Sahith Dambekodi
Playing Text-Based Games with Common Sense
Dec 04, 2020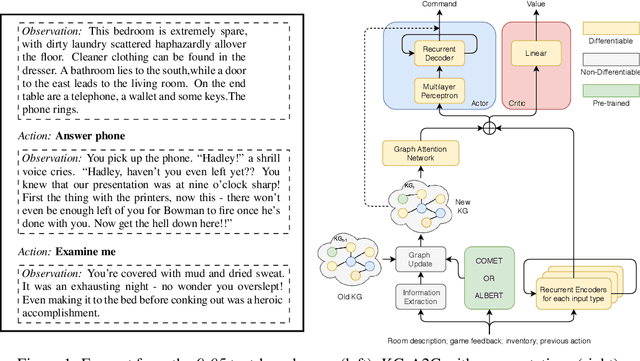
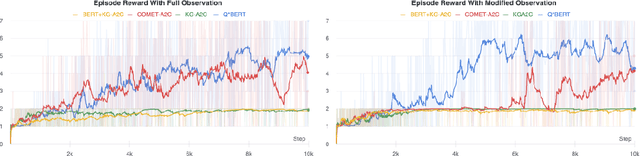
Abstract:Text based games are simulations in which an agent interacts with the world purely through natural language. They typically consist of a number of puzzles interspersed with interactions with common everyday objects and locations. Deep reinforcement learning agents can learn to solve these puzzles. However, the everyday interactions with the environment, while trivial for human players, present as additional puzzles to agents. We explore two techniques for incorporating commonsense knowledge into agents. Inferring possibly hidden aspects of the world state with either a commonsense inference model COMET, or a language model BERT. Biasing an agents exploration according to common patterns recognized by a language model. We test our technique in the 9to05 game, which is an extreme version of a text based game that requires numerous interactions with common, everyday objects in common, everyday scenarios. We conclude that agents that augment their beliefs about the world state with commonsense inferences are more robust to observational errors and omissions of common elements from text descriptions.
A study on the use of Boundary Equilibrium GAN for Approximate Frontalization of Unconstrained Faces to aid in Surveillance
Sep 14, 2018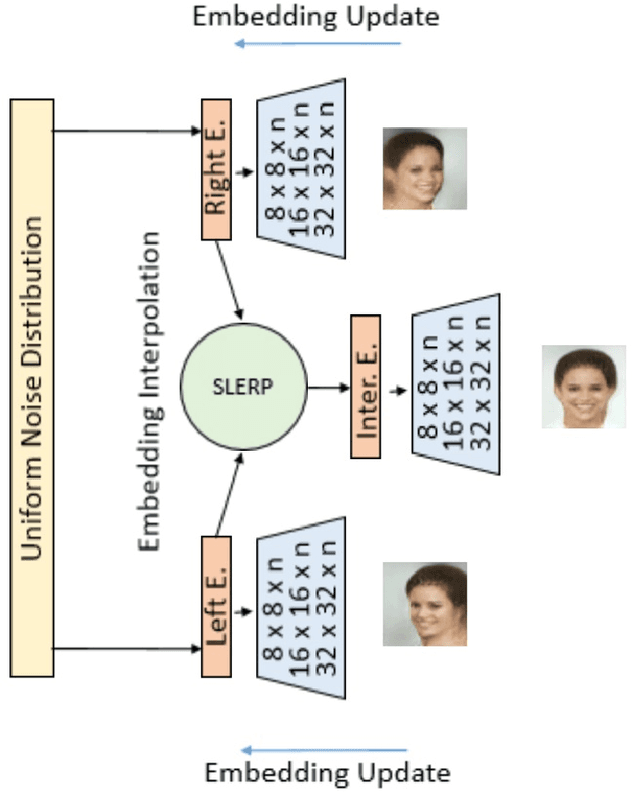

Abstract:Face frontalization is the process of synthesizing frontal facing views of faces given its angled poses. We implement a generative adversarial network (GAN) with spherical linear interpolation (Slerp) for frontalization of unconstrained facial images. Our special focus is intended towards the generation of approximate frontal faces of the side posed images captured from surveillance cameras. Specifically, the present work is a comprehensive study on the implementation of an auto-encoder based Boundary Equilibrium GAN (BEGAN) to generate frontal faces using an interpolation of a side view face and its mirrored view. To increase the quality of the interpolated output we implement a BEGAN with Slerp. This approach could produce a promising output along with a faster and more stable training for the model. The BEGAN model additionally has a balanced generator-discriminator combination, which prevents mode collapse along with a global convergence measure. It is expected that such an approximate face generation model would be able to replace face composites used in surveillance and crime detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge