Seongyeop Kim
Visual Comfort Aware-Reinforcement Learning for Depth Adjustment of Stereoscopic 3D Images
Apr 14, 2021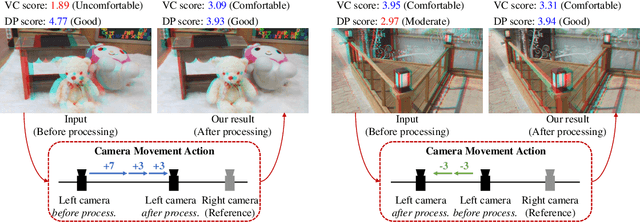
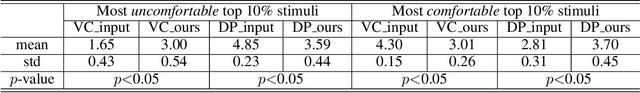
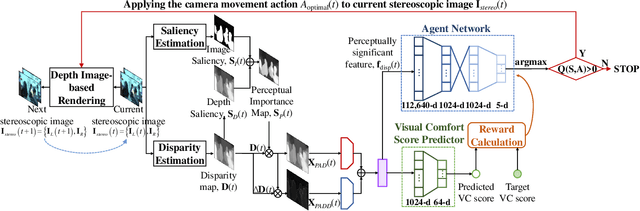
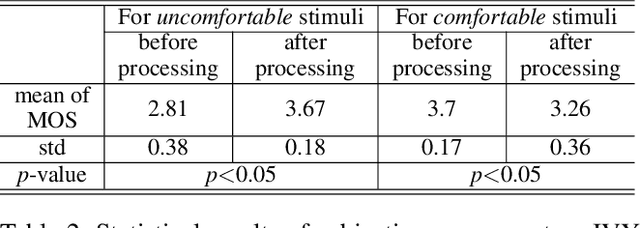
Abstract:Depth adjustment aims to enhance the visual experience of stereoscopic 3D (S3D) images, which accompanied with improving visual comfort and depth perception. For a human expert, the depth adjustment procedure is a sequence of iterative decision making. The human expert iteratively adjusts the depth until he is satisfied with the both levels of visual comfort and the perceived depth. In this work, we present a novel deep reinforcement learning (DRL)-based approach for depth adjustment named VCA-RL (Visual Comfort Aware Reinforcement Learning) to explicitly model human sequential decision making in depth editing operations. We formulate the depth adjustment process as a Markov decision process where actions are defined as camera movement operations to control the distance between the left and right cameras. Our agent is trained based on the guidance of an objective visual comfort assessment metric to learn the optimal sequence of camera movement actions in terms of perceptual aspects in stereoscopic viewing. With extensive experiments and user studies, we show the effectiveness of our VCA-RL model on three different S3D databases.
Towards a Better Understanding of VR Sickness: Physical Symptom Prediction for VR Contents
Apr 14, 2021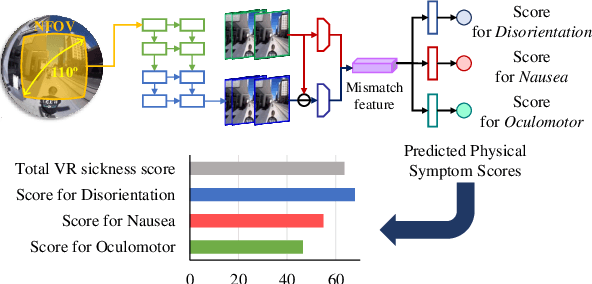
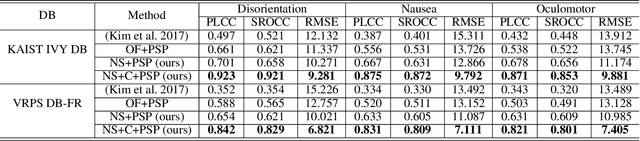
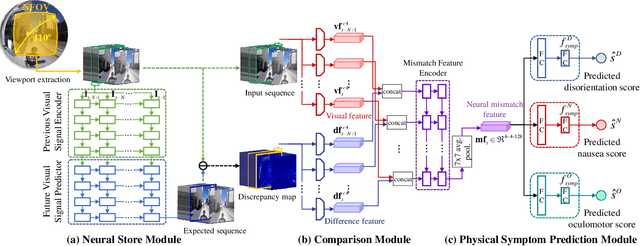
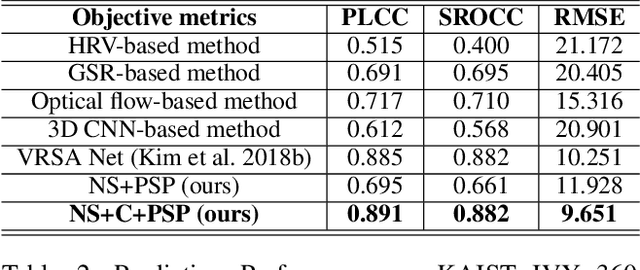
Abstract:We address the black-box issue of VR sickness assessment (VRSA) by evaluating the level of physical symptoms of VR sickness. For the VR contents inducing the similar VR sickness level, the physical symptoms can vary depending on the characteristics of the contents. Most of existing VRSA methods focused on assessing the overall VR sickness score. To make better understanding of VR sickness, it is required to predict and provide the level of major symptoms of VR sickness rather than overall degree of VR sickness. In this paper, we predict the degrees of main physical symptoms affecting the overall degree of VR sickness, which are disorientation, nausea, and oculomotor. In addition, we introduce a new large-scale dataset for VRSA including 360 videos with various frame rates, physiological signals, and subjective scores. On VRSA benchmark and our newly collected dataset, our approach shows a potential to not only achieve the highest correlation with subjective scores, but also to better understand which symptoms are the main causes of VR sickness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge