Sean Mason
An MPC Walking Framework With External Contact Forces
Feb 27, 2018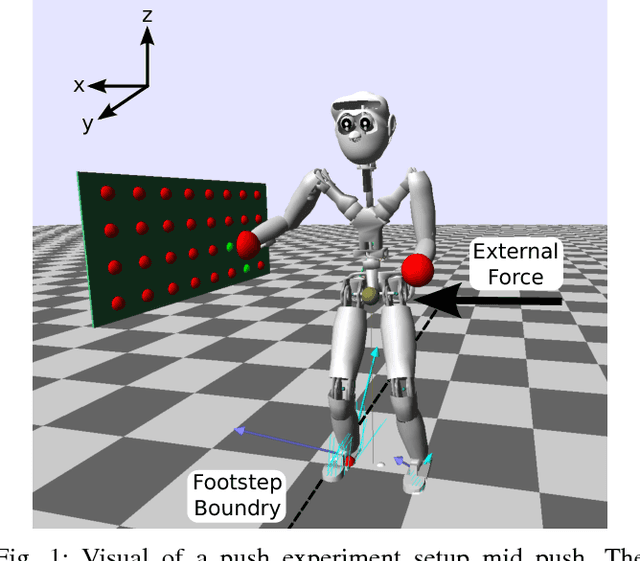
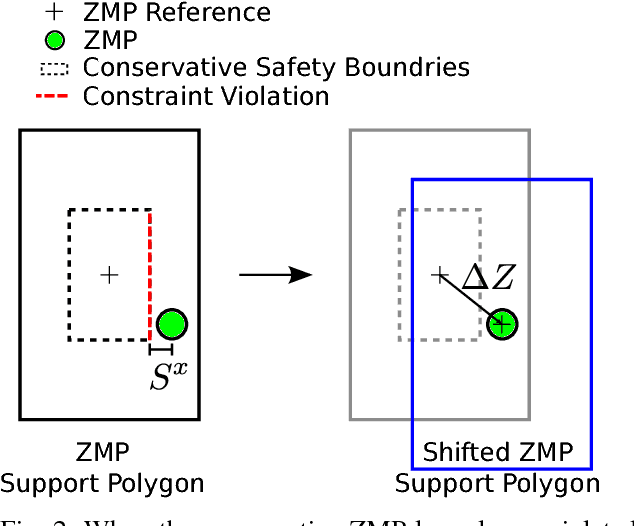
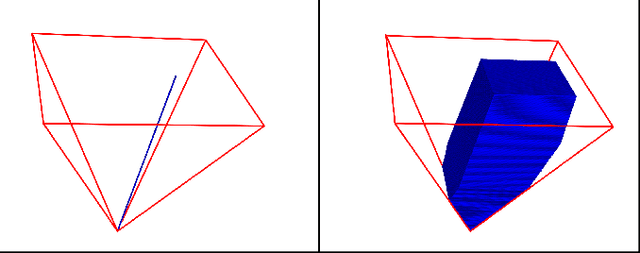
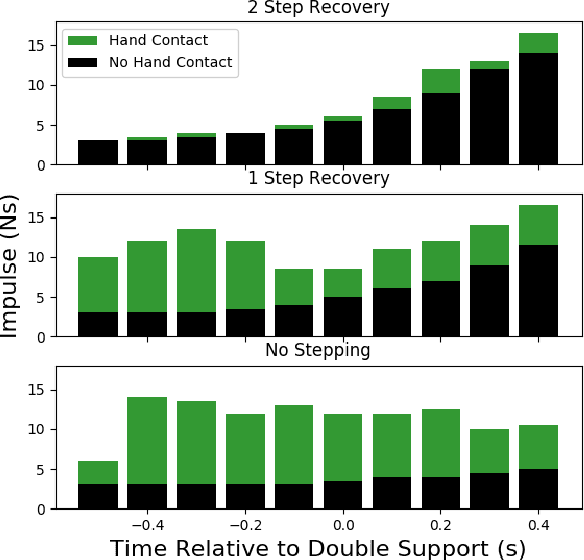
Abstract:In this work, we present an extension to a linear Model Predictive Control (MPC) scheme that plans external contact forces for the robot when given multiple contact locations and their corresponding friction cone. To this end, we set up a two-step optimization problem. In the first optimization, we compute the Center of Mass (CoM) trajectory, foot step locations, and introduce slack variables to account for violating the imposed constraints on the Zero Moment Point (ZMP). We then use the slack variables to trigger the second optimization, in which we calculate the optimal external force that compensates for the ZMP tracking error. This optimization considers multiple contacts positions within the environment by formulating the problem as a Mixed Integer Quadratic Program (MIQP) that can be solved at a speed between 100-300 Hz. Once contact is created, the MIQP reduces to a single Quadratic Program (QP) that can be solved in real-time ($<$ 1kHz). Simulations show that the presented walking control scheme can withstand disturbances 2-3x larger with the additional force provided by a hand contact.
Balancing and Walking Using Full Dynamics LQR Control With Contact Constraints
Jan 27, 2017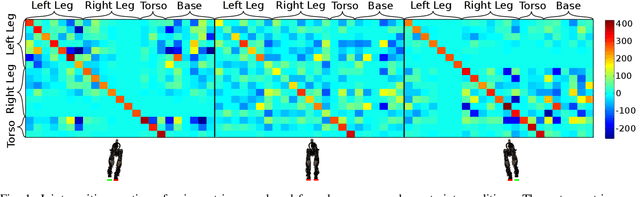
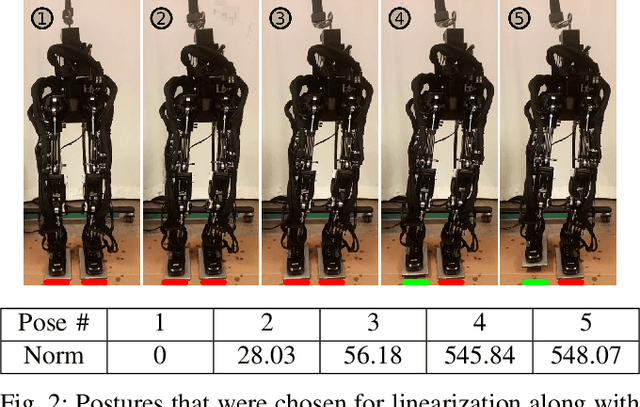
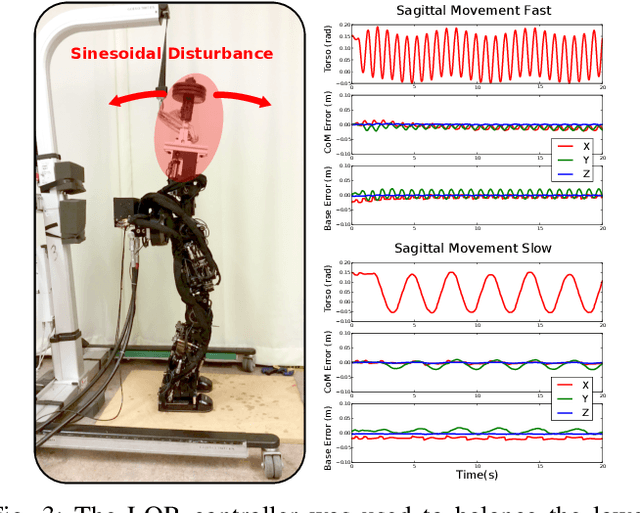
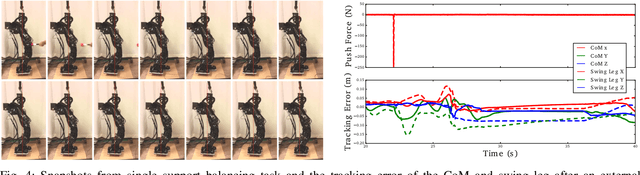
Abstract:Torque control algorithms which consider robot dynamics and contact constraints are important for creating dynamic behaviors for humanoids. As computational power increases, algorithms tend to also increase in complexity. However, it is not clear how much complexity is really required to create controllers which exhibit good performance. In this paper, we study the capabilities of a simple approach based on contact consistent LQR controllers designed around key poses to control various tasks on a humanoid robot. We present extensive experimental results on a hydraulic, torque controlled humanoid performing balancing and stepping tasks. This feedback control approach captures the necessary synergies between the DoFs of the robot to guarantee good control performance. We show that for the considered tasks, it is only necessary to re-linearize the dynamics of the robot at different contact configurations and that increasing the number of LQR controllers along desired trajectories does not improve performance. Our result suggest that very simple controllers can yield good performance competitive with current state of the art, but more complex, optimization-based whole-body controllers. A video of the experiments can be found at https://youtu.be/5T08CNKV1hw.
Inertial Sensor-Based Humanoid Joint State Estimation
Feb 16, 2016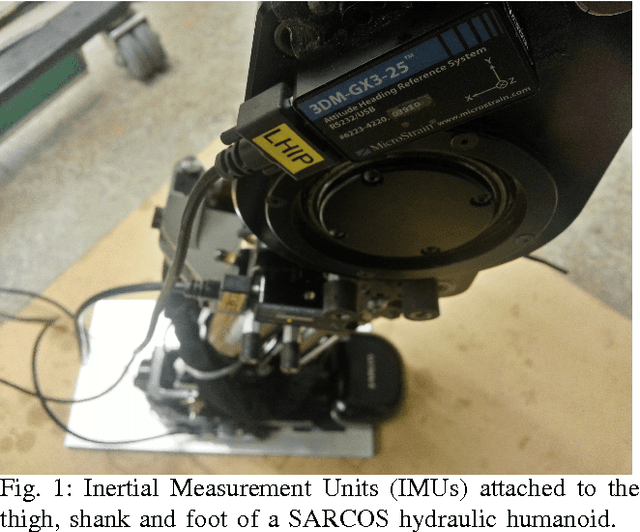
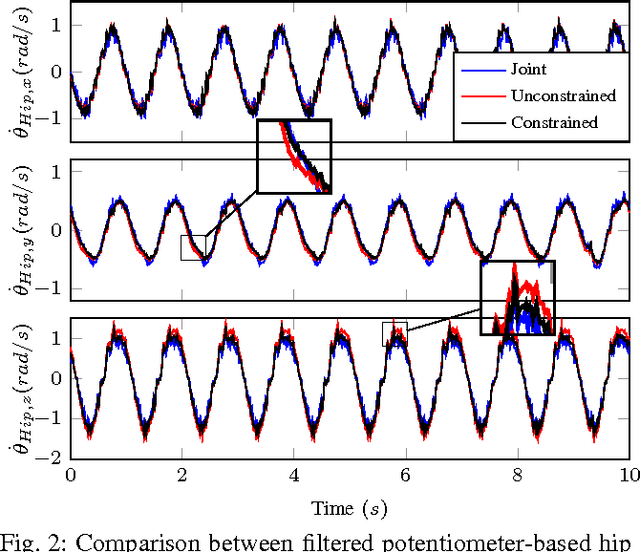
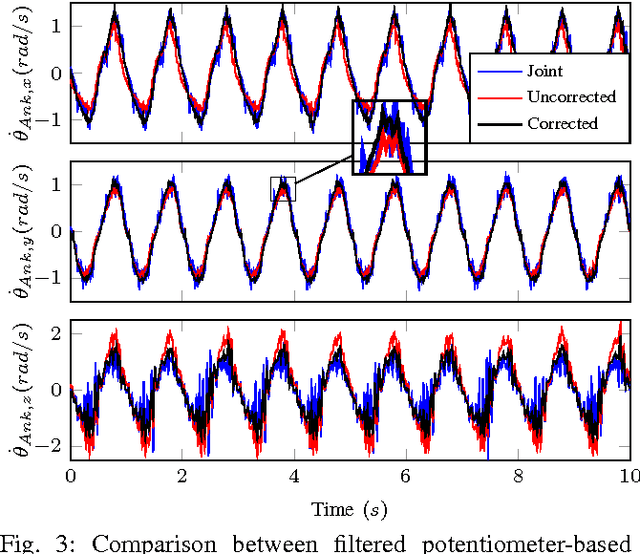
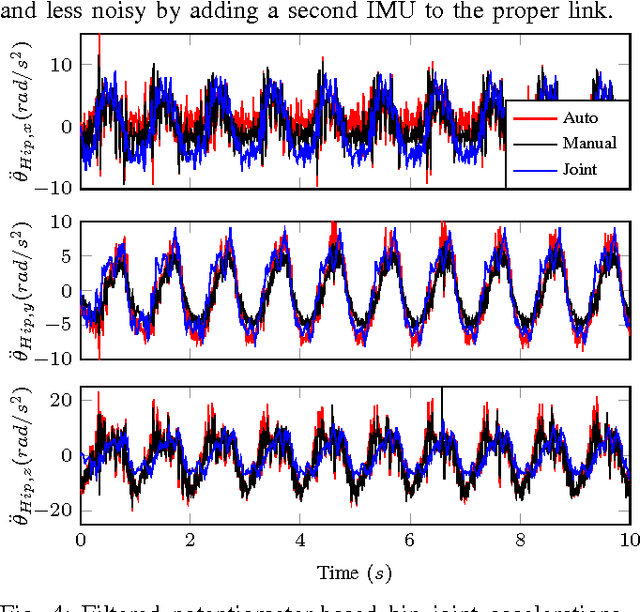
Abstract:This work presents methods for the determination of a humanoid robot's joint velocities and accelerations directly from link-mounted Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) each containing a three-axis gyroscope and a three-axis accelerometer. No information about the global pose of the floating base or its links is required and precise knowledge of the link IMU poses is not necessary due to presented calibration routines. Additionally, a filter is introduced to fuse gyroscope angular velocities with joint position measurements and compensate the computed joint velocities for time-varying gyroscope biases. The resulting joint velocities are subject to less noise and delay than filtered velocities computed from numerical differentiation of joint potentiometer signals, leading to superior performance in joint feedback control as demonstrated in experiments performed on a SARCOS hydraulic humanoid.
Momentum Control with Hierarchical Inverse Dynamics on a Torque-Controlled Humanoid
Aug 07, 2015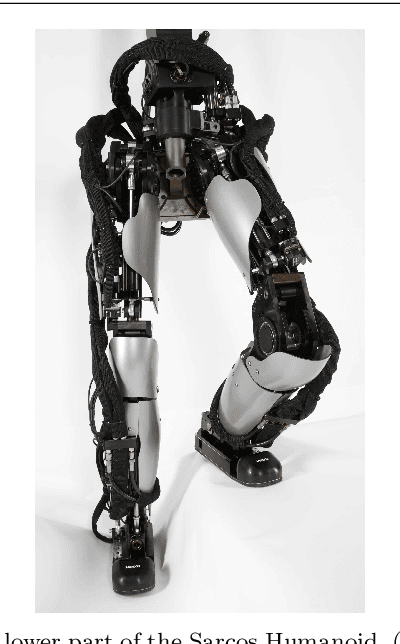

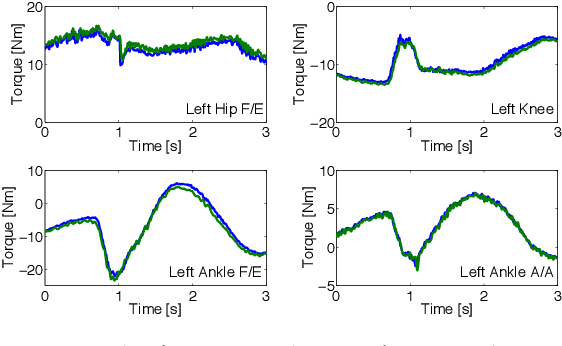
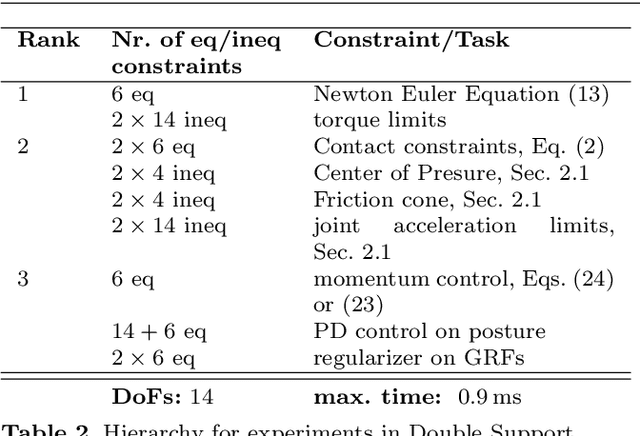
Abstract:Hierarchical inverse dynamics based on cascades of quadratic programs have been proposed for the control of legged robots. They have important benefits but to the best of our knowledge have never been implemented on a torque controlled humanoid where model inaccuracies, sensor noise and real-time computation requirements can be problematic. Using a reformulation of existing algorithms, we propose a simplification of the problem that allows to achieve real-time control. Momentum-based control is integrated in the task hierarchy and a LQR design approach is used to compute the desired associated closed-loop behavior and improve performance. Extensive experiments on various balancing and tracking tasks show very robust performance in the face of unknown disturbances, even when the humanoid is standing on one foot. Our results demonstrate that hierarchical inverse dynamics together with momentum control can be efficiently used for feedback control under real robot conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge