Scott Grigsby
Adding Multimodal Capabilities to a Text-only Translation Model
Mar 05, 2024Abstract:While most current work in multimodal machine translation (MMT) uses the Multi30k dataset for training and evaluation, we find that the resulting models overfit to the Multi30k dataset to an extreme degree. Consequently, these models perform very badly when evaluated against typical text-only testing sets such as the WMT newstest datasets. In order to perform well on both Multi30k and typical text-only datasets, we use a performant text-only machine translation (MT) model as the starting point of our MMT model. We add vision-text adapter layers connected via gating mechanisms to the MT model, and incrementally transform the MT model into an MMT model by 1) pre-training using vision-based masking of the source text and 2) fine-tuning on Multi30k.
Detecting Concrete Visual Tokens for Multimodal Machine Translation
Mar 05, 2024

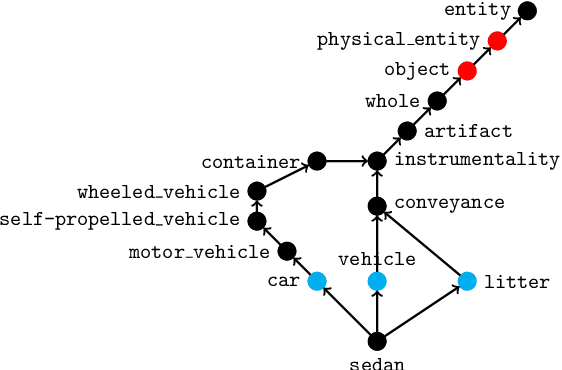

Abstract:The challenge of visual grounding and masking in multimodal machine translation (MMT) systems has encouraged varying approaches to the detection and selection of visually-grounded text tokens for masking. We introduce new methods for detection of visually and contextually relevant (concrete) tokens from source sentences, including detection with natural language processing (NLP), detection with object detection, and a joint detection-verification technique. We also introduce new methods for selection of detected tokens, including shortest $n$ tokens, longest $n$ tokens, and all detected concrete tokens. We utilize the GRAM MMT architecture to train models against synthetically collated multimodal datasets of source images with masked sentences, showing performance improvements and improved usage of visual context during translation tasks over the baseline model.
The Case for Evaluating Multimodal Translation Models on Text Datasets
Mar 05, 2024
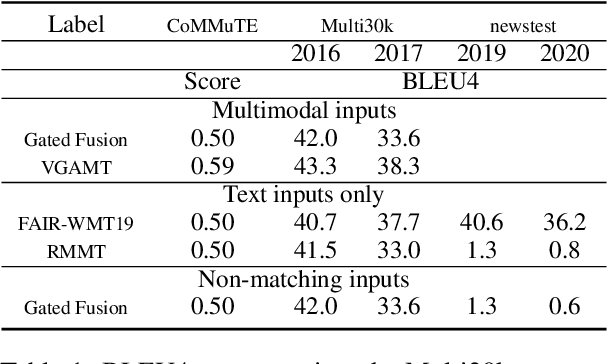
Abstract:A good evaluation framework should evaluate multimodal machine translation (MMT) models by measuring 1) their use of visual information to aid in the translation task and 2) their ability to translate complex sentences such as done for text-only machine translation. However, most current work in MMT is evaluated against the Multi30k testing sets, which do not measure these properties. Namely, the use of visual information by the MMT model cannot be shown directly from the Multi30k test set results and the sentences in Multi30k are are image captions, i.e., short, descriptive sentences, as opposed to complex sentences that typical text-only machine translation models are evaluated against. Therefore, we propose that MMT models be evaluated using 1) the CoMMuTE evaluation framework, which measures the use of visual information by MMT models, 2) the text-only WMT news translation task test sets, which evaluates translation performance against complex sentences, and 3) the Multi30k test sets, for measuring MMT model performance against a real MMT dataset. Finally, we evaluate recent MMT models trained solely against the Multi30k dataset against our proposed evaluation framework and demonstrate the dramatic drop performance against text-only testing sets compared to recent text-only MT models.
Semantic Novelty Detection and Characterization in Factual Text Involving Named Entities
Oct 31, 2022

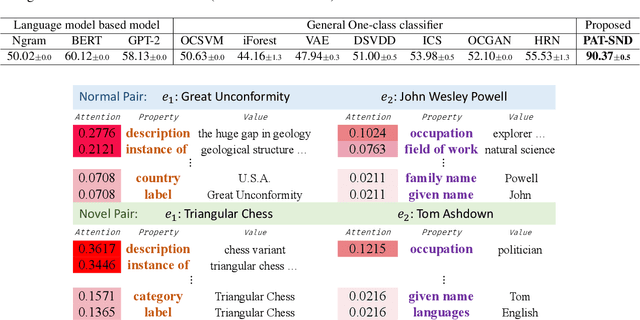
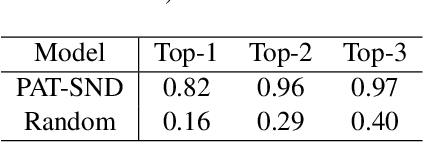
Abstract:Much of the existing work on text novelty detection has been studied at the topic level, i.e., identifying whether the topic of a document or a sentence is novel or not. Little work has been done at the fine-grained semantic level (or contextual level). For example, given that we know Elon Musk is the CEO of a technology company, the sentence "Elon Musk acted in the sitcom The Big Bang Theory" is novel and surprising because normally a CEO would not be an actor. Existing topic-based novelty detection methods work poorly on this problem because they do not perform semantic reasoning involving relations between named entities in the text and their background knowledge. This paper proposes an effective model (called PAT-SND) to solve the problem, which can also characterize the novelty. An annotated dataset is also created. Evaluation shows that PAT-SND outperforms 10 baselines by large margins.
AI Autonomy: Self-Initiation, Adaptation and Continual Learning
Mar 19, 2022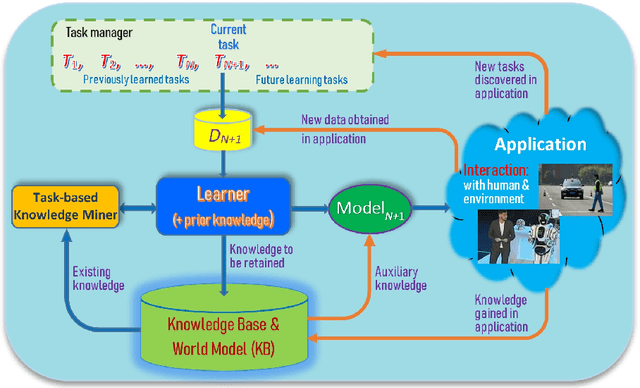
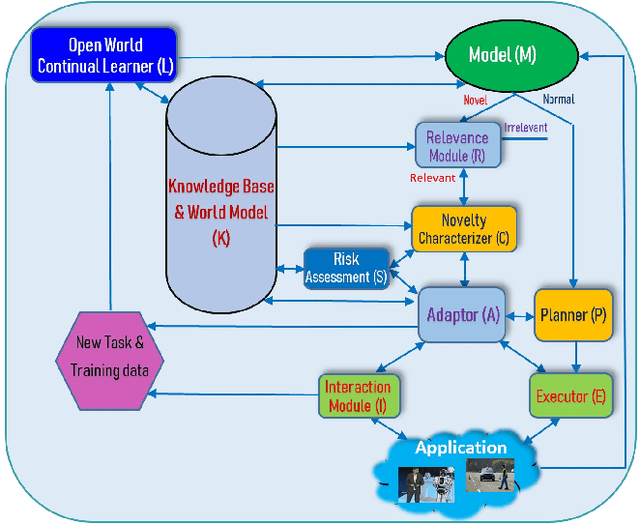
Abstract:As more and more AI agents are used in practice, it is time to think about how to make these agents fully autonomous so that they can (1) learn by themselves continually in a self-motivated and self-initiated manner rather than being retrained offline periodically on the initiation of human engineers and (2) accommodate or adapt to unexpected or novel circumstances. As the real-world is an open environment that is full of unknowns or novelties, detecting novelties, characterizing them, accommodating or adapting to them, and gathering ground-truth training data and incrementally learning the unknowns/novelties are critical to making the AI agent more and more knowledgeable and powerful over time. The key challenge is how to automate the process so that it is carried out continually on the agent's own initiative and through its own interactions with humans, other agents and the environment just like human on-the-job learning. This paper proposes a framework (called SOLA) for this learning paradigm to promote the research of building autonomous and continual learning enabled AI agents. To show feasibility, an implemented agent is also described.
Self-Initiated Open World Learning for Autonomous AI Agents
Oct 21, 2021Abstract:As more and more AI agents are used in practice, it is time to think about how to make these agents fully autonomous so that they can learn by themselves in a self-motivated and self-supervised manner rather than being retrained periodically on the initiation of human engineers using expanded training data. As the real-world is an open environment with unknowns or novelties, detecting novelties or unknowns, gathering ground-truth training data, and incrementally learning the unknowns make the agent more and more knowledgeable and powerful over time. The key challenge is how to automate the process so that it is carried out on the agent's own initiative and through its own interactions with humans and the environment. Since an AI agent usually has a performance task, characterizing each novelty becomes necessary so that the agent can formulate an appropriate response to adapt its behavior to cope with the novelty and to learn from it to improve its future responses and task performance. This paper proposes a theoretic framework for this learning paradigm to promote the research of building self-initiated open world learning agents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge