Serhad Sarica
Innovation Slowdown: Decelerating Concept Creation and Declining Originality in New Technological Concepts
Mar 23, 2023Abstract:The creation of new technological concepts through design reuses, recombination, and synthesis of prior concepts to create new ones may lead to exponential growth of the concept space over time. However, our statistical analysis of a large-scale technology semantic network consisting of over four million concepts from patent texts found evidence of a persistent deceleration in the pace of concept creation and a decline in the originality of newly created concepts. These trends may be attributed to the limitations of human intelligence in innovating beyond an expanding space of prior art. To sustain innovation, we recommend the development and implementation of creative artificial intelligence that can augment various aspects of the innovation process, including learning, creation, and evaluation.
Guiding Data-Driven Design Ideation by Knowledge Distance
Oct 18, 2022



Abstract:Data-driven conceptual design methods and tools aim to inspire human ideation for new design concepts by providing external inspirational stimuli. In prior studies, the stimuli have been limited in terms of coverage, granularity, and retrieval guidance. Here, we present a knowledge based expert system that provides design stimuli across the semantic, document and field levels simultaneously from all fields of engineering and technology and that follows creativity theories to guide the retrieval and use of stimuli according to the knowledge distance. The system is centered on the use of a network of all technology fields in the patent classification system, to store and organize the world's cumulative data on the technological knowledge, concepts, and solutions in the total patent database according to statistically estimated knowledge distance between technology fields. In turn, knowledge distance guides the network-based exploration and retrieval of inspirational stimuli for inferences across near and far fields to generate new design ideas by analogy and combination. With two case studies, we showcase the effectiveness of using the system to explore and retrieve multilevel inspirational stimuli and generate new design ideas for both problem solving and open ended innovation. These case studies also demonstrate the computer aided ideation process, which is data-driven, computationally augmented, theoretically grounded, visually inspiring, and rapid.
Patent Data for Engineering Design: A Review
Nov 15, 2021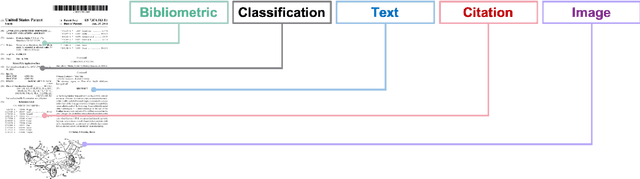
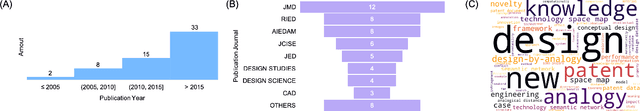
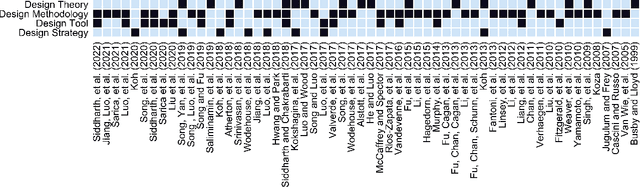
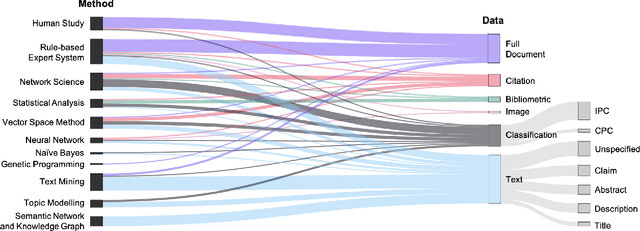
Abstract:Patent data have been utilized for engineering design research for long because it contains massive amount of design information. Recent advances in artificial intelligence and data science present unprecedented opportunities to mine, analyse and make sense of patent data to develop design theory and methodology. Herein, we survey the patent-for-design literature by their contributions to design theories, methods, tools, and strategies, as well as different forms of patent data and various methods. Our review sheds light on promising future research directions for the field.
Design Knowledge Representation with Technology Semantic Network
Dec 31, 2020



Abstract:Engineers often need to discover and learn designs from unfamiliar domains for inspiration or other particular uses. However, the complexity of the technical design descriptions and the unfamiliarity to the domain make it hard for engineers to comprehend the function, behavior, and structure of a design. To help engineers quickly understand a complex technical design description new to them, one approach is to represent it as a network graph of the design-related entities and their relations as an abstract summary of the design. While graph or network visualizations are widely adopted in the engineering design literature, the challenge remains in retrieving the design entities and deriving their relations. In this paper, we propose a network mapping method that is powered by Technology Semantic Network (TechNet). Through a case study, we showcase how TechNet's unique characteristic of being trained on a large technology-related data source advantages itself over common-sense knowledge bases, such as WordNet and ConceptNet, for design knowledge representation.
Stopwords in Technical Language Processing
Jun 04, 2020

Abstract:There are increasingly applications of natural language processing techniques for information retrieval, indexing and topic modelling in the engineering contexts. A standard component of such tasks is the removal of stopwords, which are uninformative components of the data. While researchers use readily available stopword lists which are derived for general English language, the technical jargon of engineering fields contains their own highly frequent and uninformative words and there exists no standard stopword list for technical language processing applications. Here we address this gap by rigorously identifying generic, insignificant, uninformative stopwords in engineering texts beyond the stopwords in general texts, based on the synthesis of alternative data-driven approaches, and curating a stopword list ready for technical language processing applications.
Technology Knowledge Graph Based on Patent Data
Jun 04, 2019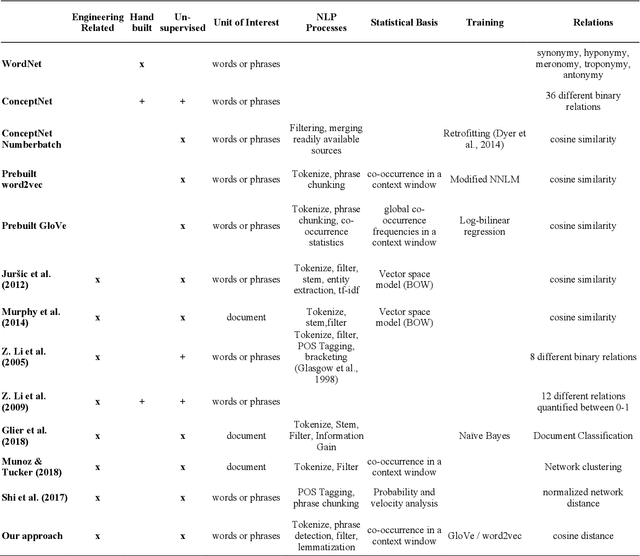
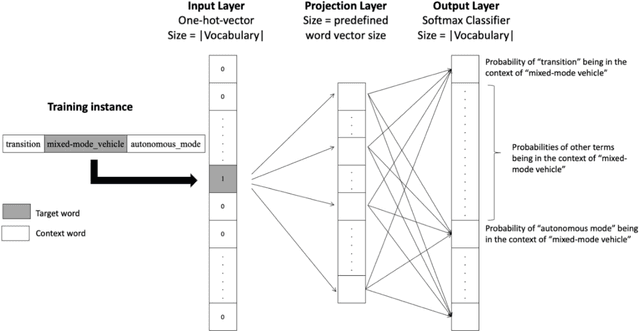
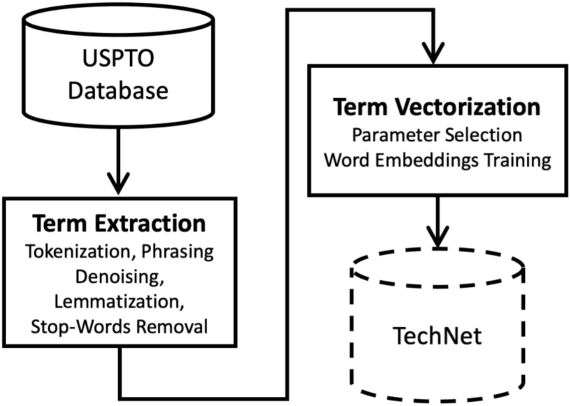
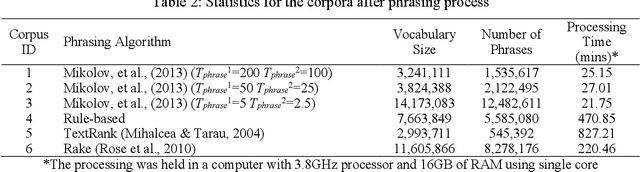
Abstract:The growing developments in general semantic networks (or knowledge graphs) have motivated us to build a large-scale comprehensive knowledge graph of engineering data for engineering knowledge discovery, technology search and retrieval, and artificial intelligence for engineering design and innovation. Specially, we constructed a technology knowledge graph (TKG) that covers the elemental concepts in all domains of technology and their semantic associations by mining the complete U.S. patent database from 1976. This paper presents natural language processing techniques to extract terms from massive patent texts and word embedding models to vectorize such terms and establish their semantic relationships. We report and evaluate the TKG technology knowledge graph for retrieving terms, semantic similarity and analogy. The TKG may serve as an infrastructure to support a wide range of applications, e.g., technical text summaries, search query predictions, relational knowledge discovery, and design ideation support, in the context of engineering and technology. To support such applications, we made the TKG public via an online interface for public users to retrieve technology-related terms and their relevancies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge