Sadegh Shirani
Simulating and Experimenting with Social Media Mobilization Using LLM Agents
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Online social networks have transformed the ways in which political mobilization messages are disseminated, raising new questions about how peer influence operates at scale. Building on the landmark 61-million-person Facebook experiment \citep{bond201261}, we develop an agent-based simulation framework that integrates real U.S. Census demographic distributions, authentic Twitter network topology, and heterogeneous large language model (LLM) agents to examine the effect of mobilization messages on voter turnout. Each simulated agent is assigned demographic attributes, a personal political stance, and an LLM variant (\texttt{GPT-4.1}, \texttt{GPT-4.1-Mini}, or \texttt{GPT-4.1-Nano}) reflecting its political sophistication. Agents interact over realistic social network structures, receiving personalized feeds and dynamically updating their engagement behaviors and voting intentions. Experimental conditions replicate the informational and social mobilization treatments of the original Facebook study. Across scenarios, the simulator reproduces qualitative patterns observed in field experiments, including stronger mobilization effects under social message treatments and measurable peer spillovers. Our framework provides a controlled, reproducible environment for testing counterfactual designs and sensitivity analyses in political mobilization research, offering a bridge between high-validity field experiments and flexible computational modeling.\footnote{Code and data available at https://github.com/CausalMP/LLM-SocioPol}
Can We Validate Counterfactual Estimations in the Presence of General Network Interference?
Feb 03, 2025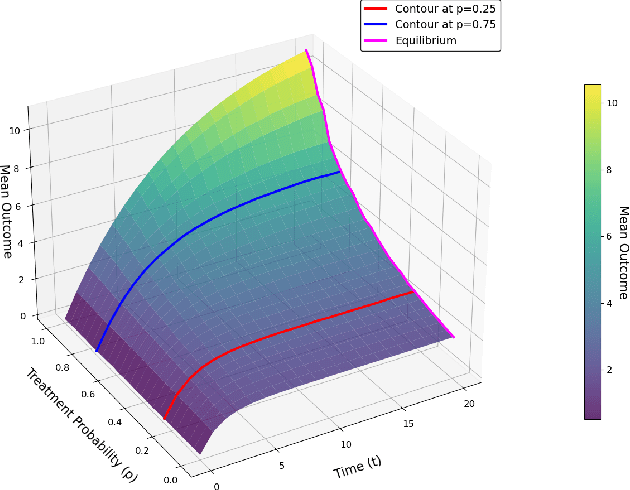
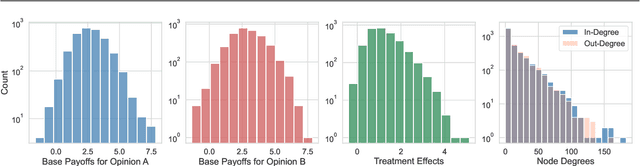
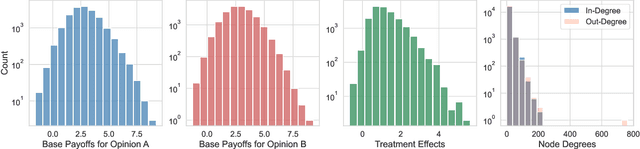
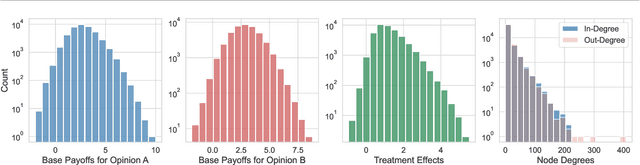
Abstract:In experimental settings with network interference, a unit's treatment can influence outcomes of other units, challenging both causal effect estimation and its validation. Classic validation approaches fail as outcomes are only observable under one treatment scenario and exhibit complex correlation patterns due to interference. To address these challenges, we introduce a new framework enabling cross-validation for counterfactual estimation. At its core is our distribution-preserving network bootstrap method -- a theoretically-grounded approach inspired by approximate message passing. This method creates multiple subpopulations while preserving the underlying distribution of network effects. We extend recent causal message-passing developments by incorporating heterogeneous unit-level characteristics and varying local interactions, ensuring reliable finite-sample performance through non-asymptotic analysis. We also develop and publicly release a comprehensive benchmark toolbox with diverse experimental environments, from networks of interacting AI agents to opinion formation in real-world communities and ride-sharing applications. These environments provide known ground truth values while maintaining realistic complexities, enabling systematic examination of causal inference methods. Extensive evaluation across these environments demonstrates our method's robustness to diverse forms of network interference. Our work provides researchers with both a practical estimation framework and a standardized platform for testing future methodological developments.
Higher-Order Causal Message Passing for Experimentation with Complex Interference
Nov 01, 2024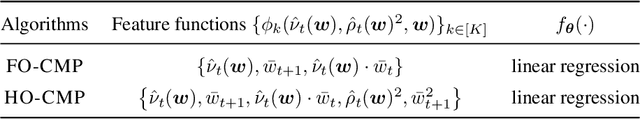
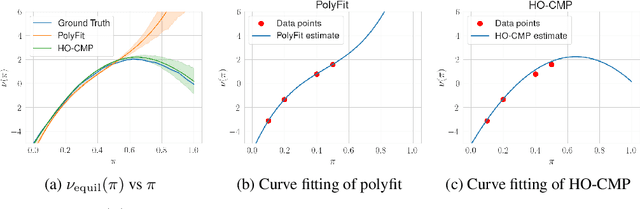
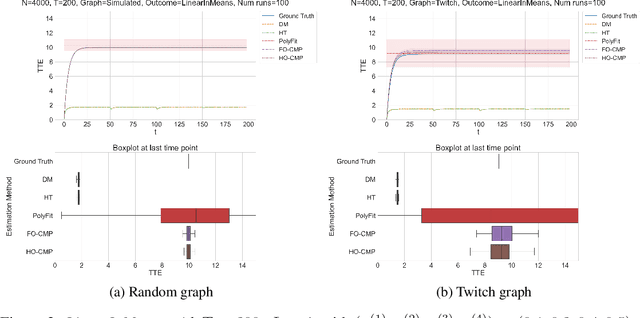
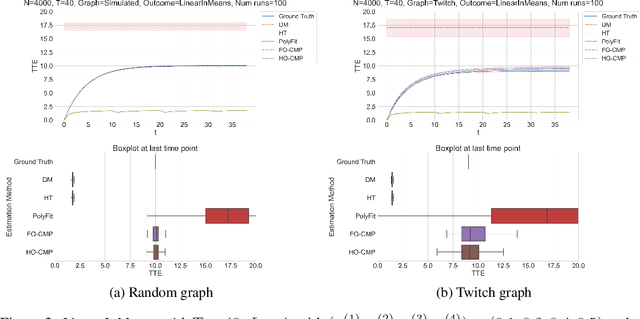
Abstract:Accurate estimation of treatment effects is essential for decision-making across various scientific fields. This task, however, becomes challenging in areas like social sciences and online marketplaces, where treating one experimental unit can influence outcomes for others through direct or indirect interactions. Such interference can lead to biased treatment effect estimates, particularly when the structure of these interactions is unknown. We address this challenge by introducing a new class of estimators based on causal message-passing, specifically designed for settings with pervasive, unknown interference. Our estimator draws on information from the sample mean and variance of unit outcomes and treatments over time, enabling efficient use of observed data to estimate the evolution of the system state. Concretely, we construct non-linear features from the moments of unit outcomes and treatments and then learn a function that maps these features to future mean and variance of unit outcomes. This allows for the estimation of the treatment effect over time. Extensive simulations across multiple domains, using synthetic and real network data, demonstrate the efficacy of our approach in estimating total treatment effect dynamics, even in cases where interference exhibits non-monotonic behavior in the probability of treatment.
Causal Message Passing: A Method for Experiments with Unknown and General Network Interference
Nov 14, 2023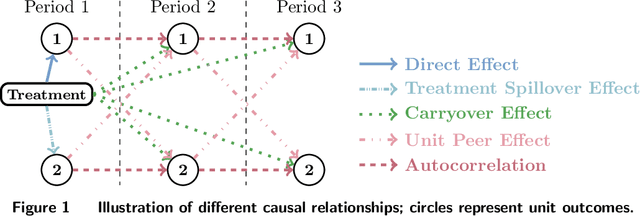
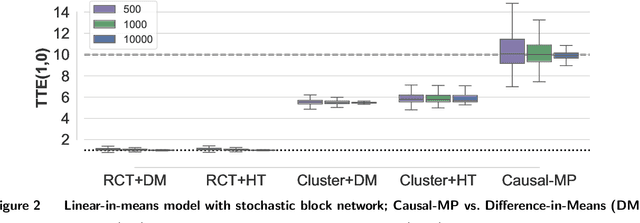
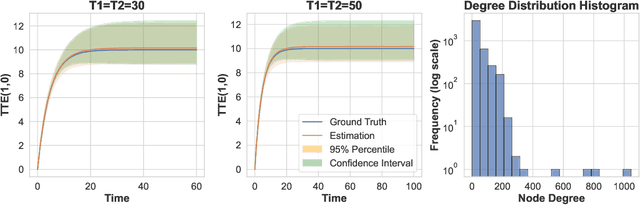
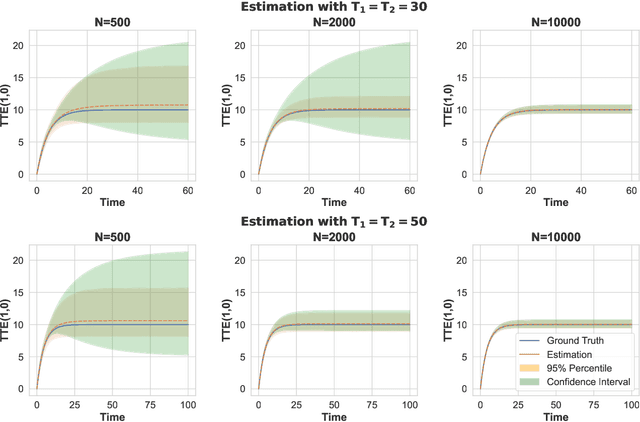
Abstract:Randomized experiments are a powerful methodology for data-driven evaluation of decisions or interventions. Yet, their validity may be undermined by network interference. This occurs when the treatment of one unit impacts not only its outcome but also that of connected units, biasing traditional treatment effect estimations. Our study introduces a new framework to accommodate complex and unknown network interference, moving beyond specialized models in the existing literature. Our framework, which we term causal message-passing, is grounded in a high-dimensional approximate message passing methodology and is specifically tailored to experimental design settings with prevalent network interference. Utilizing causal message-passing, we present a practical algorithm for estimating the total treatment effect and demonstrate its efficacy in four numerical scenarios, each with its unique interference structure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge