Sahraoui Dhelim
A Novel Double Pruning method for Imbalanced Data using Information Entropy and Roulette Wheel Selection for Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Mar 15, 2025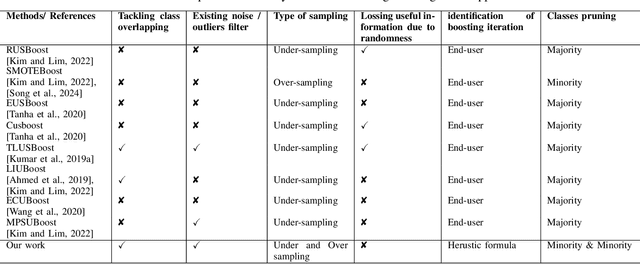
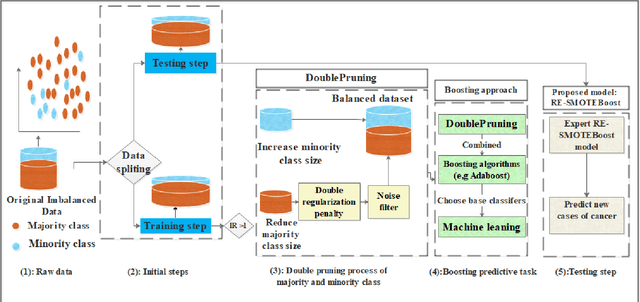
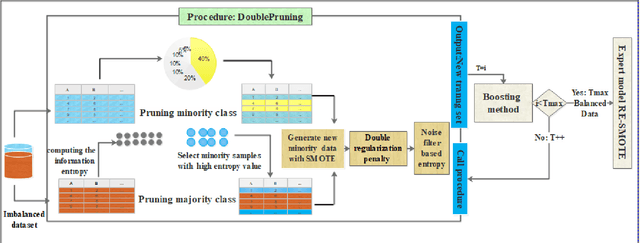
Abstract:Accurate illness diagnosis is vital for effective treatment and patient safety. Machine learning models are widely used for cancer diagnosis based on historical medical data. However, data imbalance remains a major challenge, leading to hindering classifier performance and reliability. The SMOTEBoost method addresses this issue by generating synthetic data to balance the dataset, but it may overlook crucial overlapping regions near the decision boundary and can produce noisy samples. This paper proposes RE-SMOTEBoost, an enhanced version of SMOTEBoost, designed to overcome these limitations. Firstly, RE-SMOTEBoost focuses on generating synthetic samples in overlapping regions to better capture the decision boundary using roulette wheel selection. Secondly, it incorporates a filtering mechanism based on information entropy to reduce noise, and borderline cases and improve the quality of generated data. Thirdly, we introduce a double regularization penalty to control the synthetic samples proximity to the decision boundary and avoid class overlap. These enhancements enable higher-quality oversampling of the minority class, resulting in a more balanced and effective training dataset. The proposed method outperforms existing state-of-the-art techniques when evaluated on imbalanced datasets. Compared to the top-performing sampling algorithms, RE-SMOTEBoost demonstrates a notable improvement of 3.22\% in accuracy and a variance reduction of 88.8\%. These results indicate that the proposed model offers a solid solution for medical settings, effectively overcoming data scarcity and severe imbalance caused by limited samples, data collection difficulties, and privacy constraints.
Adapting Mental Health Prediction Tasks for Cross-lingual Learning via Meta-Training and In-context Learning with Large Language Model
Apr 13, 2024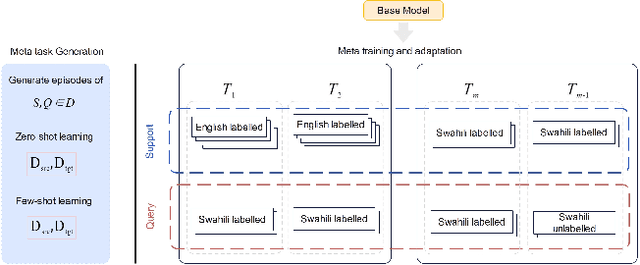
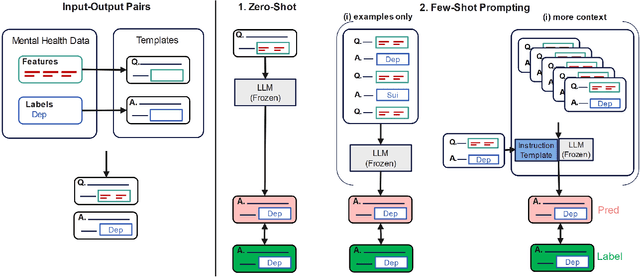
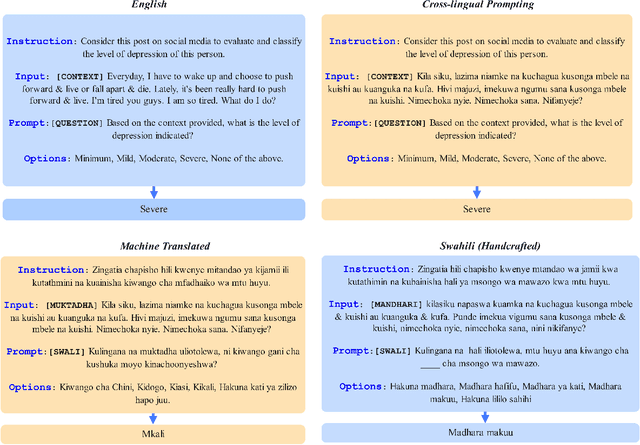
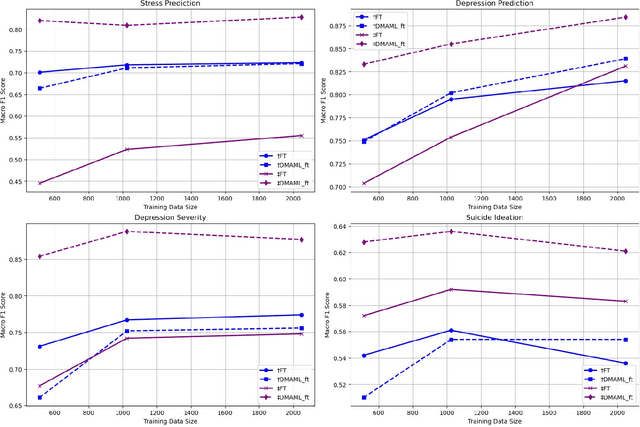
Abstract:Timely identification is essential for the efficient handling of mental health illnesses such as depression. However, the current research fails to adequately address the prediction of mental health conditions from social media data in low-resource African languages like Swahili. This study introduces two distinct approaches utilising model-agnostic meta-learning and leveraging large language models (LLMs) to address this gap. Experiments are conducted on three datasets translated to low-resource language and applied to four mental health tasks, which include stress, depression, depression severity and suicidal ideation prediction. we first apply a meta-learning model with self-supervision, which results in improved model initialisation for rapid adaptation and cross-lingual transfer. The results show that our meta-trained model performs significantly better than standard fine-tuning methods, outperforming the baseline fine-tuning in macro F1 score with 18\% and 0.8\% over XLM-R and mBERT. In parallel, we use LLMs' in-context learning capabilities to assess their performance accuracy across the Swahili mental health prediction tasks by analysing different cross-lingual prompting approaches. Our analysis showed that Swahili prompts performed better than cross-lingual prompts but less than English prompts. Our findings show that in-context learning can be achieved through cross-lingual transfer through carefully crafted prompt templates with examples and instructions.
Maximizing UAV Fog Deployment Efficiency for Critical Rescue Operations
Feb 25, 2024



Abstract:In disaster scenarios and high-stakes rescue operations, integrating Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) as fog nodes has become crucial. This integration ensures a smooth connection between affected populations and essential health monitoring devices, supported by the Internet of Things (IoT). Integrating UAVs in such environments is inherently challenging, where the primary objectives involve maximizing network connectivity and coverage while extending the network's lifetime through energy-efficient strategies to serve the maximum number of affected individuals. In this paper, We propose a novel model centred around dynamic UAV-based fog deployment that optimizes the system's adaptability and operational efficacy within the afflicted areas. First, we decomposed the problem into two subproblems. Connectivity and coverage subproblem, and network lifespan optimization subproblem. We shape our UAV fog deployment problem as a uni-objective optimization and introduce a specialized UAV fog deployment algorithm tailored specifically for UAV fog nodes deployed in rescue missions. While the network lifespan optimization subproblem is efficiently solved via a one-dimensional swapping method. Following that, We introduce a novel optimization strategy for UAV fog node placement in dynamic networks during evacuation scenarios, with a primary focus on ensuring robust connectivity and maximal coverage for mobile users, while extending the network's lifespan. Finally, we introduce Adaptive Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) for fog node deployment in a dynamic network. Its agility, rapid convergence, and low computational demands make it an ideal fit for high-pressure environments.
Selective Task offloading for Maximum Inference Accuracy and Energy efficient Real-Time IoT Sensing Systems
Feb 24, 2024Abstract:The recent advancements in small-size inference models facilitated AI deployment on the edge. However, the limited resource nature of edge devices poses new challenges especially for real-time applications. Deploying multiple inference models (or a single tunable model) varying in size and therefore accuracy and power consumption, in addition to an edge server inference model, can offer a dynamic system in which the allocation of inference models to inference jobs is performed according to the current resource conditions. Therefore, in this work, we tackle the problem of selectively allocating inference models to jobs or offloading them to the edge server to maximize inference accuracy under time and energy constraints. This problem is shown to be an instance of the unbounded multidimensional knapsack problem which is considered a strongly NP-hard problem. We propose a lightweight hybrid genetic algorithm (LGSTO) to solve this problem. We introduce a termination condition and neighborhood exploration techniques for faster evolution of populations. We compare LGSTO with the Naive and Dynamic programming solutions. In addition to classic genetic algorithms using different reproduction methods including NSGA-II, and finally we compare to other evolutionary methods such as Particle swarm optimization (PSO) and Ant colony optimization (ACO). Experiment results show that LGSTO performed 3 times faster than the fastest comparable schemes while producing schedules with higher average accuracy.
IP-UNet: Intensity Projection UNet Architecture for 3D Medical Volume Segmentation
Aug 24, 2023

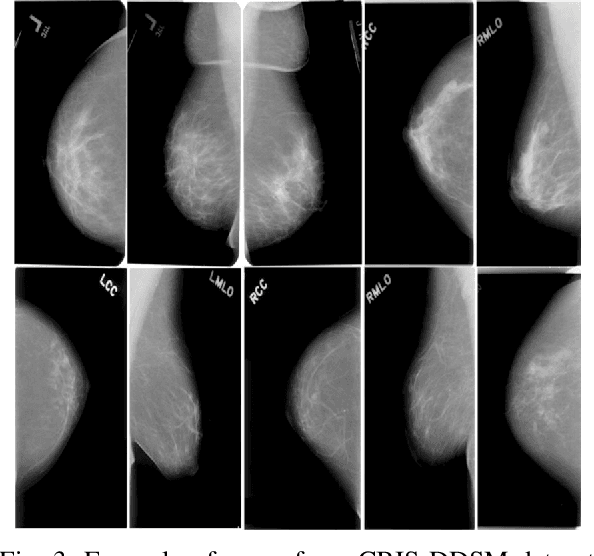
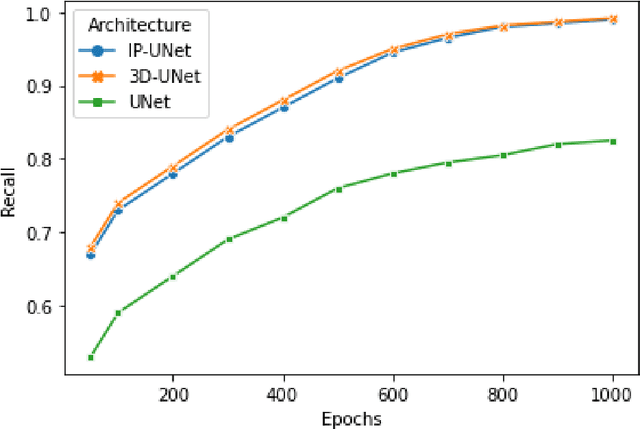
Abstract:CNNs have been widely applied for medical image analysis. However, limited memory capacity is one of the most common drawbacks of processing high-resolution 3D volumetric data. 3D volumes are usually cropped or downsized first before processing, which can result in a loss of resolution, increase class imbalance, and affect the performance of the segmentation algorithms. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end deep learning approach called IP-UNet. IP-UNet is a UNet-based model that performs multi-class segmentation on Intensity Projection (IP) of 3D volumetric data instead of the memory-consuming 3D volumes. IP-UNet uses limited memory capability for training without losing the original 3D image resolution. We compare the performance of three models in terms of segmentation accuracy and computational cost: 1) Slice-by-slice 2D segmentation of the CT scan images using a conventional 2D UNet model. 2) IP-UNet that operates on data obtained by merging the extracted Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP), Closest Vessel Projection (CVP), and Average Intensity Projection (AvgIP) representations of the source 3D volumes, then applying the UNet model on the output IP images. 3) 3D-UNet model directly reads the 3D volumes constructed from a series of CT scan images and outputs the 3D volume of the predicted segmentation. We test the performance of these methods on 3D volumetric images for automatic breast calcification detection. Experimental results show that IP-Unet can achieve similar segmentation accuracy with 3D-Unet but with much better performance. It reduces the training time by 70\% and memory consumption by 92\%.
Context-Aware Service Recommendation System for the Social Internet of Things
Aug 14, 2023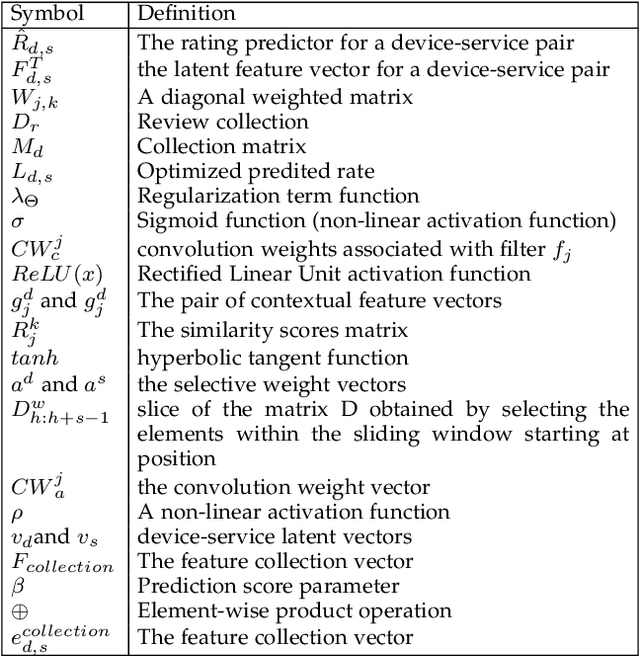
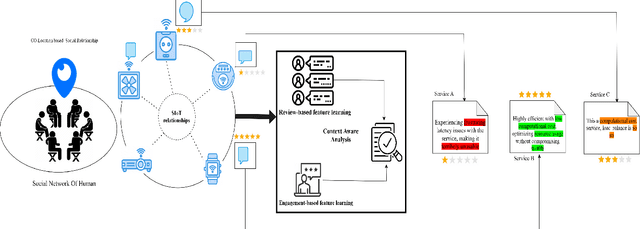
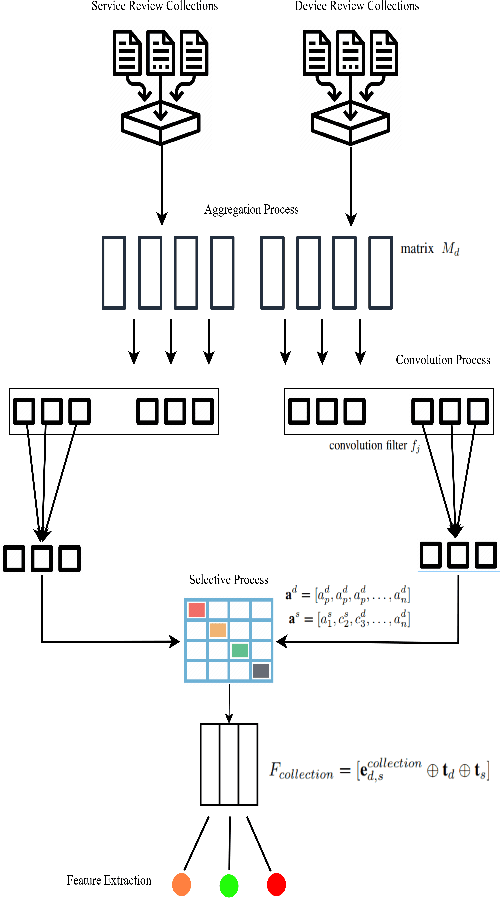
Abstract:The Social Internet of Things (SIoT) enables interconnected smart devices to share data and services, opening up opportunities for personalized service recommendations. However, existing research often overlooks crucial aspects that can enhance the accuracy and relevance of recommendations in the SIoT context. Specifically, existing techniques tend to consider the extraction of social relationships between devices and neglect the contextual presentation of service reviews. This study aims to address these gaps by exploring the contextual representation of each device-service pair. Firstly, we propose a latent features combination technique that can capture latent feature interactions, by aggregating the device-device relationships within the SIoT. Then, we leverage Factorization Machines to model higher-order feature interactions specific to each SIoT device-service pair to accomplish accurate rating prediction. Finally, we propose a service recommendation framework for SIoT based on review aggregation and feature learning processes. The experimental evaluation demonstrates the framework's effectiveness in improving service recommendation accuracy and relevance.
Task Offloading for Smart Glasses in Healthcare: Enhancing Detection of Elevated Body Temperature
Aug 14, 2023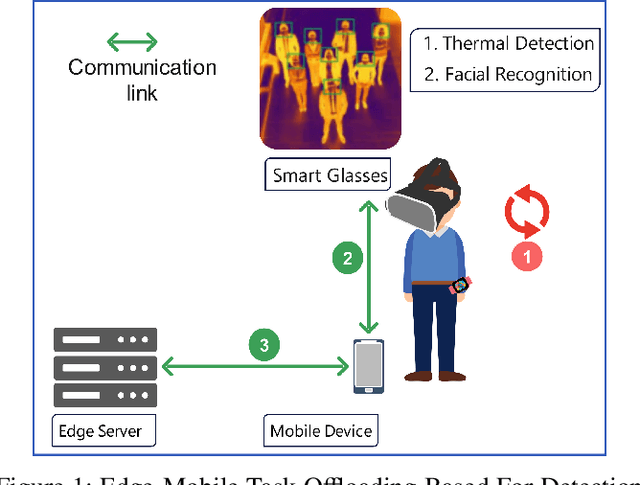
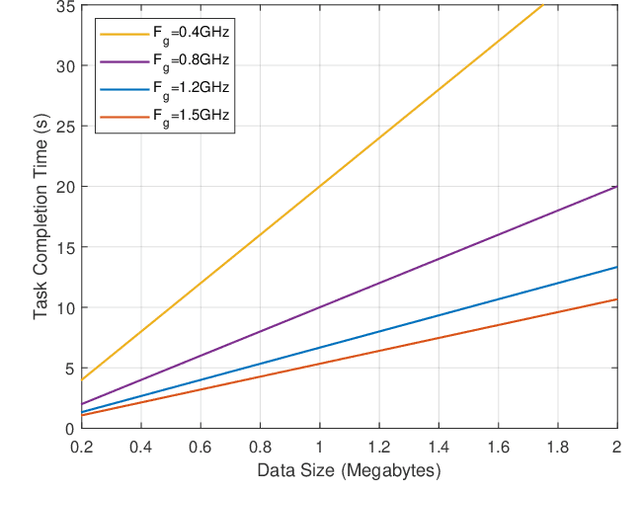
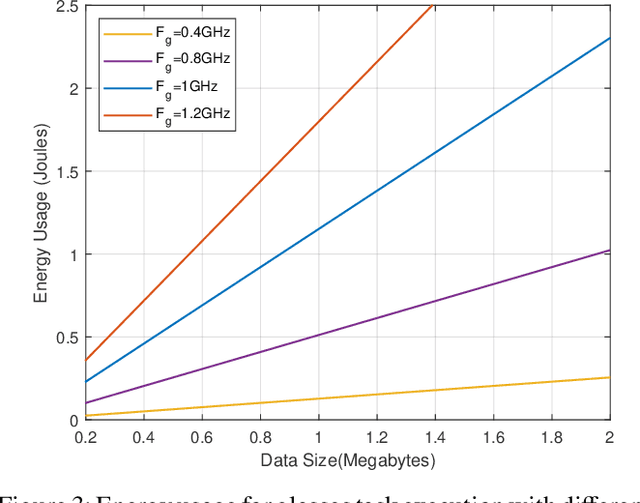
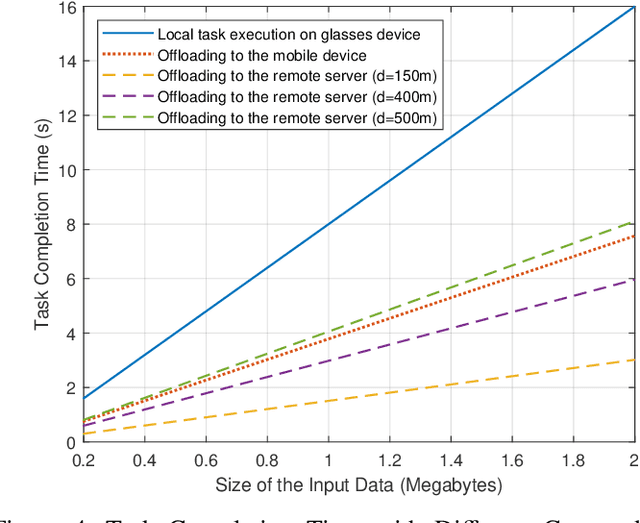
Abstract:Wearable devices like smart glasses have gained popularity across various applications. However, their limited computational capabilities pose challenges for tasks that require extensive processing, such as image and video processing, leading to drained device batteries. To address this, offloading such tasks to nearby powerful remote devices, such as mobile devices or remote servers, has emerged as a promising solution. This paper focuses on analyzing task-offloading scenarios for a healthcare monitoring application performed on smart wearable glasses, aiming to identify the optimal conditions for offloading. The study evaluates performance metrics including task completion time, computing capabilities, and energy consumption under realistic conditions. A specific use case is explored within an indoor area like an airport, where security agents wearing smart glasses to detect elevated body temperature in individuals, potentially indicating COVID-19. The findings highlight the potential benefits of task offloading for wearable devices in healthcare settings, demonstrating its practicality and relevance.
A Multi-Modal Latent-Features based Service Recommendation System for the Social Internet of Things
Jun 01, 2023



Abstract:The Social Internet of Things (SIoT), is revolutionizing how we interact with our everyday lives. By adding the social dimension to connecting devices, the SIoT has the potential to drastically change the way we interact with smart devices. This connected infrastructure allows for unprecedented levels of convenience, automation, and access to information, allowing us to do more with less effort. However, this revolutionary new technology also brings an eager need for service recommendation systems. As the SIoT grows in scope and complexity, it becomes increasingly important for businesses and individuals, and SIoT objects alike to have reliable sources for products, services, and information that are tailored to their specific needs. Few works have been proposed to provide service recommendations for SIoT environments. However, these efforts have been confined to only focusing on modeling user-item interactions using contextual information, devices' SIoT relationships, and correlation social groups but these schemes do not account for latent semantic item-item structures underlying the sparse multi-modal contents in SIoT environment. In this paper, we propose a latent-based SIoT recommendation system that learns item-item structures and aggregates multiple modalities to obtain latent item graphs which are then used in graph convolutions to inject high-order affinities into item representations. Experiments showed that the proposed recommendation system outperformed state-of-the-art SIoT recommendation methods and validated its efficacy at mining latent relationships from multi-modal features.
Artificial Intelligence for Suicide Assessment using Audiovisual Cues: A Review
Jan 22, 2022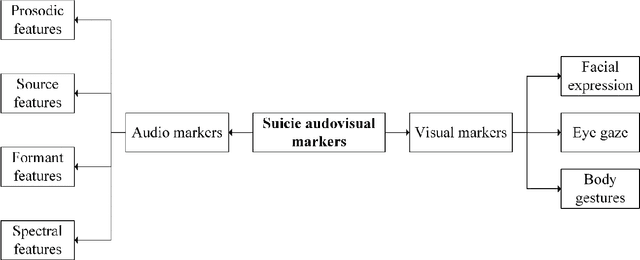
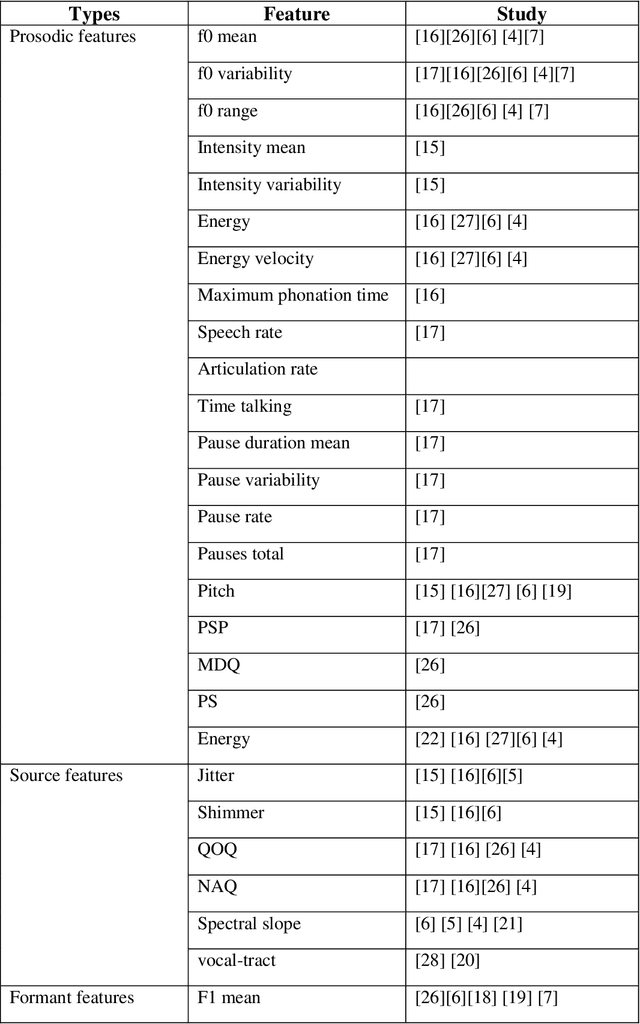
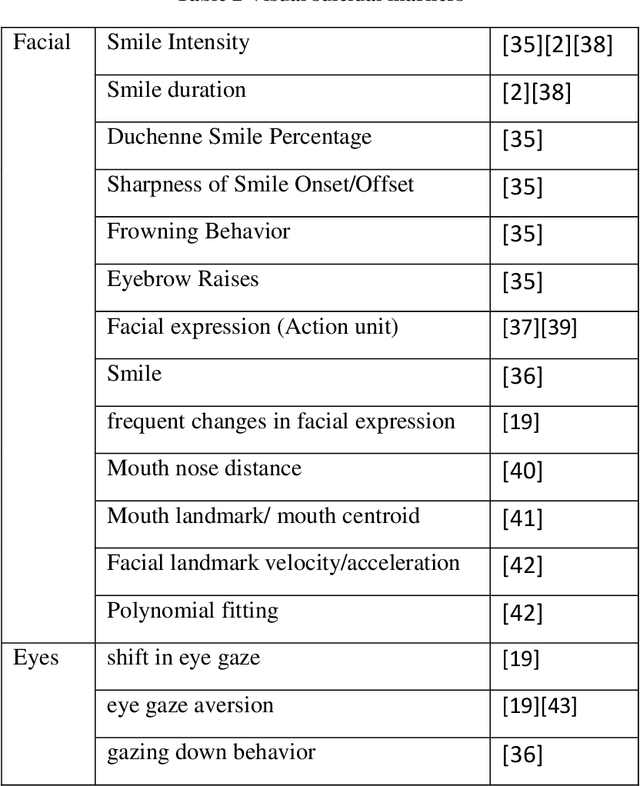
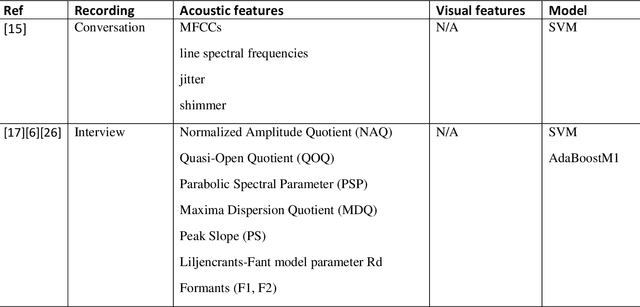
Abstract:Death by suicide is the seventh of the leading death cause worldwide. The recent advancement in Artificial Intelligence (AI), specifically AI application in image and voice processing, has created a promising opportunity to revolutionize suicide risk assessment. Subsequently, we have witnessed fast-growing literature of researches that applies AI to extract audiovisual non-verbal cues for mental illness assessment. However, the majority of the recent works focus on depression, despite the evident difference between depression signs and suicidal behavior non-verbal cues. In this paper, we review the recent works that study suicide ideation and suicide behavior detection through audiovisual feature analysis, mainly suicidal voice/speech acoustic features analysis and suicidal visual cues.
Big-Five, MPTI, Eysenck or HEXACO: The Ideal Personality Model for Personality-aware Recommendation Systems
Jun 06, 2021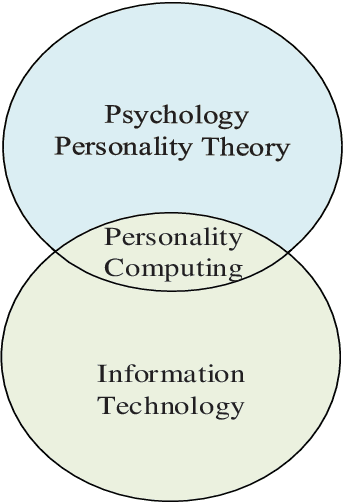
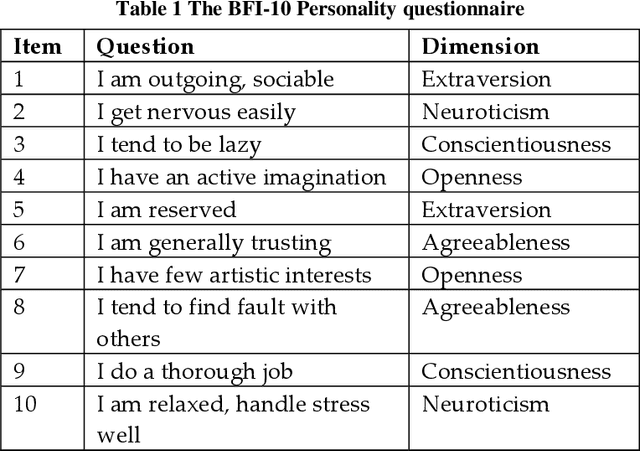
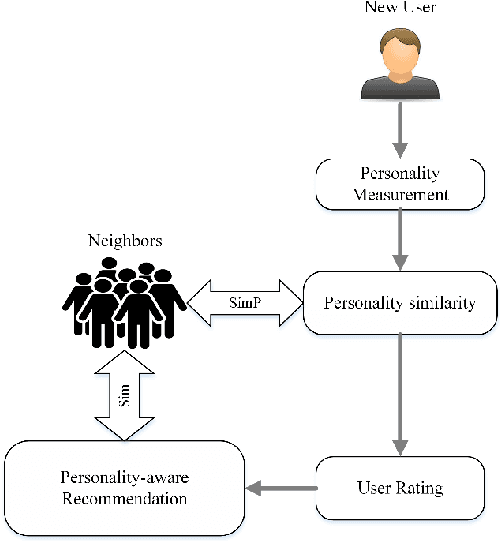
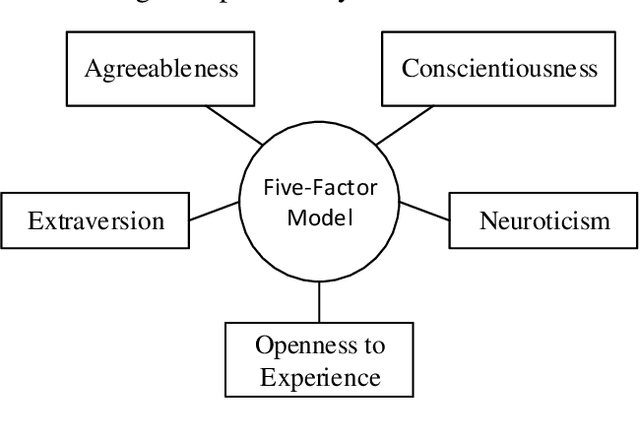
Abstract:Personality-aware recommendation systems have been proven to achieve high accuracy compared to conventional recommendation systems. In addition to that, personality-aware recommendation systems could help alleviate cold start and data sparsity problems. Most of the existing works use Big-Five personality model to represent the user's personality, this is due to the popularity of Big-Five model in the literature of psychology. However, from personality computing perspective, the choice of the most suitable personality model that satisfy the requirements of the recommendation application and the recommended content type still needs further investigation. In this paper, we study and compare four personality-aware recommendation systems based on different personality models, namely Big-Five, Eysenck and HEXACO from the personality traits theory, and Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MPTI) from the personality types theory. Following that, we propose a hybrid personality model for recommendation that takes advantage of the personality traits models, as well as the personality types models. Through extensive experiments on recommendation dataset, we prove the efficiency of the proposed model, especially in cold start settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge