significantly facilitate the precise expression of information in a written form. The formulation of text readability assessment demands the identification of meaningful properties of the text and correct conversion of features to the right readability level. Sophisticated features and models are being used to evaluate the comprehensibility of texts accurately. Still, these models are challenging to implement, heavily language-dependent, and do not perform well on short texts. Deep reinforcement learning models are demonstrated to be helpful in further improvement of state-of-the-art text readability assessment models. The main contributions of the proposed approach are the automation of feature extraction, loosening the tight language dependency of text readability assessment task, and efficient use of text by finding the minimum portion of a text required to assess its readability. The experiments on Weebit, Cambridge Exams, and Persian readability datasets display the model's state-of-the-art precision, efficiency, and the capability to be applied to other languages.
A Machine Learning Approach to Persian Text Readability Assessment Using a Crowdsourced Dataset
Oct 19, 2018



Abstract:An automated approach to text readability assessment is essential to a language and can be a powerful tool for improving the understandability of texts written and published in that language. However, the Persian language, which is spoken by over 110 million speakers, lacks such a system. Unlike other languages such as English, French, and Chinese, very limited research studies have been carried out to build an accurate and reliable text readability assessment system for the Persian language. In the present research, the first Persian dataset for text readability assessment was gathered and the first model for Persian text readability assessment using machine learning was introduced. The experiments showed that this model was accurate and could assess the readability of Persian texts with a high degree of confidence. The results of this study can be used in a number of applications such as medical and educational text readability evaluation and have the potential to be the cornerstone of future studies in Persian text readability assessment.
New S-norm and T-norm Operators for Active Learning Method
Feb 07, 2011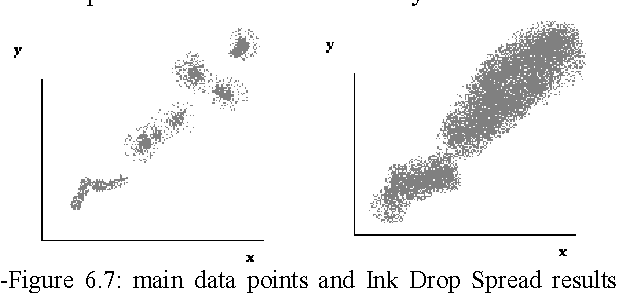

Abstract:Active Learning Method (ALM) is a soft computing method used for modeling and control based on fuzzy logic. All operators defined for fuzzy sets must serve as either fuzzy S-norm or fuzzy T-norm. Despite being a powerful modeling method, ALM does not possess operators which serve as S-norms and T-norms which deprive it of a profound analytical expression/form. This paper introduces two new operators based on morphology which satisfy the following conditions: First, they serve as fuzzy S-norm and T-norm. Second, they satisfy Demorgans law, so they complement each other perfectly. These operators are investigated via three viewpoints: Mathematics, Geometry and fuzzy logic.
Extended Active Learning Method
Jan 17, 2011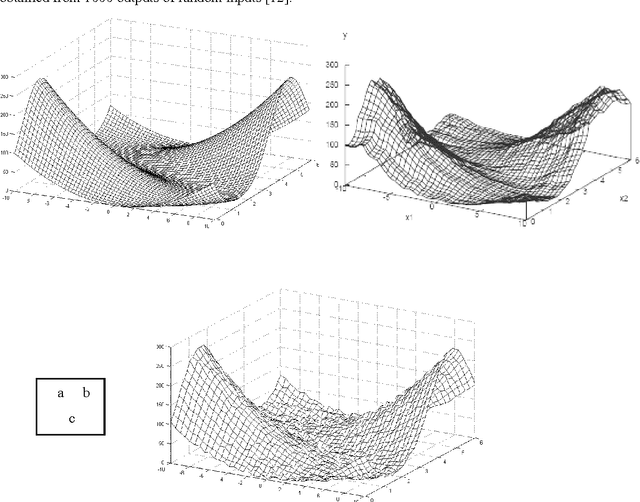

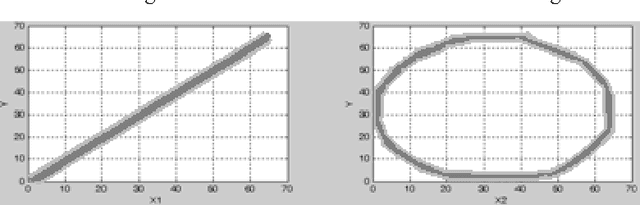
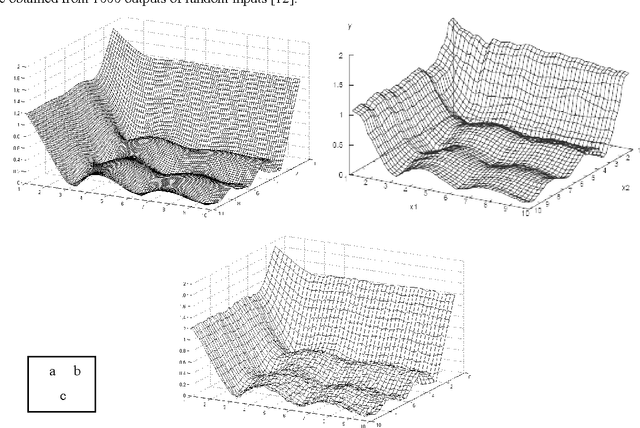
Abstract:Active Learning Method (ALM) is a soft computing method which is used for modeling and control, based on fuzzy logic. Although ALM has shown that it acts well in dynamic environments, its operators cannot support it very well in complex situations due to losing data. Thus ALM can find better membership functions if more appropriate operators be chosen for it. This paper substituted two new operators instead of ALM original ones; which consequently renewed finding membership functions in a way superior to conventional ALM. This new method is called Extended Active Learning Method (EALM).
A New Sufficient Condition for 1-Coverage to Imply Connectivity
Nov 07, 2010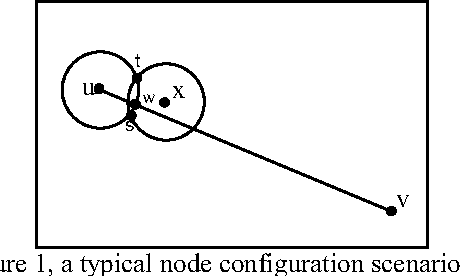
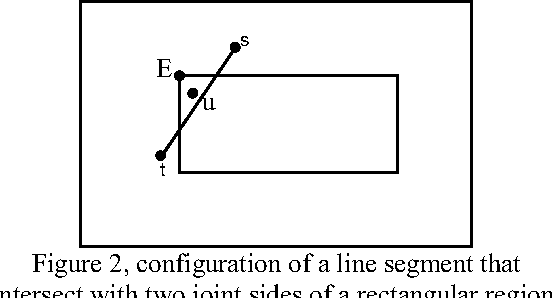
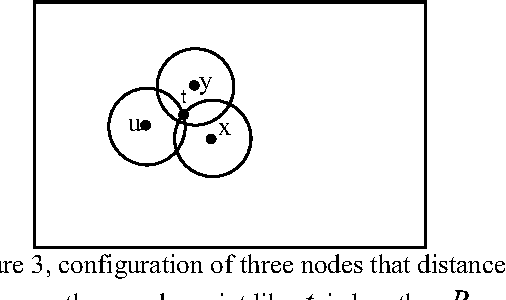
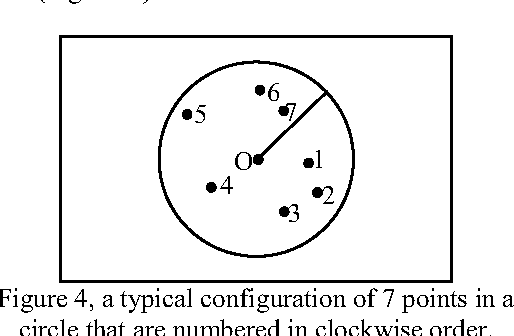
Abstract:An effective approach for energy conservation in wireless sensor networks is scheduling sleep intervals for extraneous nodes while the remaining nodes stay active to provide continuous service. For the sensor network to operate successfully the active nodes must maintain both sensing coverage and network connectivity, It proved before if the communication range of nodes is at least twice the sensing range, complete coverage of a convex area implies connectivity among the working set of nodes. In this paper we consider a rectangular region A = a *b, such that R a R b s s {\pounds}, {\pounds}, where s R is the sensing range of nodes. and put a constraint on minimum allowed distance between nodes(s). according to this constraint we present a new lower bound for communication range relative to sensing range of sensors(s 2 + 3 *R) that complete coverage of considered area implies connectivity among the working set of nodes; also we present a new distribution method, that satisfy our constraint.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge