Samra Irshad
Adversarial Wear and Tear: Exploiting Natural Damage for Generating Physical-World Adversarial Examples
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:The presence of adversarial examples in the physical world poses significant challenges to the deployment of Deep Neural Networks in safety-critical applications such as autonomous driving. Most existing methods for crafting physical-world adversarial examples are ad-hoc, relying on temporary modifications like shadows, laser beams, or stickers that are tailored to specific scenarios. In this paper, we introduce a new class of physical-world adversarial examples, AdvWT, which draws inspiration from the naturally occurring phenomenon of `wear and tear', an inherent property of physical objects. Unlike manually crafted perturbations, `wear and tear' emerges organically over time due to environmental degradation, as seen in the gradual deterioration of outdoor signboards. To achieve this, AdvWT follows a two-step approach. First, a GAN-based, unsupervised image-to-image translation network is employed to model these naturally occurring damages, particularly in the context of outdoor signboards. The translation network encodes the characteristics of damaged signs into a latent `damage style code'. In the second step, we introduce adversarial perturbations into the style code, strategically optimizing its transformation process. This manipulation subtly alters the damage style representation, guiding the network to generate adversarial images where the appearance of damages remains perceptually realistic, while simultaneously ensuring their effectiveness in misleading neural networks. Through comprehensive experiments on two traffic sign datasets, we show that AdvWT effectively misleads DNNs in both digital and physical domains. AdvWT achieves an effective attack success rate, greater robustness, and a more natural appearance compared to existing physical-world adversarial examples. Additionally, integrating AdvWT into training enhances a model's generalizability to real-world damaged signs.
Improved Abdominal Multi-Organ Segmentation via 3D Boundary-Constrained Deep Neural Networks
Oct 09, 2022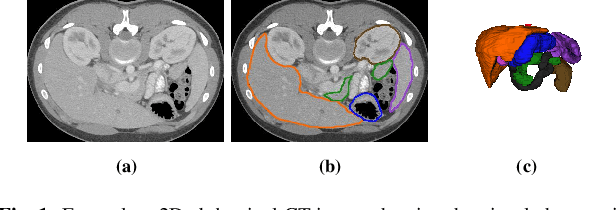
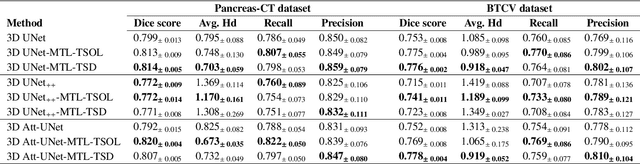
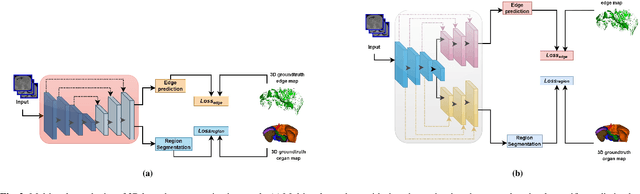
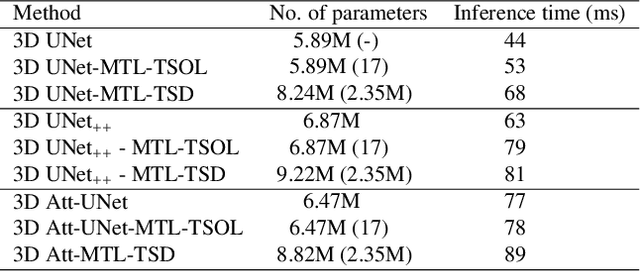
Abstract:Quantitative assessment of the abdominal region from clinically acquired CT scans requires the simultaneous segmentation of abdominal organs. Thanks to the availability of high-performance computational resources, deep learning-based methods have resulted in state-of-the-art performance for the segmentation of 3D abdominal CT scans. However, the complex characterization of organs with fuzzy boundaries prevents the deep learning methods from accurately segmenting these anatomical organs. Specifically, the voxels on the boundary of organs are more vulnerable to misprediction due to the highly-varying intensity of inter-organ boundaries. This paper investigates the possibility of improving the abdominal image segmentation performance of the existing 3D encoder-decoder networks by leveraging organ-boundary prediction as a complementary task. To address the problem of abdominal multi-organ segmentation, we train the 3D encoder-decoder network to simultaneously segment the abdominal organs and their corresponding boundaries in CT scans via multi-task learning. The network is trained end-to-end using a loss function that combines two task-specific losses, i.e., complete organ segmentation loss and boundary prediction loss. We explore two different network topologies based on the extent of weights shared between the two tasks within a unified multi-task framework. To evaluate the utilization of complementary boundary prediction task in improving the abdominal multi-organ segmentation, we use three state-of-the-art encoder-decoder networks: 3D UNet, 3D UNet++, and 3D Attention-UNet. The effectiveness of utilizing the organs' boundary information for abdominal multi-organ segmentation is evaluated on two publically available abdominal CT datasets. A maximum relative improvement of 3.5% and 3.6% is observed in Mean Dice Score for Pancreas-CT and BTCV datasets, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge