Sadra Safadoust
Self-Evolving Depth-Supervised 3D Gaussian Splatting from Rendered Stereo Pairs
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (GS) significantly struggles to accurately represent the underlying 3D scene geometry, resulting in inaccuracies and floating artifacts when rendering depth maps. In this paper, we address this limitation, undertaking a comprehensive analysis of the integration of depth priors throughout the optimization process of Gaussian primitives, and present a novel strategy for this purpose. This latter dynamically exploits depth cues from a readily available stereo network, processing virtual stereo pairs rendered by the GS model itself during training and achieving consistent self-improvement of the scene representation. Experimental results on three popular datasets, breaking ground as the first to assess depth accuracy for these models, validate our findings.
Multi-Object Discovery by Low-Dimensional Object Motion
Jul 16, 2023



Abstract:Recent work in unsupervised multi-object segmentation shows impressive results by predicting motion from a single image despite the inherent ambiguity in predicting motion without the next image. On the other hand, the set of possible motions for an image can be constrained to a low-dimensional space by considering the scene structure and moving objects in it. We propose to model pixel-wise geometry and object motion to remove ambiguity in reconstructing flow from a single image. Specifically, we divide the image into coherently moving regions and use depth to construct flow bases that best explain the observed flow in each region. We achieve state-of-the-art results in unsupervised multi-object segmentation on synthetic and real-world datasets by modeling the scene structure and object motion. Our evaluation of the predicted depth maps shows reliable performance in monocular depth estimation.
DepthP+P: Metric Accurate Monocular Depth Estimation using Planar and Parallax
Jan 05, 2023Abstract:Current self-supervised monocular depth estimation methods are mostly based on estimating a rigid-body motion representing camera motion. These methods suffer from the well-known scale ambiguity problem in their predictions. We propose DepthP+P, a method that learns to estimate outputs in metric scale by following the traditional planar parallax paradigm. We first align the two frames using a common ground plane which removes the effect of the rotation component in the camera motion. With two neural networks, we predict the depth and the camera translation, which is easier to predict alone compared to predicting it together with rotation. By assuming a known camera height, we can then calculate the induced 2D image motion of a 3D point and use it for reconstructing the target image in a self-supervised monocular approach. We perform experiments on the KITTI driving dataset and show that the planar parallax approach, which only needs to predict camera translation, can be a metrically accurate alternative to the current methods that rely on estimating 6DoF camera motion.
Stochastic Video Prediction with Structure and Motion
Mar 20, 2022
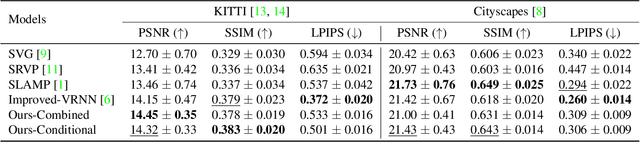
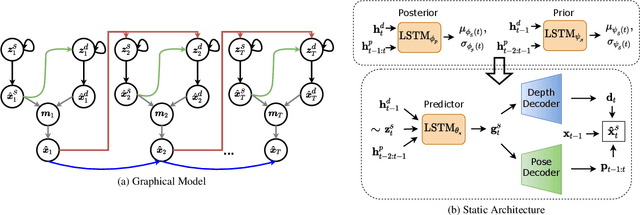
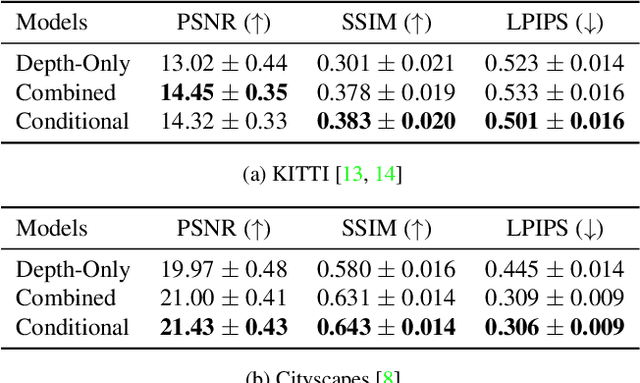
Abstract:While stochastic video prediction models enable future prediction under uncertainty, they mostly fail to model the complex dynamics of real-world scenes. For example, they cannot provide reliable predictions for scenes with a moving camera and independently moving foreground objects in driving scenarios. The existing methods fail to fully capture the dynamics of the structured world by only focusing on changes in pixels. In this paper, we assume that there is an underlying process creating observations in a video and propose to factorize it into static and dynamic components. We model the static part based on the scene structure and the ego-motion of the vehicle, and the dynamic part based on the remaining motion of the dynamic objects. By learning separate distributions of changes in foreground and background, we can decompose the scene into static and dynamic parts and separately model the change in each. Our experiments demonstrate that disentangling structure and motion helps stochastic video prediction, leading to better future predictions in complex driving scenarios on two real-world driving datasets, KITTI and Cityscapes.
Self-Supervised Monocular Scene Decomposition and Depth Estimation
Oct 21, 2021



Abstract:Self-supervised monocular depth estimation approaches either ignore independently moving objects in the scene or need a separate segmentation step to identify them. We propose MonoDepthSeg to jointly estimate depth and segment moving objects from monocular video without using any ground-truth labels. We decompose the scene into a fixed number of components where each component corresponds to a region on the image with its own transformation matrix representing its motion. We estimate both the mask and the motion of each component efficiently with a shared encoder. We evaluate our method on three driving datasets and show that our model clearly improves depth estimation while decomposing the scene into separately moving components.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge