Sang-Hyun Park
Near-Field Challenges in Ultra-Wideband ISAC: Beamforming Strategies and System Insights
Aug 26, 2025



Abstract:The shift toward sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks places integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) at the core of future applications such as autonomous driving, extended reality, and smart manufacturing. However, the combination of large antenna arrays and ultra-wide bandwidths brings near-field propagation effects and beam squint to the forefront, fundamentally challenging traditional far-field designs. True time delay units (TTDs) offer a potential solution, but their cost and hardware complexity limit scalability. In this article, we present practical beamforming strategies for near-field ultra-wideband ISAC systems. We explore codebook designs across analog and digital domains that mitigate beam squint, ensure reliable user coverage, and enhance sensing accuracy. We further validate these approaches through large-scale system-level simulations, including 3D map-based evaluations that reflect real-world urban environments. Our results demonstrate how carefully designed beamforming can balance communication throughput with sensing performance, achieving reliable coverage and efficient resource use even under severe near-field conditions. We conclude by highlighting open challenges in hardware, algorithms, and system integration, pointing toward research directions that will shape the deployment of 6G-ready ISAC networks.
TIPO: Text to Image with Text Presampling for Prompt Optimization
Nov 12, 2024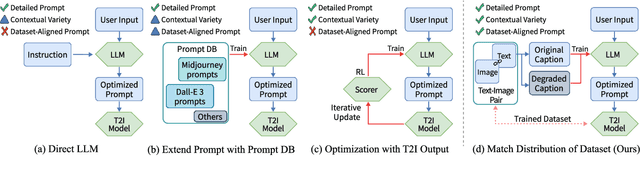
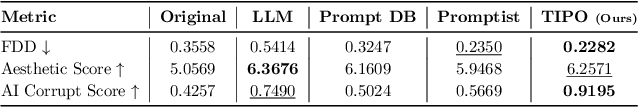
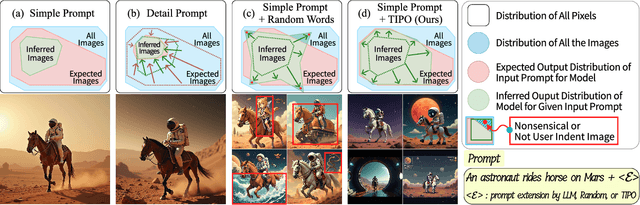
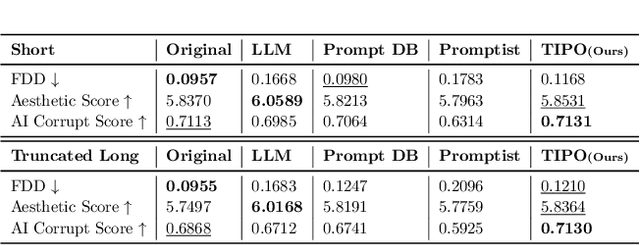
Abstract:TIPO (Text to Image with text pre-sampling for Prompt Optimization) is an innovative framework designed to enhance text-to-image (T2I) generation by language model (LM) for automatic prompt engineering. By refining and extending user-provided prompts, TIPO bridges the gap between simple inputs and the detailed prompts required for high-quality image generation. Unlike previous approaches that rely on Large Language Models (LLMs) or reinforcement learning (RL), TIPO adjusts user input prompts with the distribution of a trained prompt dataset, eliminating the need for complex runtime cost via lightweight model. This pre-sampling approach enables efficient and scalable prompt optimization, grounded in the model's training distribution. Experimental results demonstrate TIPO's effectiveness in improving aesthetic scores, reducing image corruption, and better aligning generated images with dataset distributions. These findings highlight the critical role of prompt engineering in T2I systems and open avenues for broader applications of automatic prompt refinement.
Demo: A Transparent Antenna System for In-Building Networks
May 19, 2022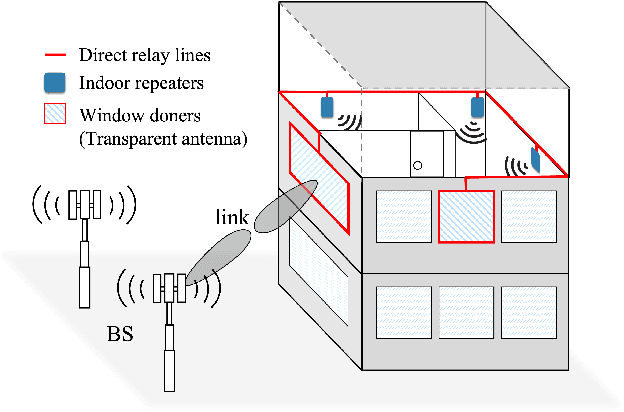
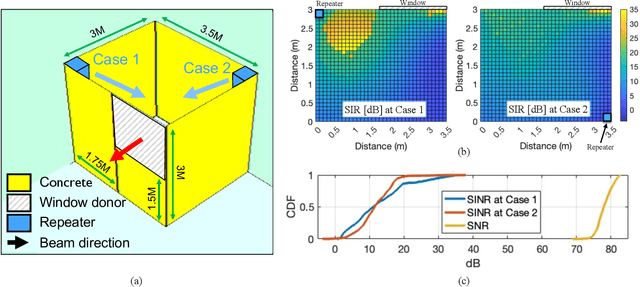
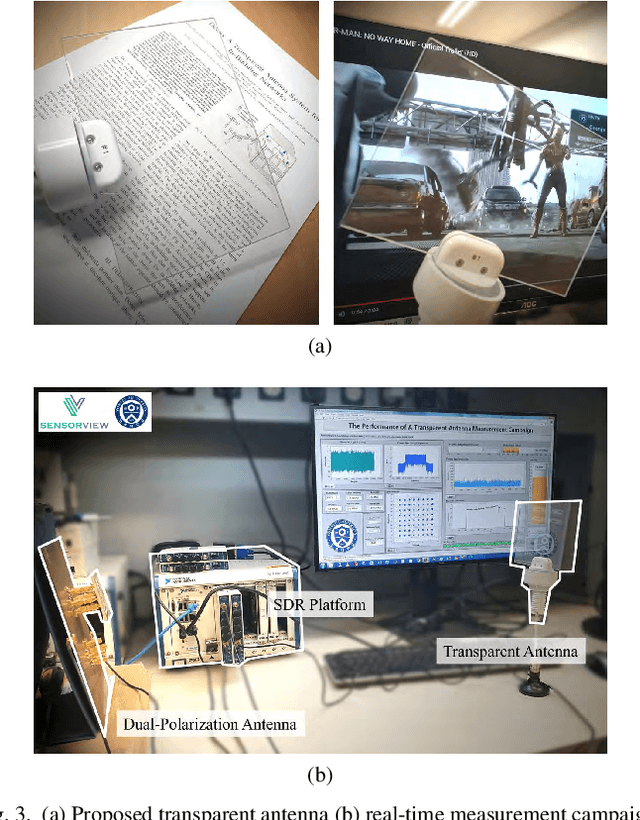
Abstract:For in-building networks, the potential of transparent antennas, which are used as windows of a building, is presented in this paper. In this scenario, a transparent window antenna communicates with outdoor devices or base stations, and the indoor repeaters act as relay stations of the transparent window antenna for indoor devices. At indoor, back lobe waves of the transparent window antenna are defined as interference to in-building networks. Hence, we analyze different SIR and SINR results according to the location of an indoor repeater through 3D ray tracing system-level simulation. Furthermore, a link-level simulation through a full-duplex software-defined radio platform with the fabricated transparent antenna is presented to examine the feasibility of the transparent antenna.
Beam Squint in Ultra-wideband mmWave Systems: RF Lens Array vs. Phase-Shifter-Based Array
Dec 08, 2021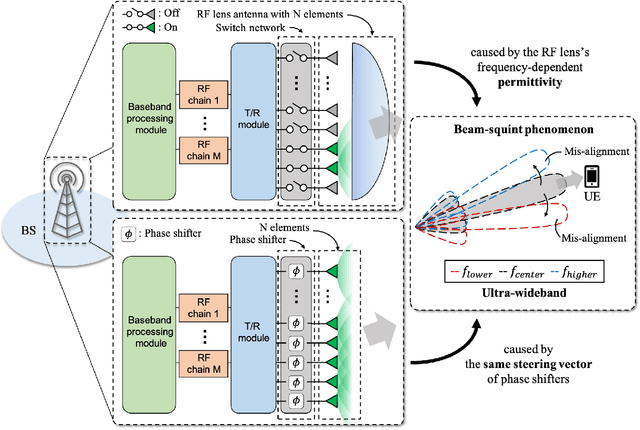
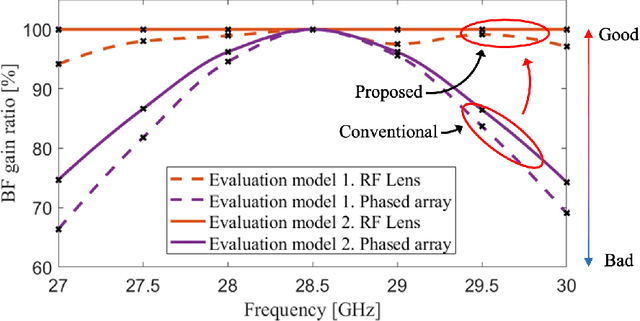
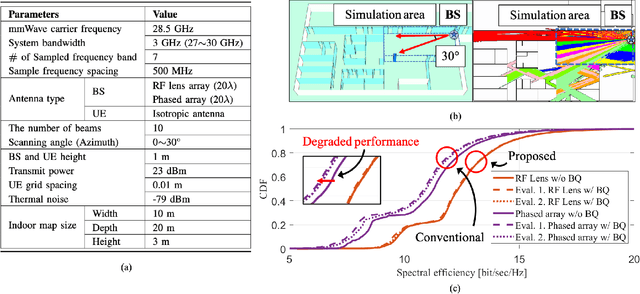
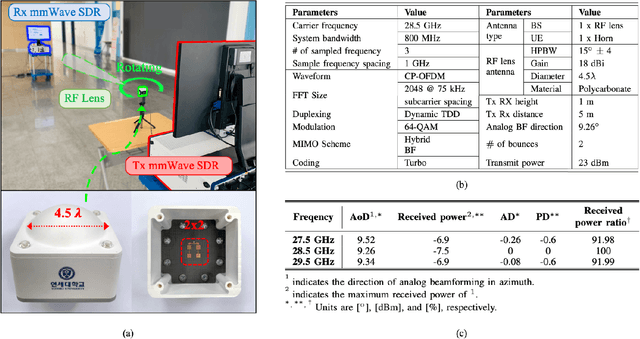
Abstract:In this article, we discuss the potential of radio frequency (RF) lens for ultra-wideband millimeter-wave (mmWave) systems. In terms of the beam squint, we compare the proposed RF lens antenna with the phase shifter-based array for hybrid beamforming. To reduce the complexities for fully digital beamforming, researchers have come up with RF lens-based hybrid beamforming. The use of mmWave systems, however, causes an increase in bandwidth, which gives rise to the beam squint phenomenon. We first find the causative factors for beam squint in the dielectric RF lens antenna. Based on the beamforming gain at each frequency, we verify that, in a specific situation, RF lens can be free of the beam squint effect. We use 3D electromagnetic analysis software to numerically interpret the beam squint of each antenna type. Based on the results, we present the degraded spectral efficiency by system-level simulations with 3D indoor ray tracing. Finally, to verify our analysis, we fabricate an actual RF lens antenna and demonstrate the real performance using a mmWave, NI PXIe, software-defined radio system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge