S. Chen
School of Computer Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, 430072, China
Automated Retinal Layer and Fluid Segmentation and Cross-sectional Analysis using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Images for Diabetic Retinopathy
Mar 03, 2025



Abstract:This study presents an AI-driven pipeline for automated retinal segmentation and thickness analysis in diabetic retinopathy (DR) using SD-OCT imaging. A deep neural network was trained to segment ten retinal layers, intra-retinal fluid, and hyperreflective foci (HRF), with performance evaluated across multiple architectures. SwinUNETR achieved the highest segmentation accuracy, while VM-Unet excelled in specific layers. Analysis revealed distinct thickness variations between NPDR and PDR, with correlations between layer thickness and visual acuity. The proposed method enhances DR assessment by reducing manual annotation effort and providing clinically relevant thickness maps for disease monitoring and treatment planning.
End-to-End UAV Simulation for Visual SLAM and Navigation
Dec 01, 2020



Abstract:Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (v-SLAM) and navigation of multirotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) in an unknown environment have grown in popularity for both research and education. However, due to the complex hardware setup, safety precautions, and battery constraints, extensive physical testing can be expensive and time-consuming. As an alternative solution, simulation tools lower the barrier to carry out the algorithm testing and validation before field trials. In this letter, we customize the ROS-Gazebo-PX4 simulator in deep and provide an end-to-end simulation solution for the UAV v-SLAM and navigation study. A set of localization, mapping, and path planning kits were also integrated into the simulation platform. In our simulation, various aspects, including complex environments and onboard sensors, can simultaneously interact with our navigation framework to achieve specific surveillance missions. In this end-to-end simulation, we achieved click and fly level autonomy UAV navigation. The source code is open to the research community.
S$^{2}$OMGAN: Shortcut from Remote Sensing Images to Online Maps
Jan 21, 2020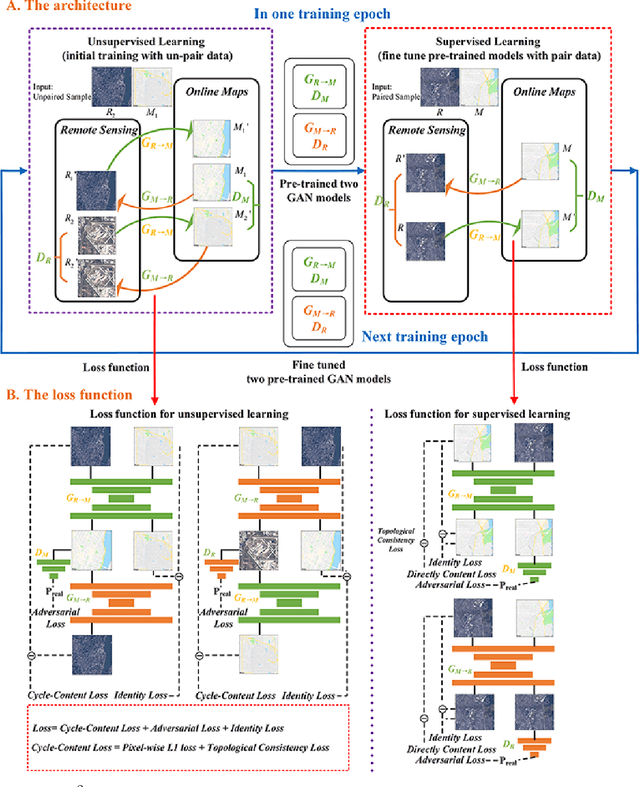
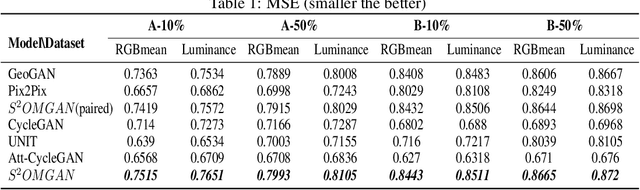
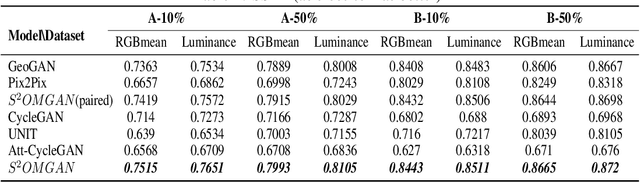
Abstract:Traditional online maps, widely used on Internet such as Google map and Baidu map, are rendered from vector data. Timely updating online maps from vector data, of which the generating is time-consuming, is a difficult mission. It is a shortcut to generate online maps in time from remote sensing images, which can be acquired timely without vector data. However, this mission used to be challenging or even impossible. Inspired by image-to-image translation (img2img) techniques based on generative adversarial network (GAN), we propose a semi-supervised structure-augmented online map GAN (S$^{2}$OMGAN) model to generate online maps directly from remote sensing images. In this model, we designed a semi-supervised learning strategy to pre-train S$^{2}$OMGAN on rich unpaired samples and finetune it on limited paired samples in reality. We also designed image gradient L1 loss and image gradient structure loss to generate an online map with global topological relationship and detailed edge curves of objects, which are important in cartography. Moreover, we propose edge structural similarity index (ESSI) as a metric to evaluate the quality of topological consistency between generated online maps and ground truths. Experimental results present that S$^{2}$OMGAN outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) works according to mean squared error, structural similarity index and ESSI. Also, S$^{2}$OMGAN wins more approval than SOTA in the human perceptual test on visual realism of cartography. Our work shows that S$^{2}$OMGAN is potentially a new paradigm to produce online maps. Our implementation of the S$^{2}$OMGAN is available at \url{https://github.com/imcsq/S2OMGAN}.
Gaze Gestures and Their Applications in human-computer interaction with a head-mounted display
Oct 16, 2019



Abstract:A head-mounted display (HMD) is a portable and interactive display device. With the development of 5G technology, it may become a general-purpose computing platform in the future. Human-computer interaction (HCI) technology for HMDs has also been of significant interest in recent years. In addition to tracking gestures and speech, tracking human eyes as a means of interaction is highly effective. In this paper, we propose two UnityEyes-based convolutional neural network models, UEGazeNet and UEGazeNet*, which can be used for input images with low resolution and high resolution, respectively. These models can perform rapid interactions by classifying gaze trajectories (GTs), and a GTgestures dataset containing data for 10,200 "eye-painting gestures" collected from 15 individuals is established with our gaze-tracking method. We evaluated the performance both indoors and outdoors and the UEGazeNet can obtaine results 52\% and 67\% better than those of state-of-the-art networks. The generalizability of our GTgestures dataset using a variety of gaze-tracking models is evaluated, and an average recognition rate of 96.71\% is obtained by our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge