Causal Message Passing: A Method for Experiments with Unknown and General Network Interference
Paper and Code
Nov 14, 2023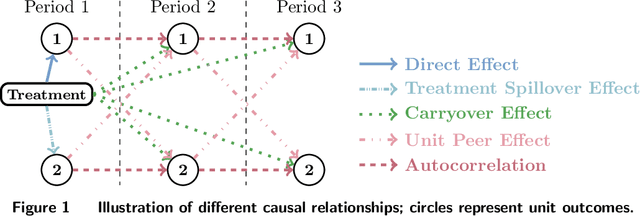
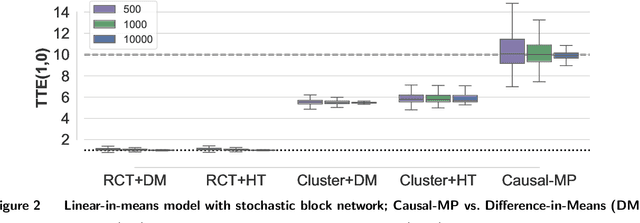
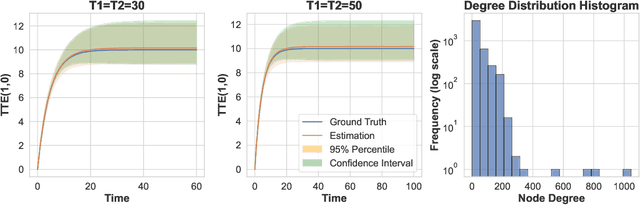
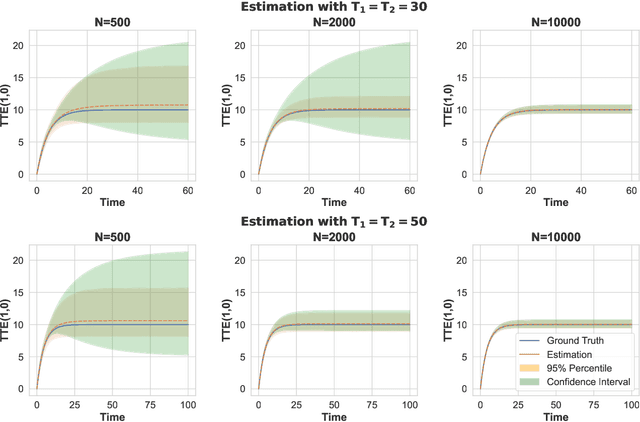
Randomized experiments are a powerful methodology for data-driven evaluation of decisions or interventions. Yet, their validity may be undermined by network interference. This occurs when the treatment of one unit impacts not only its outcome but also that of connected units, biasing traditional treatment effect estimations. Our study introduces a new framework to accommodate complex and unknown network interference, moving beyond specialized models in the existing literature. Our framework, which we term causal message-passing, is grounded in a high-dimensional approximate message passing methodology and is specifically tailored to experimental design settings with prevalent network interference. Utilizing causal message-passing, we present a practical algorithm for estimating the total treatment effect and demonstrate its efficacy in four numerical scenarios, each with its unique interference structure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge