Saikat Mondal
Why Are AI Agent Involved Pull Requests (Fix-Related) Remain Unmerged? An Empirical Study
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Autonomous coding agents (e.g., OpenAI Codex, Devin, GitHub Copilot) are increasingly used to generate fix-related pull requests (PRs) in real world software repositories. However, their practical effectiveness depends on whether these contributions are accepted and merged by project maintainers. In this paper, we present an empirical study of AI agent involved fix related PRs, examining both their integration outcomes, latency, and the factors that hinder successful merging. We first analyze 8,106 fix related PRs authored by five widely used AI coding agents from the AIDEV POP dataset to quantify the proportions of PRs that are merged, closed without merging, or remain open. We then conduct a manual qualitative analysis of a statistically significant sample of 326 closed but unmerged PRs, spending approximately 100 person hours to construct a structured catalog of 12 failure reasons. Our results indicate that test case failures and prior resolution of the same issues by other PRs are the most common causes of non integration, whereas build or deployment failures are comparatively rare. Overall, our findings expose key limitations of current AI coding agents in real world settings and highlight directions for their further improvement and for more effective human AI collaboration in software maintenance.
Human-Aligned Enhancement of Programming Answers with LLMs Guided by User Feedback
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are widely used to support software developers in tasks such as code generation, optimization, and documentation. However, their ability to improve existing programming answers in a human-like manner remains underexplored. On technical question-and-answer platforms such as Stack Overflow (SO), contributors often revise answers based on user comments that identify errors, inefficiencies, or missing explanations. Yet roughly one-third of this feedback is never addressed due to limited time, expertise, or visibility, leaving many answers incomplete or outdated. This study investigates whether LLMs can enhance programming answers by interpreting and incorporating comment-based feedback. We make four main contributions. First, we introduce ReSOlve, a benchmark consisting of 790 SO answers with associated comment threads, annotated for improvement-related and general feedback. Second, we evaluate four state-of-the-art LLMs on their ability to identify actionable concerns, finding that DeepSeek achieves the best balance between precision and recall. Third, we present AUTOCOMBAT, an LLM-powered tool that improves programming answers by jointly leveraging user comments and question context. Compared to human revised references, AUTOCOMBAT produces near-human quality improvements while preserving the original intent and significantly outperforming the baseline. Finally, a user study with 58 practitioners shows strong practical value, with 84.5 percent indicating they would adopt or recommend the tool. Overall, AUTOCOMBAT demonstrates the potential of scalable, feedback-driven answer refinement to improve the reliability and trustworthiness of technical knowledge platforms.
From Questions to Insights: Exploring XAI Challenges Reported on Stack Overflow Questions
Apr 03, 2025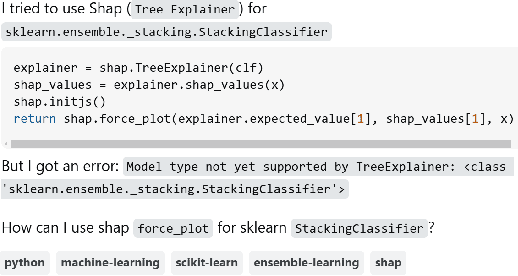

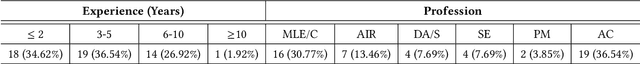
Abstract:The lack of interpretability is a major barrier that limits the practical usage of AI models. Several eXplainable AI (XAI) techniques (e.g., SHAP, LIME) have been employed to interpret these models' performance. However, users often face challenges when leveraging these techniques in real-world scenarios and thus submit questions in technical Q&A forums like Stack Overflow (SO) to resolve these challenges. We conducted an exploratory study to expose these challenges, their severity, and features that can make XAI techniques more accessible and easier to use. Our contributions to this study are fourfold. First, we manually analyzed 663 SO questions that discussed challenges related to XAI techniques. Our careful investigation produced a catalog of seven challenges (e.g., disagreement issues). We then analyzed their prevalence and found that model integration and disagreement issues emerged as the most prevalent challenges. Second, we attempt to estimate the severity of each XAI challenge by determining the correlation between challenge types and answer metadata (e.g., the presence of accepted answers). Our analysis suggests that model integration issues is the most severe challenge. Third, we attempt to perceive the severity of these challenges based on practitioners' ability to use XAI techniques effectively in their work. Practitioners' responses suggest that disagreement issues most severely affect the use of XAI techniques. Fourth, we seek agreement from practitioners on improvements or features that could make XAI techniques more accessible and user-friendly. The majority of them suggest consistency in explanations and simplified integration. Our study findings might (a) help to enhance the accessibility and usability of XAI and (b) act as the initial benchmark that can inspire future research.
Precise Stock Price Prediction for Optimized Portfolio Design Using an LSTM Model
Mar 02, 2022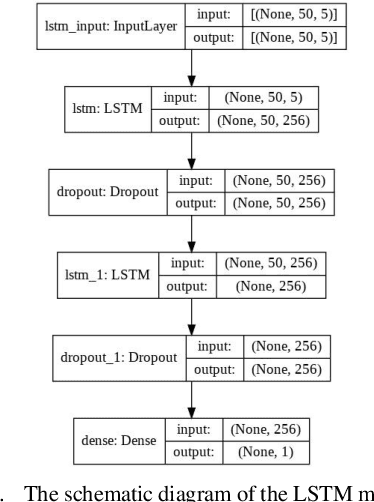
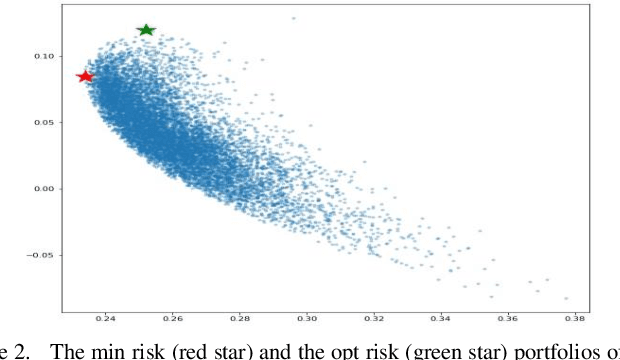
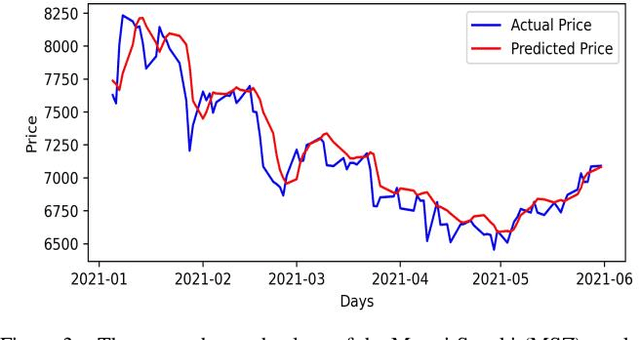
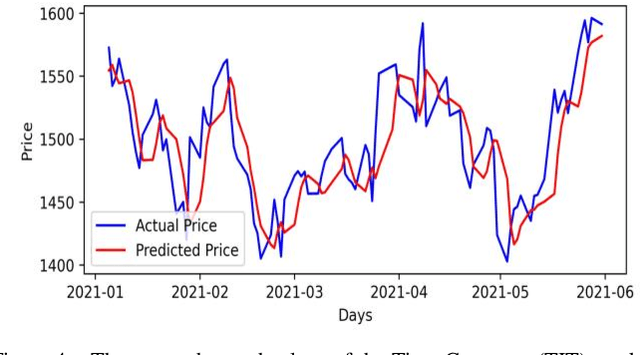
Abstract:Accurate prediction of future prices of stocks is a difficult task to perform. Even more challenging is to design an optimized portfolio of stocks with the identification of proper weights of allocation to achieve the optimized values of return and risk. We present optimized portfolios based on the seven sectors of the Indian economy. The past prices of the stocks are extracted from the web from January 1, 2016, to December 31, 2020. Optimum portfolios are designed on the selected seven sectors. An LSTM regression model is also designed for predicting future stock prices. Five months after the construction of the portfolios, i.e., on June 1, 2021, the actual and predicted returns and risks of each portfolio are computed. The predicted and the actual returns indicate the very high accuracy of the LSTM model.
Robust Portfolio Design and Stock Price Prediction Using an Optimized LSTM Model
Mar 02, 2022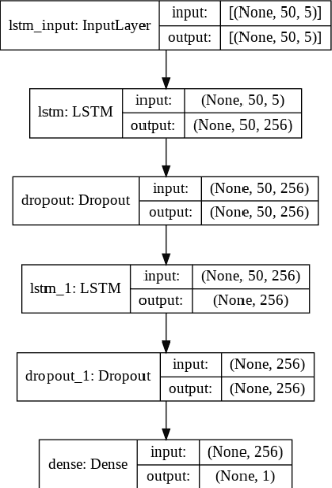
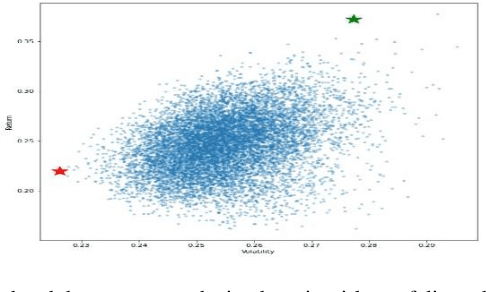

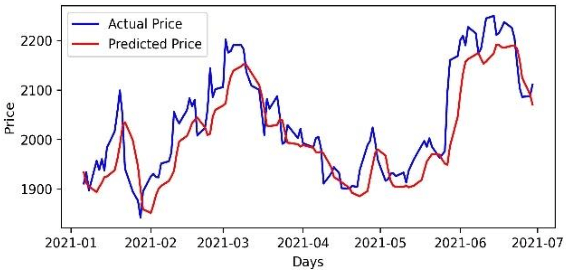
Abstract:Accurate prediction of future prices of stocks is a difficult task to perform. Even more challenging is to design an optimized portfolio with weights allocated to the stocks in a way that optimizes its return and the risk. This paper presents a systematic approach towards building two types of portfolios, optimum risk, and eigen, for four critical economic sectors of India. The prices of the stocks are extracted from the web from Jan 1, 2016, to Dec 31, 2020. Sector-wise portfolios are built based on their ten most significant stocks. An LSTM model is also designed for predicting future stock prices. Six months after the construction of the portfolios, i.e., on Jul 1, 2021, the actual returns and the LSTM-predicted returns for the portfolios are computed. A comparison of the predicted and the actual returns indicate a high accuracy level of the LSTM model.
Hierarchical Risk Parity and Minimum Variance Portfolio Design on NIFTY 50 Stocks
Feb 06, 2022

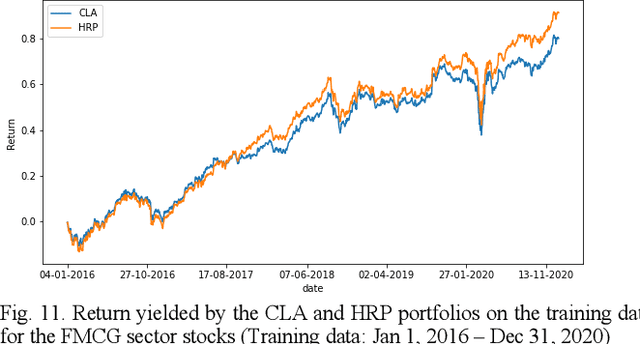
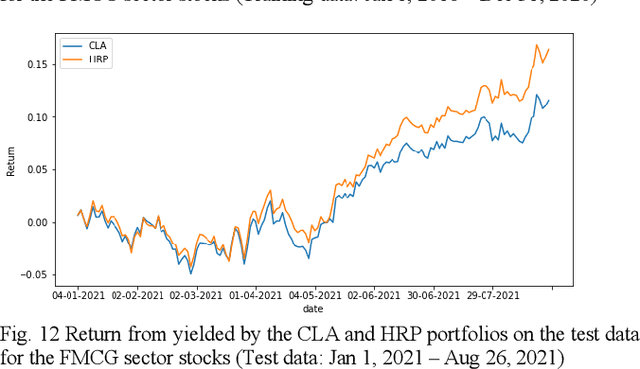
Abstract:Portfolio design and optimization have been always an area of research that has attracted a lot of attention from researchers from the finance domain. Designing an optimum portfolio is a complex task since it involves accurate forecasting of future stock returns and risks and making a suitable tradeoff between them. This paper proposes a systematic approach to designing portfolios using two algorithms, the critical line algorithm, and the hierarchical risk parity algorithm on eight sectors of the Indian stock market. While the portfolios are designed using the stock price data from Jan 1, 2016, to Dec 31, 2020, they are tested on the data from Jan 1, 2021, to Aug 26, 2021. The backtesting results of the portfolios indicate while the performance of the CLA algorithm is superior on the training data, the HRP algorithm has outperformed the CLA algorithm on the test data.
Portfolio Optimization on NIFTY Thematic Sector Stocks Using an LSTM Model
Feb 06, 2022Abstract:Portfolio optimization has been a broad and intense area of interest for quantitative and statistical finance researchers and financial analysts. It is a challenging task to design a portfolio of stocks to arrive at the optimized values of the return and risk. This paper presents an algorithmic approach for designing optimum risk and eigen portfolios for five thematic sectors of the NSE of India. The prices of the stocks are extracted from the web from Jan 1, 2016, to Dec 31, 2020. Optimum risk and eigen portfolios for each sector are designed based on ten critical stocks from the sector. An LSTM model is designed for predicting future stock prices. Seven months after the portfolios were formed, on Aug 3, 2021, the actual returns of the portfolios are compared with the LSTM-predicted returns. The predicted and the actual returns indicate a very high-level accuracy of the LSTM model.
Analysis of Sectoral Profitability of the Indian Stock Market Using an LSTM Regression Model
Nov 09, 2021



Abstract:Predictive model design for accurately predicting future stock prices has always been considered an interesting and challenging research problem. The task becomes complex due to the volatile and stochastic nature of the stock prices in the real world which is affected by numerous controllable and uncontrollable variables. This paper presents an optimized predictive model built on long-and-short-term memory (LSTM) architecture for automatically extracting past stock prices from the web over a specified time interval and predicting their future prices for a specified forecast horizon, and forecasts the future stock prices. The model is deployed for making buy and sell transactions based on its predicted results for 70 important stocks from seven different sectors listed in the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India. The profitability of each sector is derived based on the total profit yielded by the stocks in that sector over a period from Jan 1, 2010 to Aug 26, 2021. The sectors are compared based on their profitability values. The prediction accuracy of the model is also evaluated for each sector. The results indicate that the model is highly accurate in predicting future stock prices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge