Salma Tarmoun
A Local Polyak-Lojasiewicz and Descent Lemma of Gradient Descent For Overparametrized Linear Models
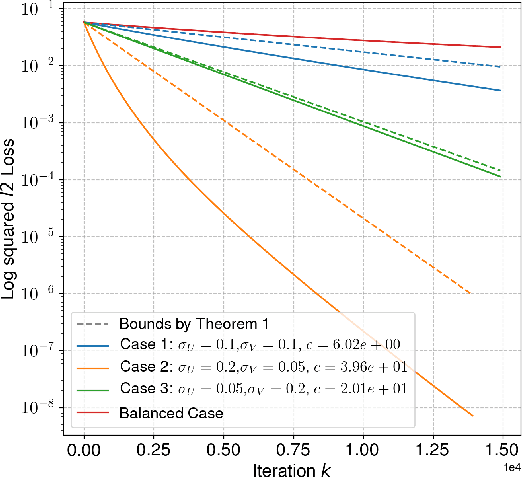
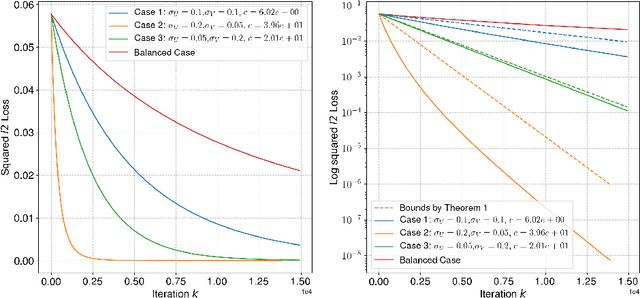
May 16, 2025Abstract:Most prior work on the convergence of gradient descent (GD) for overparameterized neural networks relies on strong assumptions on the step size (infinitesimal), the hidden-layer width (infinite), or the initialization (large, spectral, balanced). Recent efforts to relax these assumptions focus on two-layer linear networks trained with the squared loss. In this work, we derive a linear convergence rate for training two-layer linear neural networks with GD for general losses and under relaxed assumptions on the step size, width, and initialization. A key challenge in deriving this result is that classical ingredients for deriving convergence rates for nonconvex problems, such as the Polyak-{\L}ojasiewicz (PL) condition and Descent Lemma, do not hold globally for overparameterized neural networks. Here, we prove that these two conditions hold locally with local constants that depend on the weights. Then, we provide bounds on these local constants, which depend on the initialization of the weights, the current loss, and the global PL and smoothness constants of the non-overparameterized model. Based on these bounds, we derive a linear convergence rate for GD. Our convergence analysis not only improves upon prior results but also suggests a better choice for the step size, as verified through our numerical experiments.
Understanding the Learning Dynamics of LoRA: A Gradient Flow Perspective on Low-Rank Adaptation in Matrix Factorization
Mar 10, 2025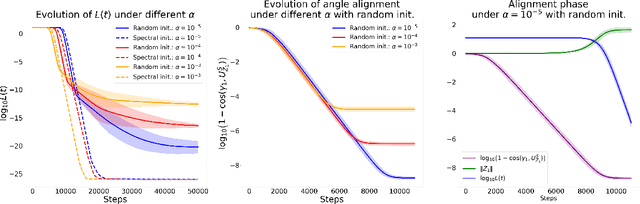
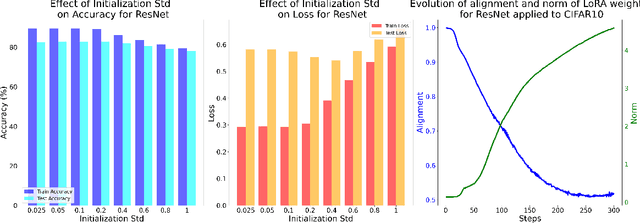
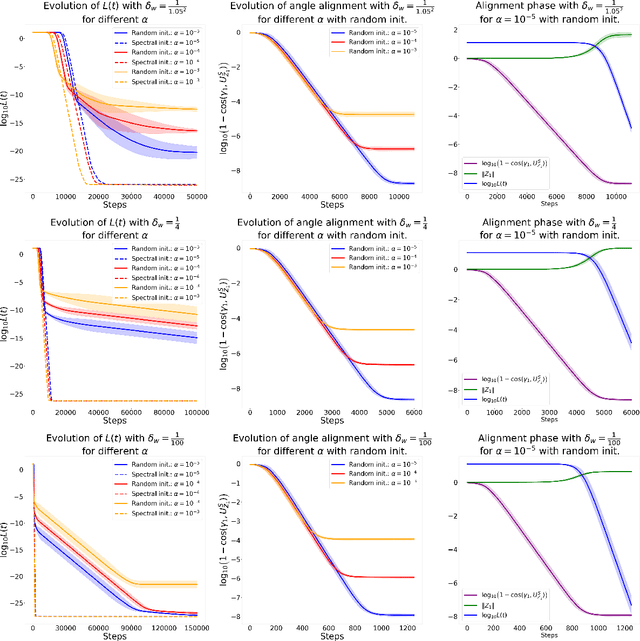
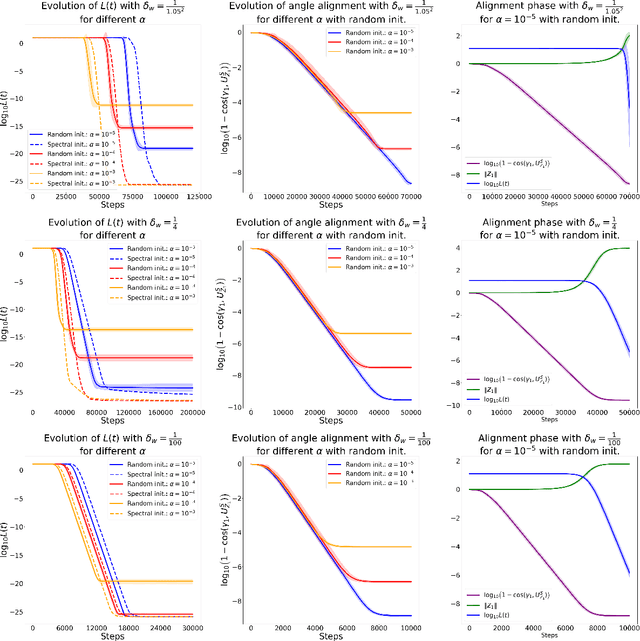
Abstract:Despite the empirical success of Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) in fine-tuning pre-trained models, there is little theoretical understanding of how first-order methods with carefully crafted initialization adapt models to new tasks. In this work, we take the first step towards bridging this gap by theoretically analyzing the learning dynamics of LoRA for matrix factorization (MF) under gradient flow (GF), emphasizing the crucial role of initialization. For small initialization, we theoretically show that GF converges to a neighborhood of the optimal solution, with smaller initialization leading to lower final error. Our analysis shows that the final error is affected by the misalignment between the singular spaces of the pre-trained model and the target matrix, and reducing the initialization scale improves alignment. To address this misalignment, we propose a spectral initialization for LoRA in MF and theoretically prove that GF with small spectral initialization converges to the fine-tuning task with arbitrary precision. Numerical experiments from MF and image classification validate our findings.
On the Explicit Role of Initialization on the Convergence and Implicit Bias of Overparametrized Linear Networks
May 13, 2021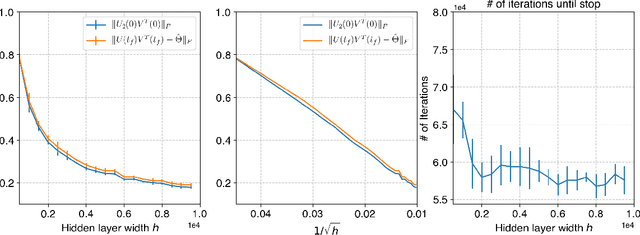
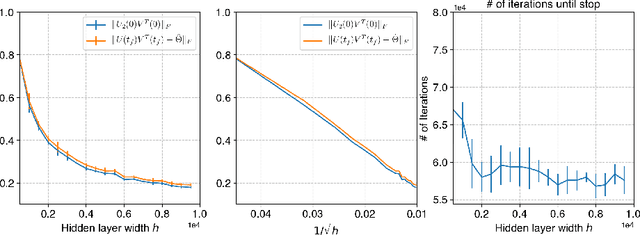
Abstract:Neural networks trained via gradient descent with random initialization and without any regularization enjoy good generalization performance in practice despite being highly overparametrized. A promising direction to explain this phenomenon is to study how initialization and overparametrization affect convergence and implicit bias of training algorithms. In this paper, we present a novel analysis of single-hidden-layer linear networks trained under gradient flow, which connects initialization, optimization, and overparametrization. Firstly, we show that the squared loss converges exponentially to its optimum at a rate that depends on the level of imbalance of the initialization. Secondly, we show that proper initialization constrains the dynamics of the network parameters to lie within an invariant set. In turn, minimizing the loss over this set leads to the min-norm solution. Finally, we show that large hidden layer width, together with (properly scaled) random initialization, ensures proximity to such an invariant set during training, allowing us to derive a novel non-asymptotic upper-bound on the distance between the trained network and the min-norm solution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge