T. Xu
School of Computer Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, 430072, China
Secrecy Capacity Analysis of 4-WFRFT Based Physical Layer Security in MIMO System
May 29, 2023



Abstract:The traditional information security based on cryptosystem is seriously threatened due to the exponential growth of computing capacity. In order to improve for the upper cryptosystem security, the secure transmission at the physical layer is introduced into the wireless communication system. However, considering the openness of wireless channel, the performance analysis of security wireless communication systems has become a hot issue in recent years. Due to the existence of the upper layer cryptosystem being cracked and the openness of wireless channel security problems, the Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) technology increases the difference between channels, the development of its rich spatial degrees of freedom can greatly improve the channel capacity and achieve the purpose of enhancing the Physical layer security (PLS); On this basis, Weighted Type Fractional Fourier Transform (WFrFT) technology rotates and splits the constellation points of signals, it is equivalent to increasing the artificial noise to enhance the PLS. The Average security capacity is an important index to measure the PLS, Therefore, this paper deduces the Average security capacity in MIMO scenario and gives a specific closed expression when considering the channel correlation. By analyzing the expression, the increase of the number of MIMO antennas will improve the Average security capacity. When the estimated bias is 1 in 4-WFRFT, the Average security capacity will be significantly improved; the Average security capacity will reach the maximum value, thus enhancing the PLS.
S$^{2}$OMGAN: Shortcut from Remote Sensing Images to Online Maps
Jan 21, 2020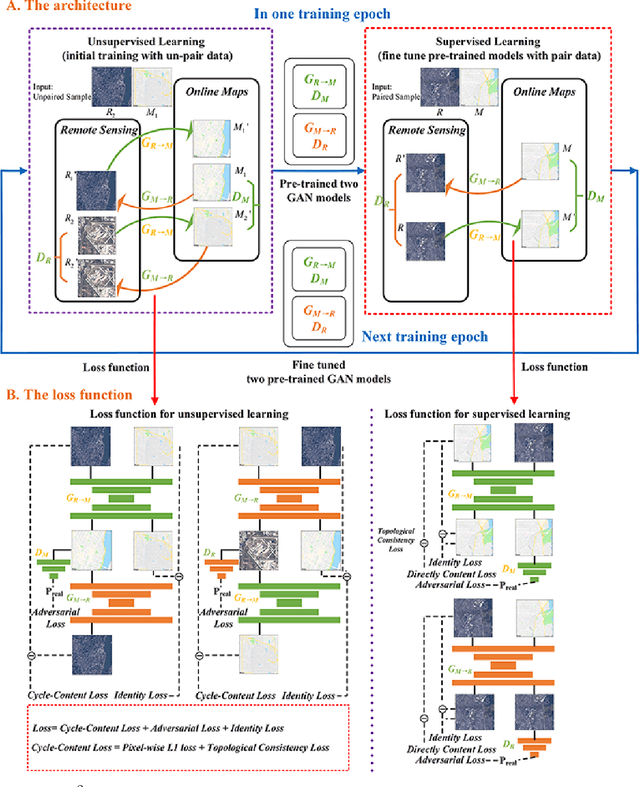
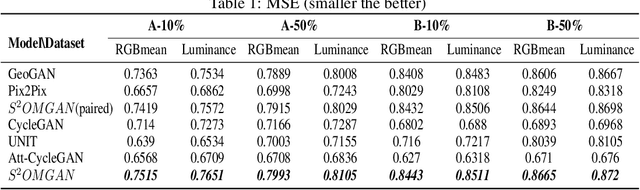
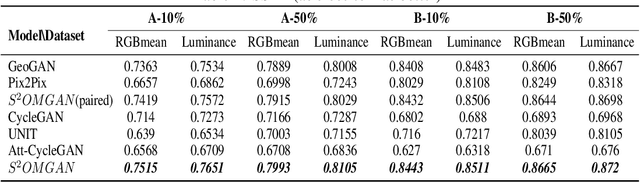
Abstract:Traditional online maps, widely used on Internet such as Google map and Baidu map, are rendered from vector data. Timely updating online maps from vector data, of which the generating is time-consuming, is a difficult mission. It is a shortcut to generate online maps in time from remote sensing images, which can be acquired timely without vector data. However, this mission used to be challenging or even impossible. Inspired by image-to-image translation (img2img) techniques based on generative adversarial network (GAN), we propose a semi-supervised structure-augmented online map GAN (S$^{2}$OMGAN) model to generate online maps directly from remote sensing images. In this model, we designed a semi-supervised learning strategy to pre-train S$^{2}$OMGAN on rich unpaired samples and finetune it on limited paired samples in reality. We also designed image gradient L1 loss and image gradient structure loss to generate an online map with global topological relationship and detailed edge curves of objects, which are important in cartography. Moreover, we propose edge structural similarity index (ESSI) as a metric to evaluate the quality of topological consistency between generated online maps and ground truths. Experimental results present that S$^{2}$OMGAN outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) works according to mean squared error, structural similarity index and ESSI. Also, S$^{2}$OMGAN wins more approval than SOTA in the human perceptual test on visual realism of cartography. Our work shows that S$^{2}$OMGAN is potentially a new paradigm to produce online maps. Our implementation of the S$^{2}$OMGAN is available at \url{https://github.com/imcsq/S2OMGAN}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge